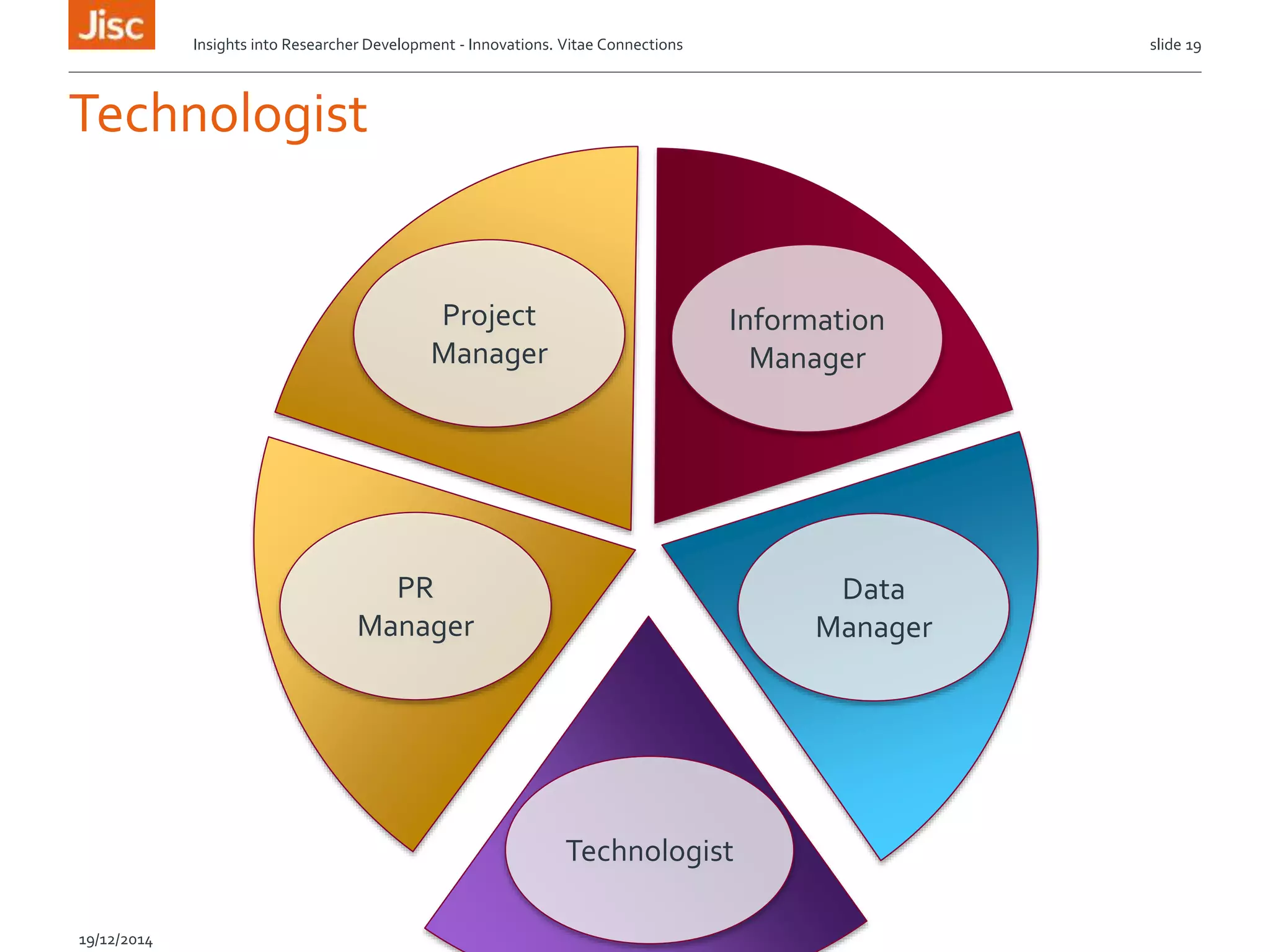
