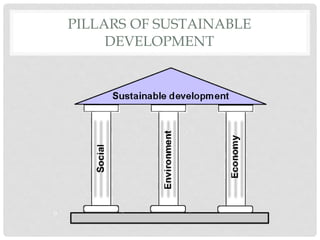
The document discusses the topic of sustainable development. It begins with introducing the term and providing definitions. It then outlines the objectives, pillars and goals of sustainable development. Examples are given of sustainable practices like solar and wind energy. The importance is described in providing essential needs, supporting agriculture, managing climate change and creating financial stability. Barriers to sustainable development are also reviewed, such as upfront expenses and lack of education. The conclusion reiterates that sustainable development considers environmental, social and economic impacts.