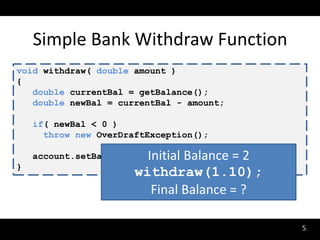
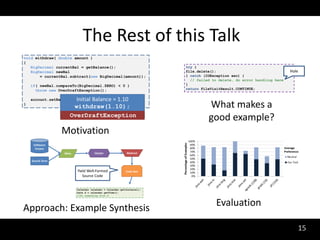
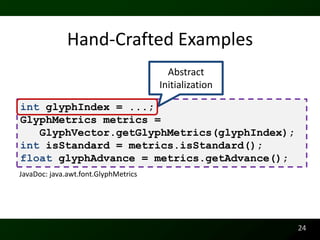
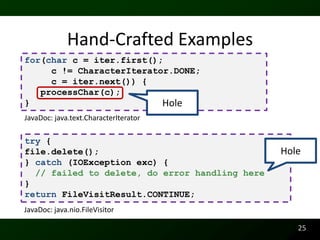
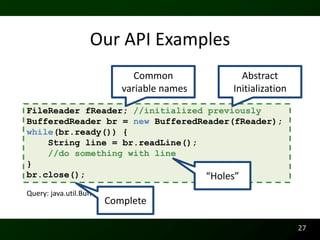
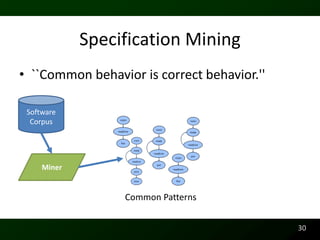
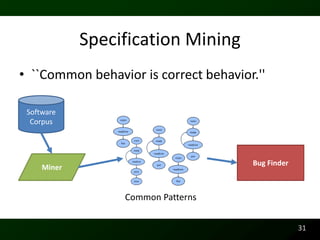
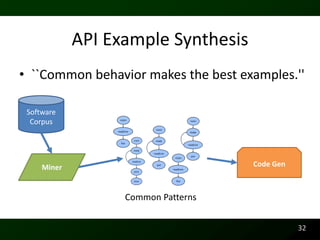
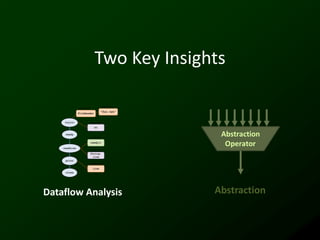
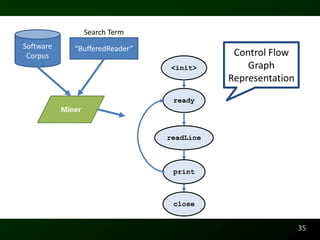
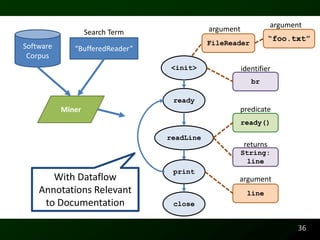
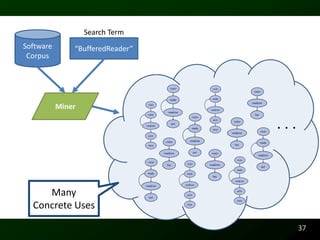
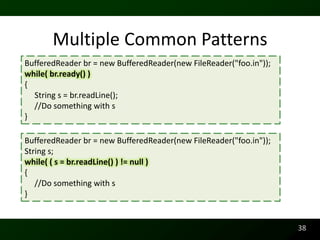
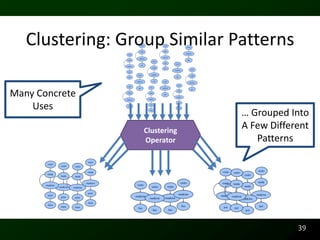
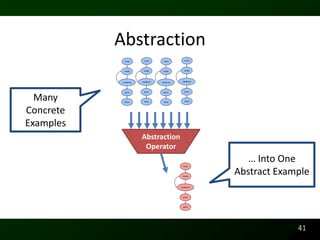
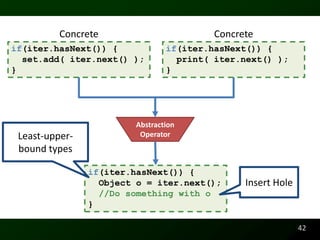
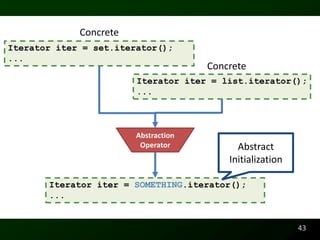
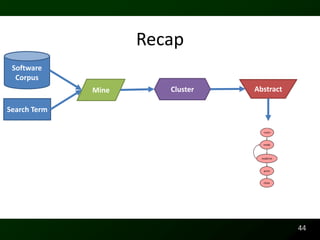
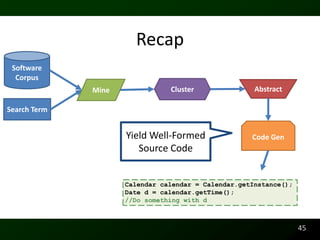
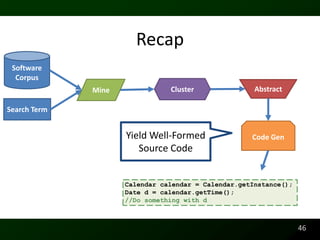
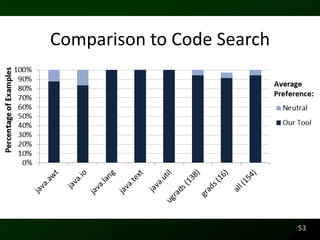
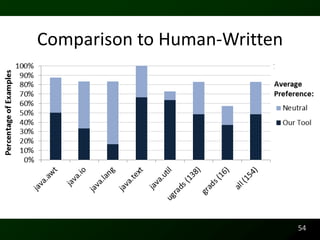
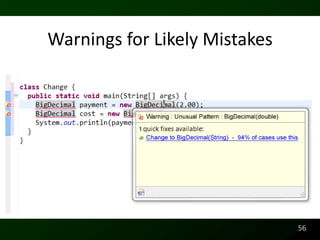
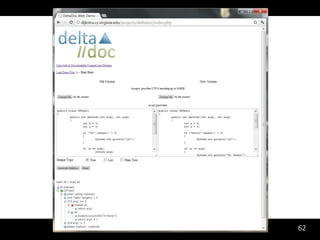
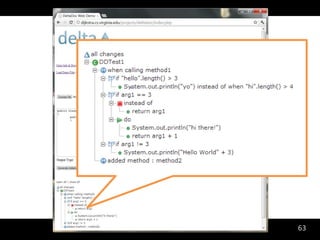
The document discusses synthesizing API usage examples from source code. It describes mining common API usage patterns from a software corpus and generating code snippets that exemplify the common patterns. The approach uses dataflow analysis to extract control flow graphs and then abstracts the graphs to generate examples that cover typical usage scenarios while removing implementation details. This allows automatically generating documentation in the form of code examples that is always up to date and complete.