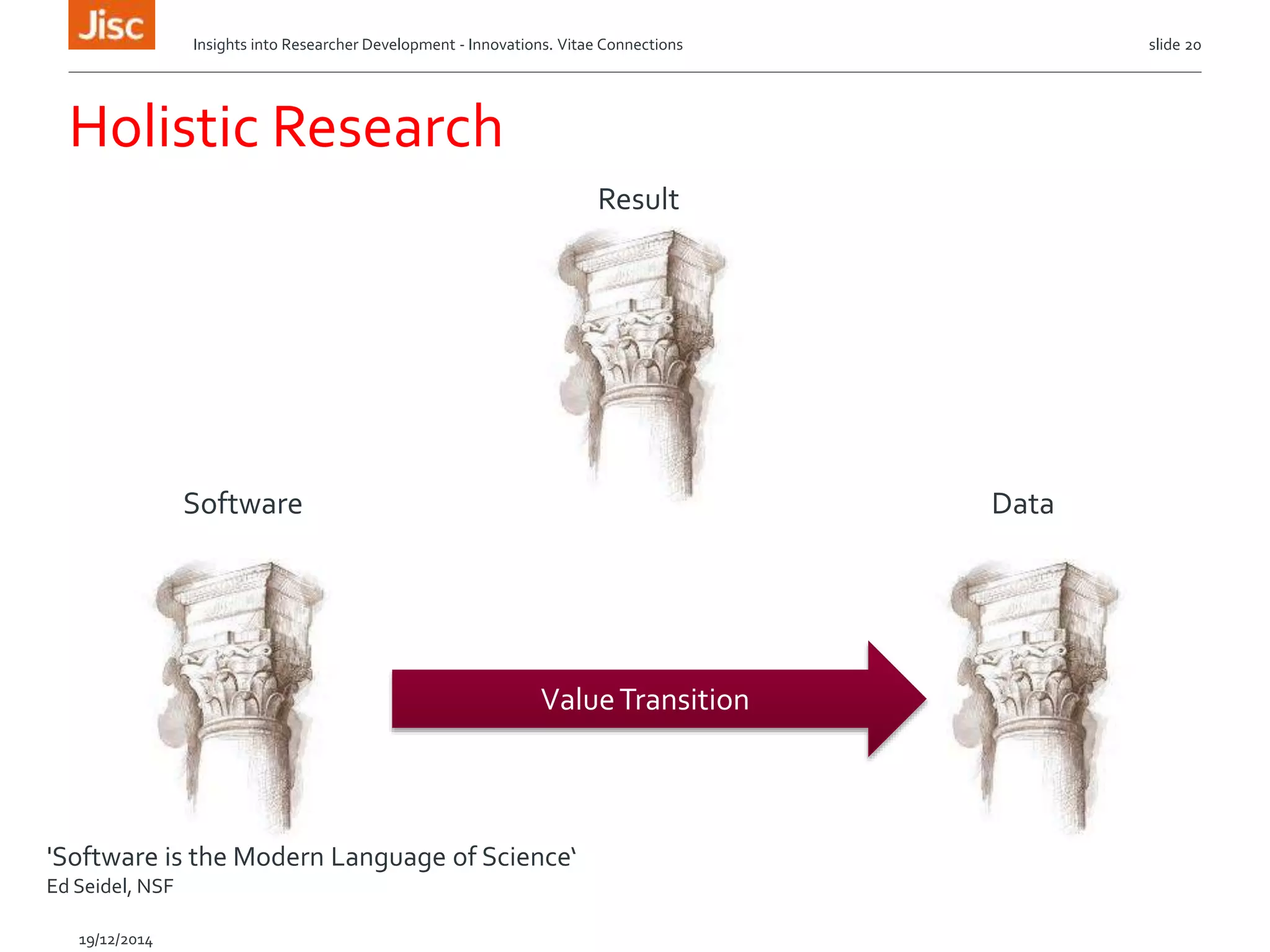
