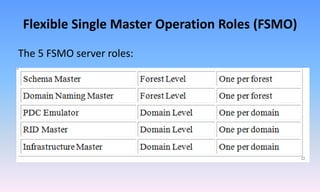
This document discusses local, global, and universal groups and their differences. It also discusses group nesting, domain controllers, domains, forests, global catalogs, sites, and FSMO roles. Additionally, it covers virtualization concepts like hypervisors, hosts, guests, virtual machines, Hyper-V snapshots, and common virtual machine file types.