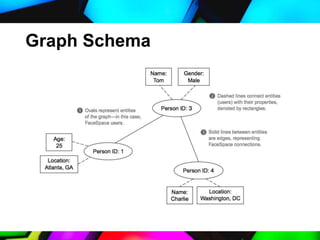
This document discusses big data and functional programming. It defines big data in terms of volume, velocity, and variety of data. It provides examples of big data analysis in healthcare, Google, and Amazon. It then explains that functional programming is suitable for big data due to its lack of side effects, statelessness, support for higher-order functions, and forbidding of assignment, which allows for parallel processing. Finally, it describes the fact-based model for representing changing data over time and graph schemas for capturing relationships between data.