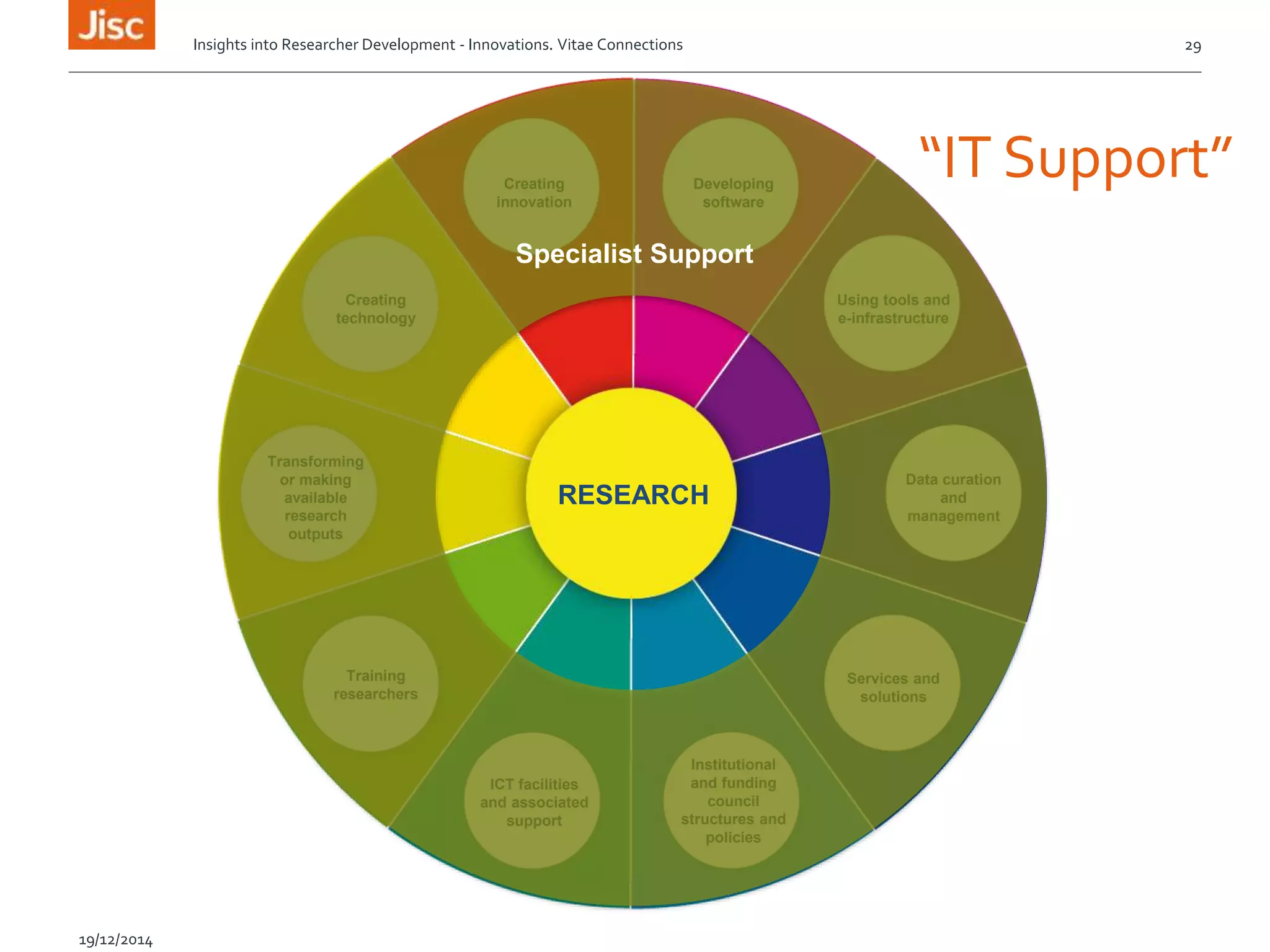
