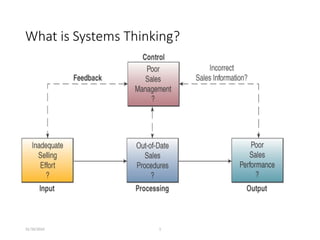
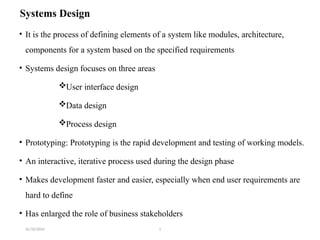
The document outlines the processes involved in understanding and developing information systems solutions, emphasizing the importance of defining problems and opportunities. It discusses methodologies, such as business planning and the system development life cycle, to guide solution implementation, including design, technology selection, and user training. Additionally, it covers various conversion strategies and maintenance categories to ensure system efficacy post-implementation.