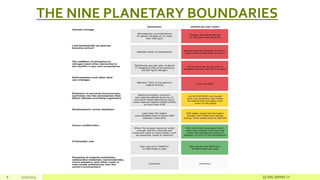
The document discusses the concept of leaving resources in their pristine state or returning them to that state as a definition of sustainable development. It notes that overexploitation of natural resources over the past 50 years has harmed the environment. It also outlines the nine planetary boundaries that scientists have identified as necessary to maintain a stable environment. Finally, it argues that awareness campaigns and international cooperation are needed to restore degraded ecosystems and reduce consumption to return the planet to a pristine state for future generations.