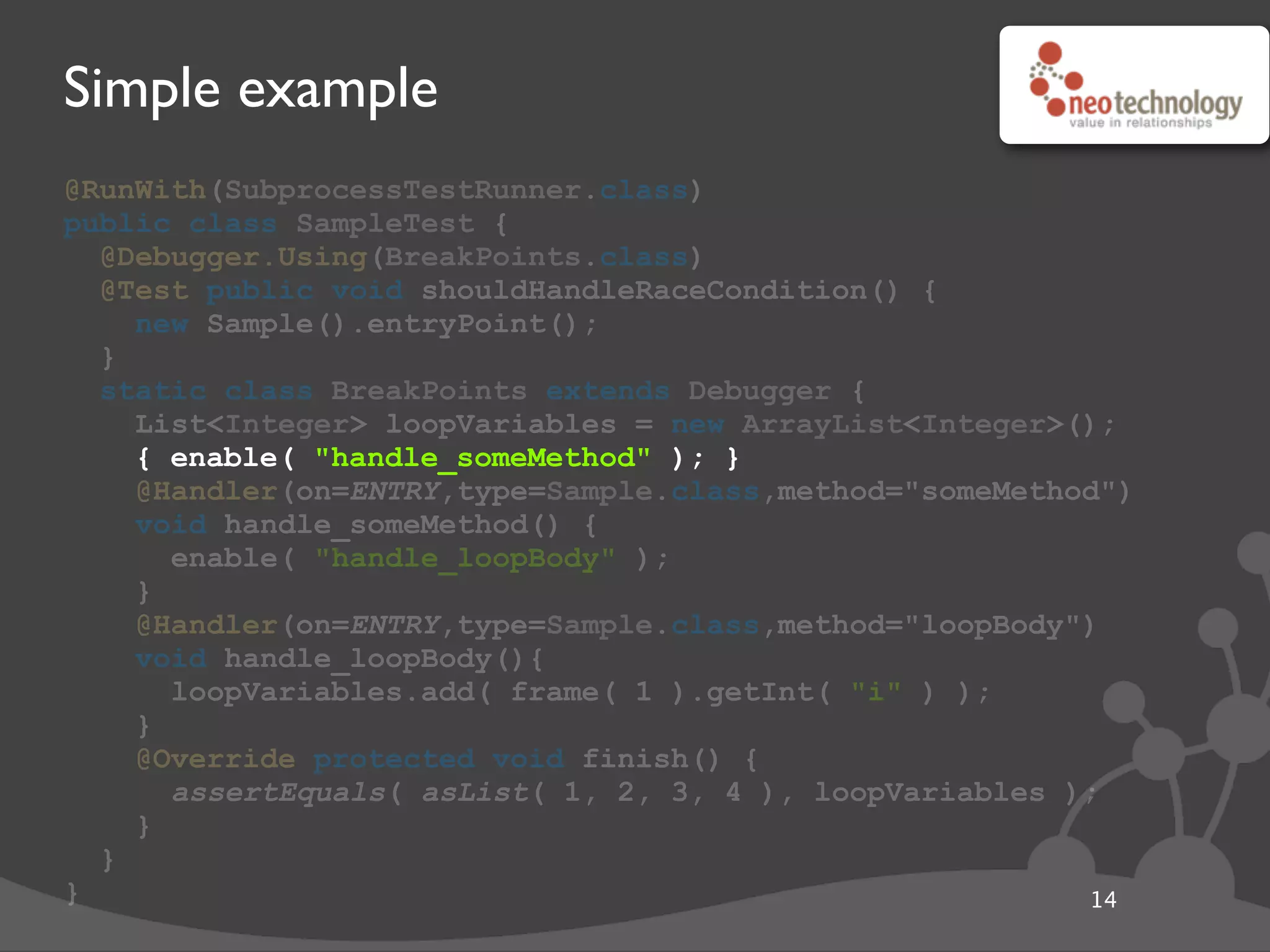
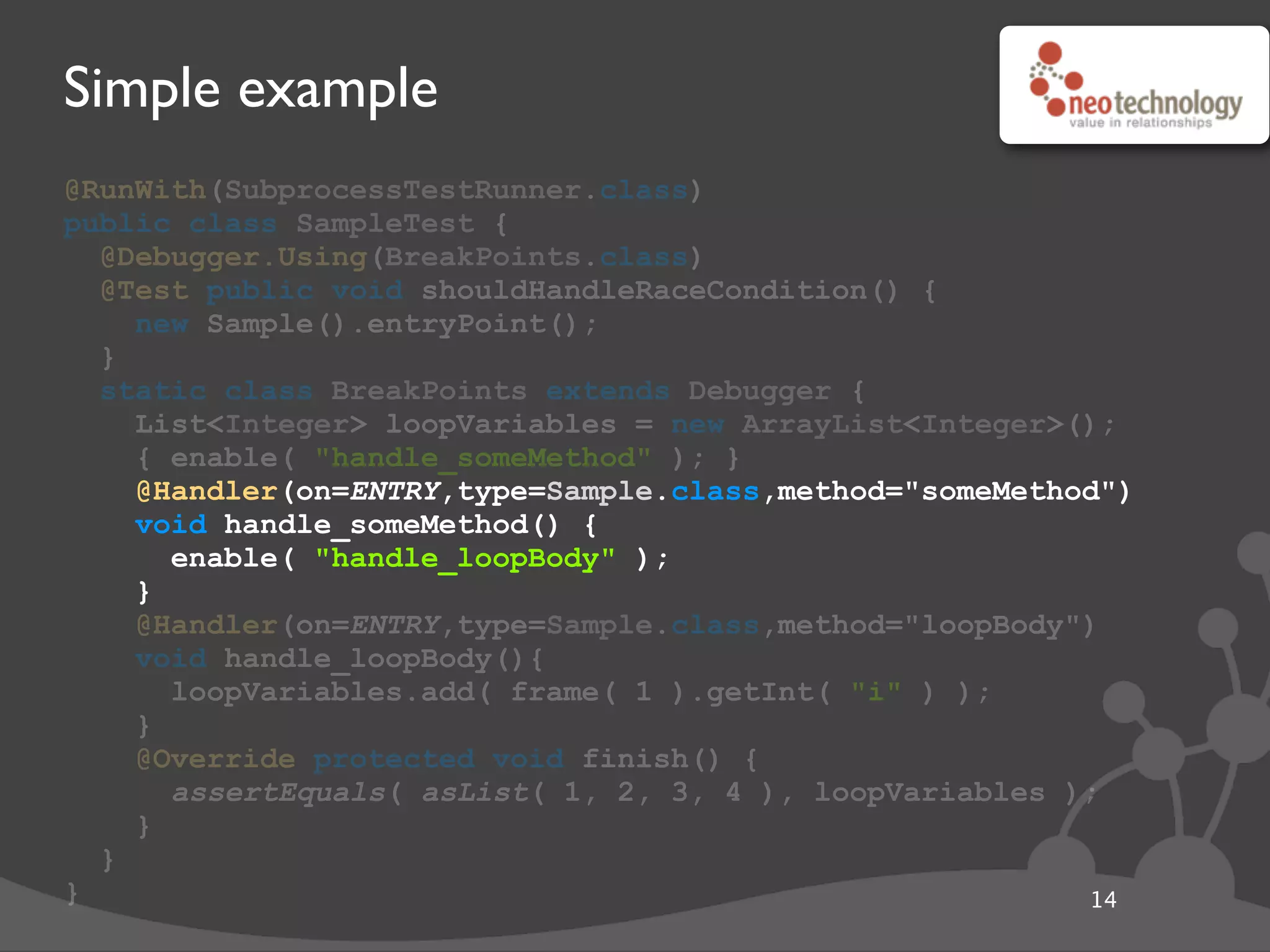
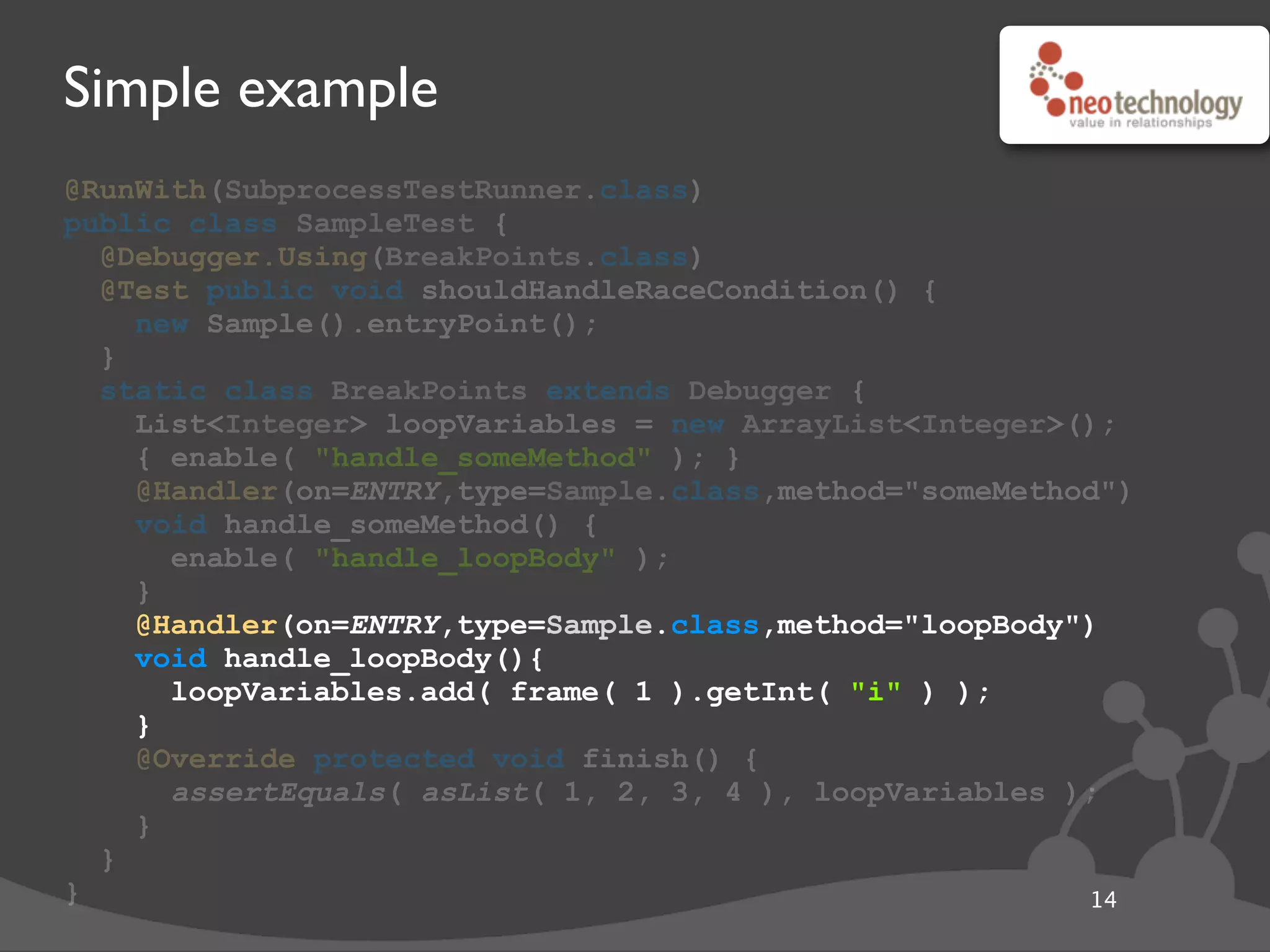
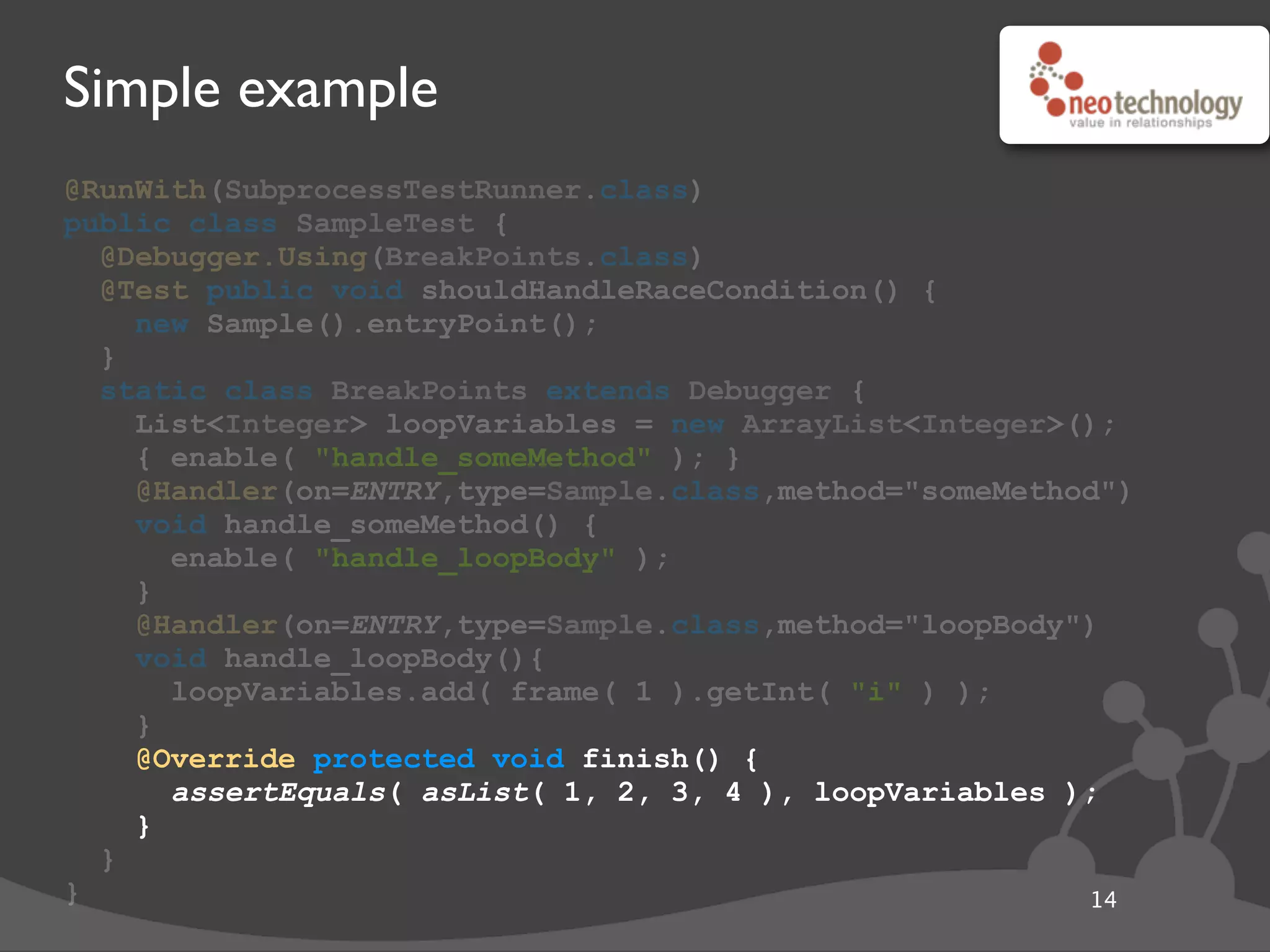
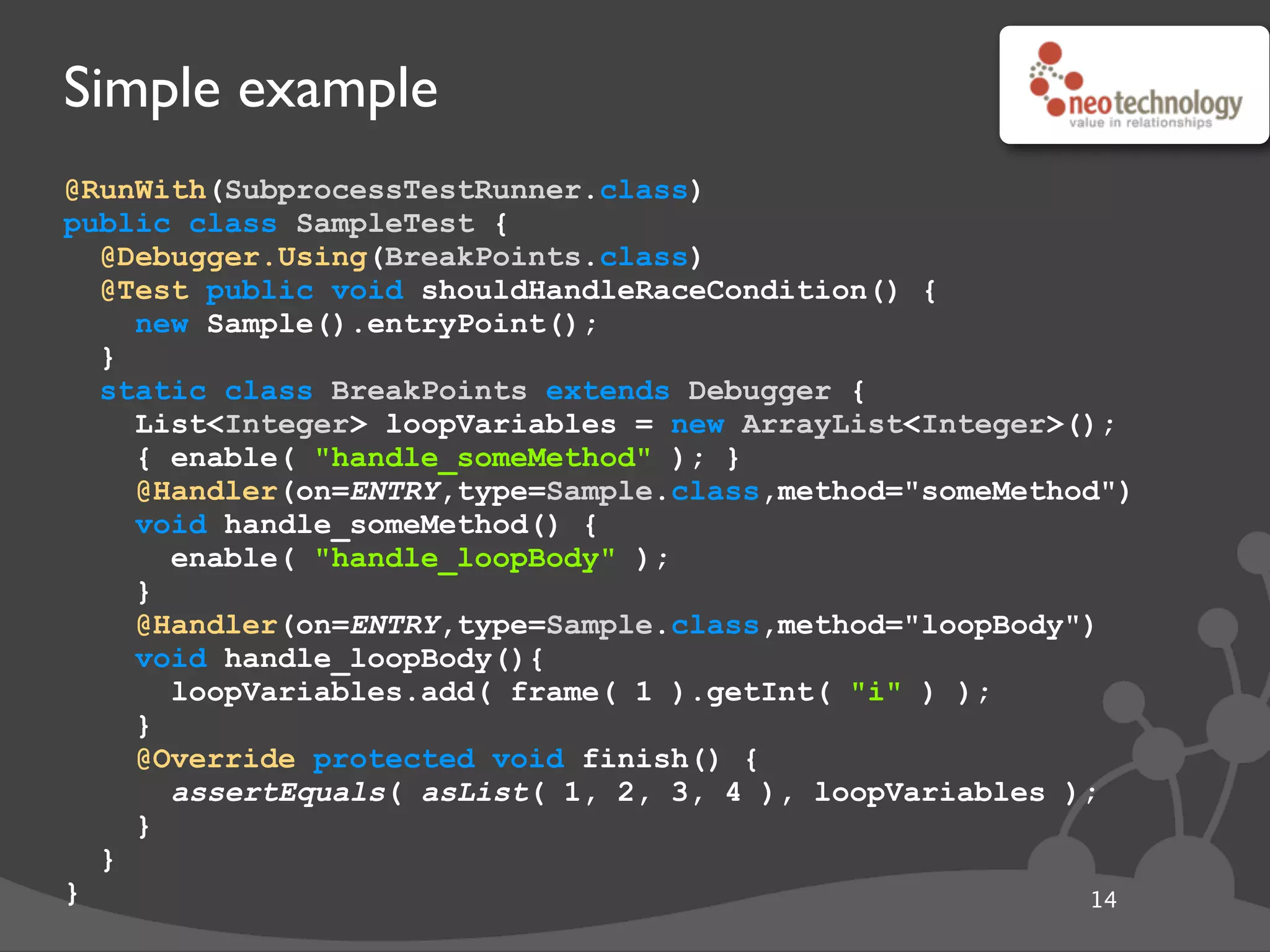
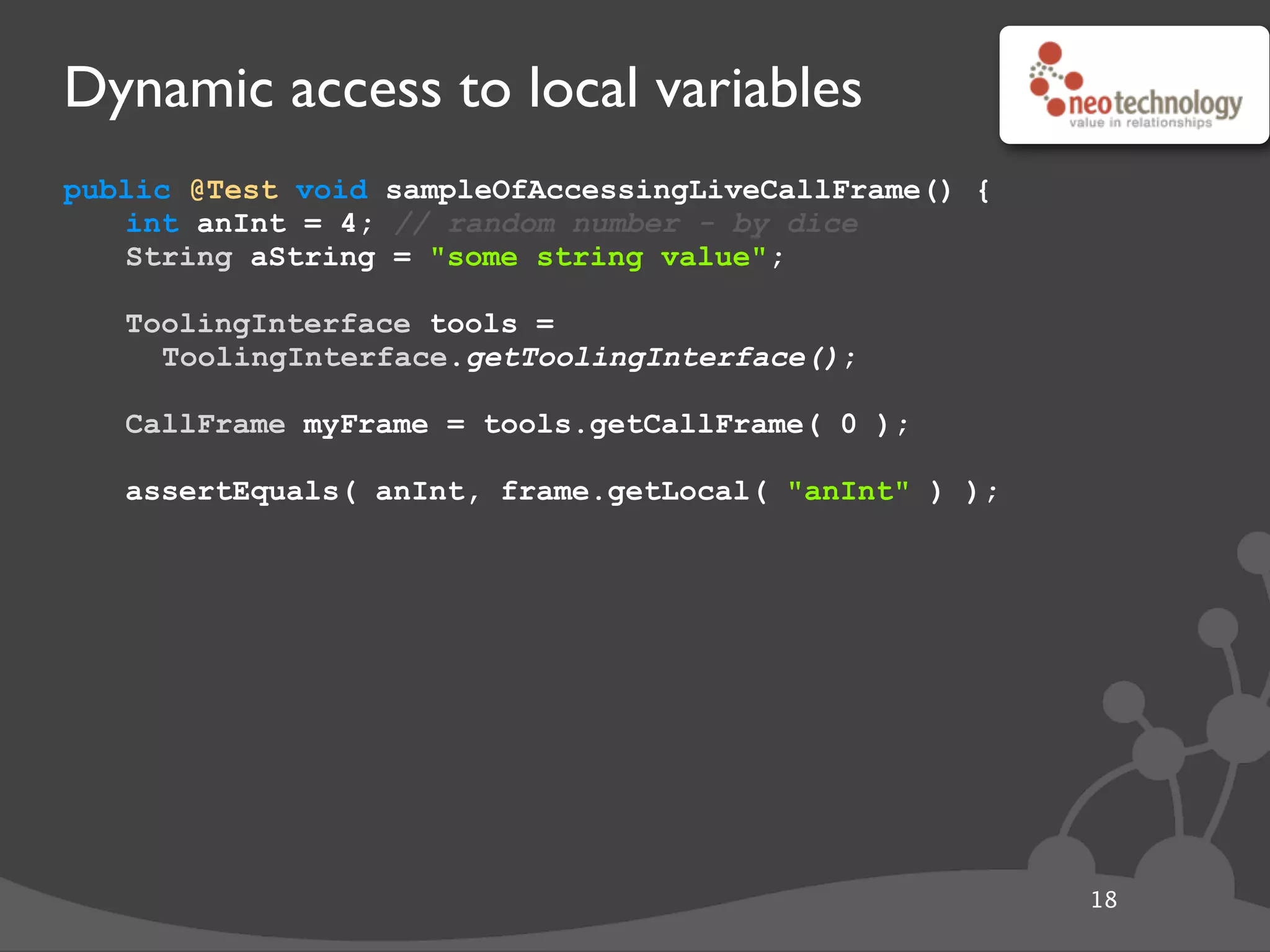
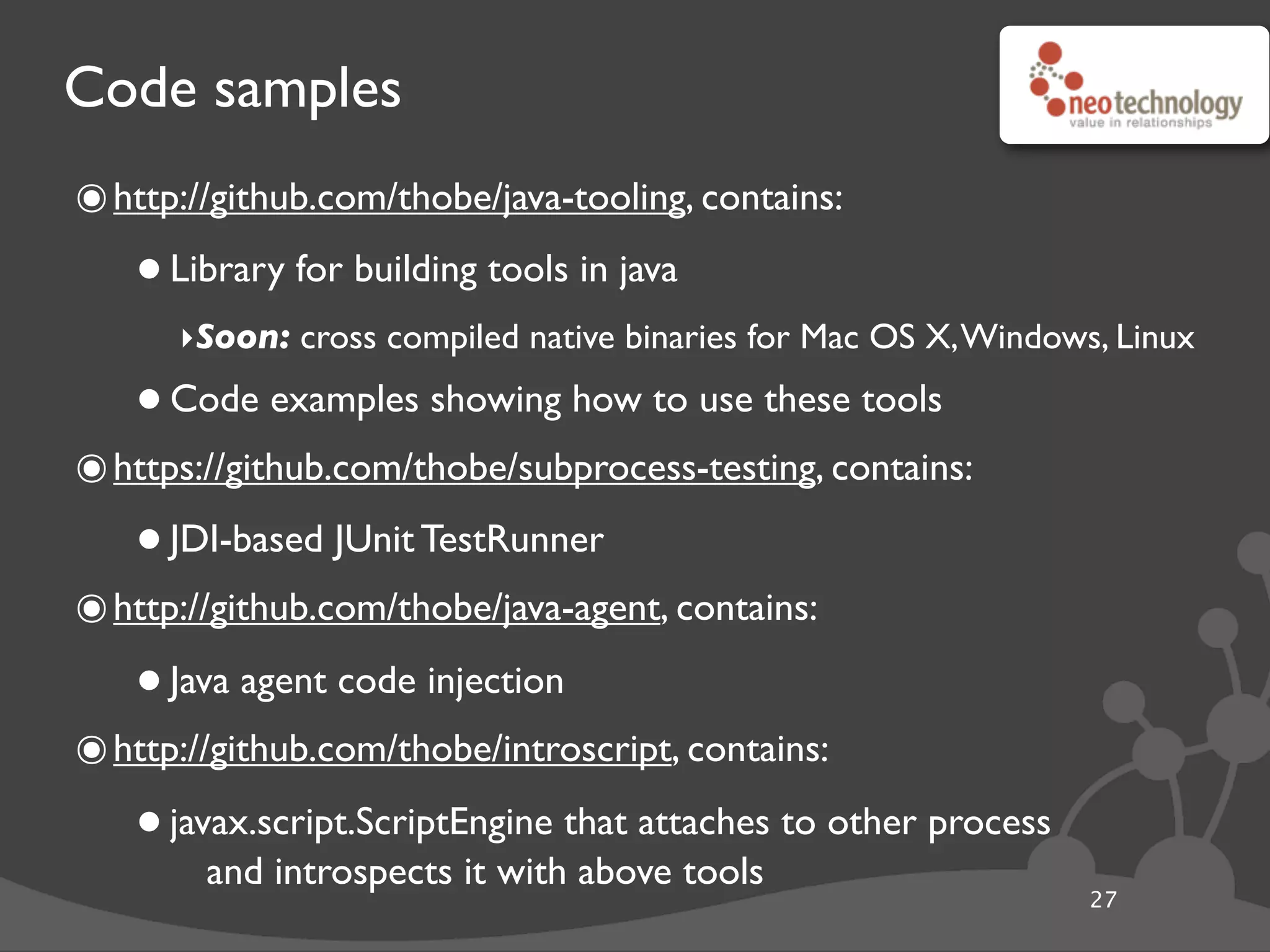
