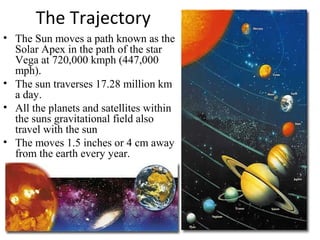
The document discusses signs from verses 37-40 of Surah Yaseen related to the sun, moon, night and day. It provides information about the sun such as its size, temperature, and role in providing light and heat to Earth. It describes the Earth's rotation causing day and night and its orbit around the sun causing seasons. It discusses the moon's phases from new to full as it orbits Earth, and that the sun and moon orbit independently without overtaking each other in accordance with divine will.

![37) And a sign
for them is the
night. We remove
from it [the light
of] day, so they
are [left] in
darkness.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surah-yasin37-40-130822034932-phpapp01/85/Surah-yasin-37-40-2-320.jpg)



![38) And the sun runs [on
course] toward its stopping
point. That is the
determination of the
Exalted in Might, the
Knowing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surah-yasin37-40-130822034932-phpapp01/85/Surah-yasin-37-40-6-320.jpg)
![39) And the moon –
We have determined
for it phases, until it
returns [appearing]
like the old date stalk.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/surah-yasin37-40-130822034932-phpapp01/85/Surah-yasin-37-40-8-320.jpg)


