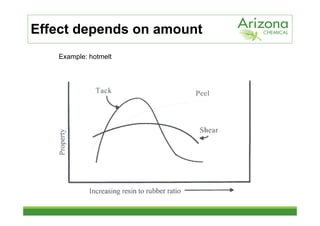
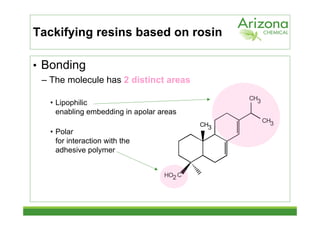
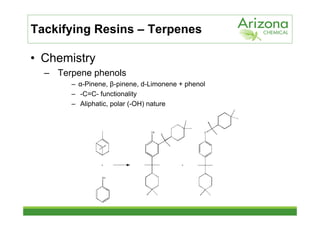
This document discusses tackifiers, which are additives used in adhesives to improve tack and bonding. It describes how tackifiers work on a molecular level to enhance mobility and provide anchor points. The document outlines different types of tackifier chemistries, including rosin derivatives, hydrocarbons, and terpenes. It also examines the effect of tackifiers in formulations like EVA, acrylates, and synthetic rubbers. Dynamical mechanical analysis is presented as a way to measure the impact of tackifiers and plasticizers.