This document provides an overview of tools available in the Java Development Kit (JDK) that allow for powerful introspection and manipulation of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and running applications. It discusses the java.lang.instrument API for injecting Java agents, the Java Debugging Interface (JDI) for debugging, the JVM Tool Interface (JVMTI) for heap and frame introspection, and examples of using these tools to build interactive debuggers, inject code at runtime, and test concurrency. Code samples and links to further resources are also provided.



![java.lang.instrument.Instrumentation
๏The “missing” sizeof() operation:
•long getObjectSize( Object )
๏Inspecting loaded classes:
•Class[] getAllLoadedClasses()
•Class[] getInitiatedClasses( ClassLoader )
๏Transforming classes:
•redefineClasses( ClassDefinition(Class, byte[])... )
•addTransformer( ClassFileTransformer )
‣byte[] transform( ClassLoader, name, Class, byte[] )
•retransformClasses(Class...)
•setNativeMethodPrefix( ClassFileTransformer, String ) 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdkpowertools-130627062511-phpapp02/75/JDK-Power-Tools-4-2048.jpg)
![public static void premain(
String agentArgs, Instrumentation inst)
5
๏java ... -javaagent:<jarfile>[=options]
๏Instrumentation parameter is optional in the signature
๏META-INF/MANIFEST.MF:
•Premain-Class [required; qualified classname of premain class]
•Boot-Class-Path [optional; class path]
•Can-Redefine-Classes [optional; true/false - request capability]
•Can-Retransform-Classes [optional; true/false - request capability]
•Can-Set-Native-Method-Prefix [optional; true/false - request capability]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdkpowertools-130627062511-phpapp02/75/JDK-Power-Tools-5-2048.jpg)