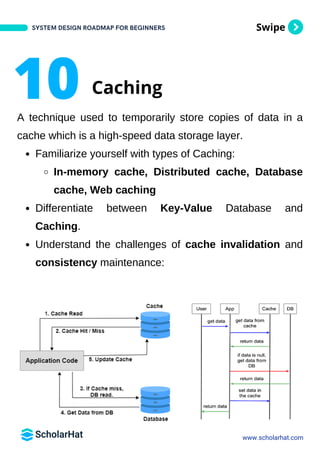
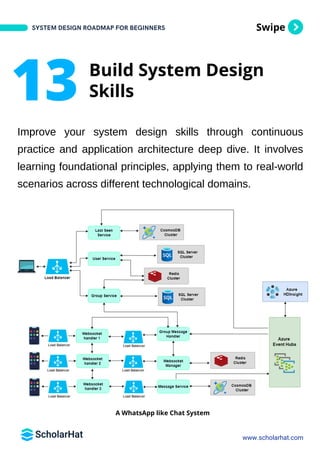
The document outlines a comprehensive roadmap for beginners to learn system design, detailing key concepts, components, and processes involved in creating effective systems. It covers topics such as reliability, load balancing, microservices, storage, caching, API contracts, and containerization, offering practical guidance and tools for aspiring system designers. The roadmap emphasizes the importance of foundational skills, hands-on project experience, and preparation for interviews in the tech industry.