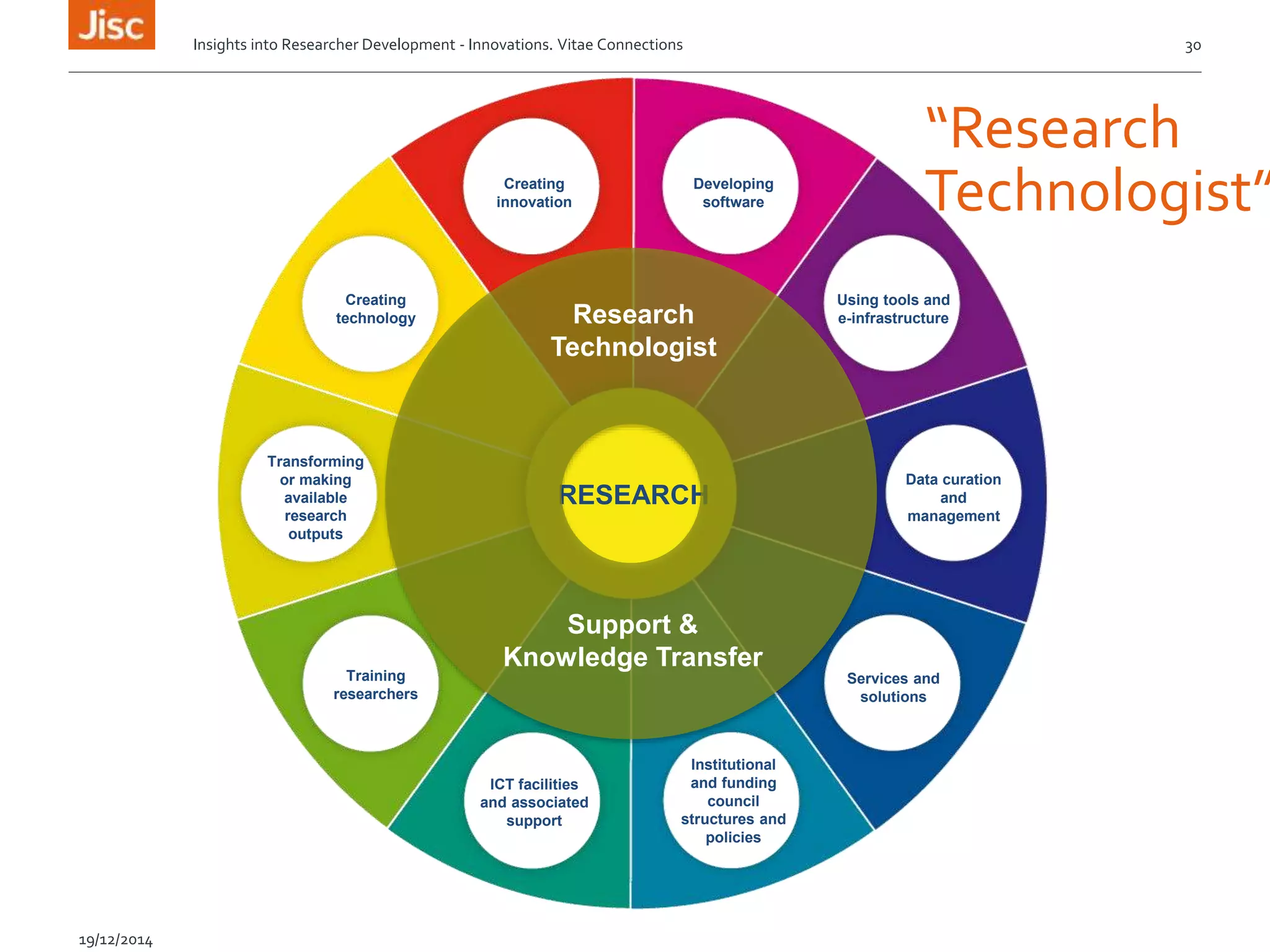
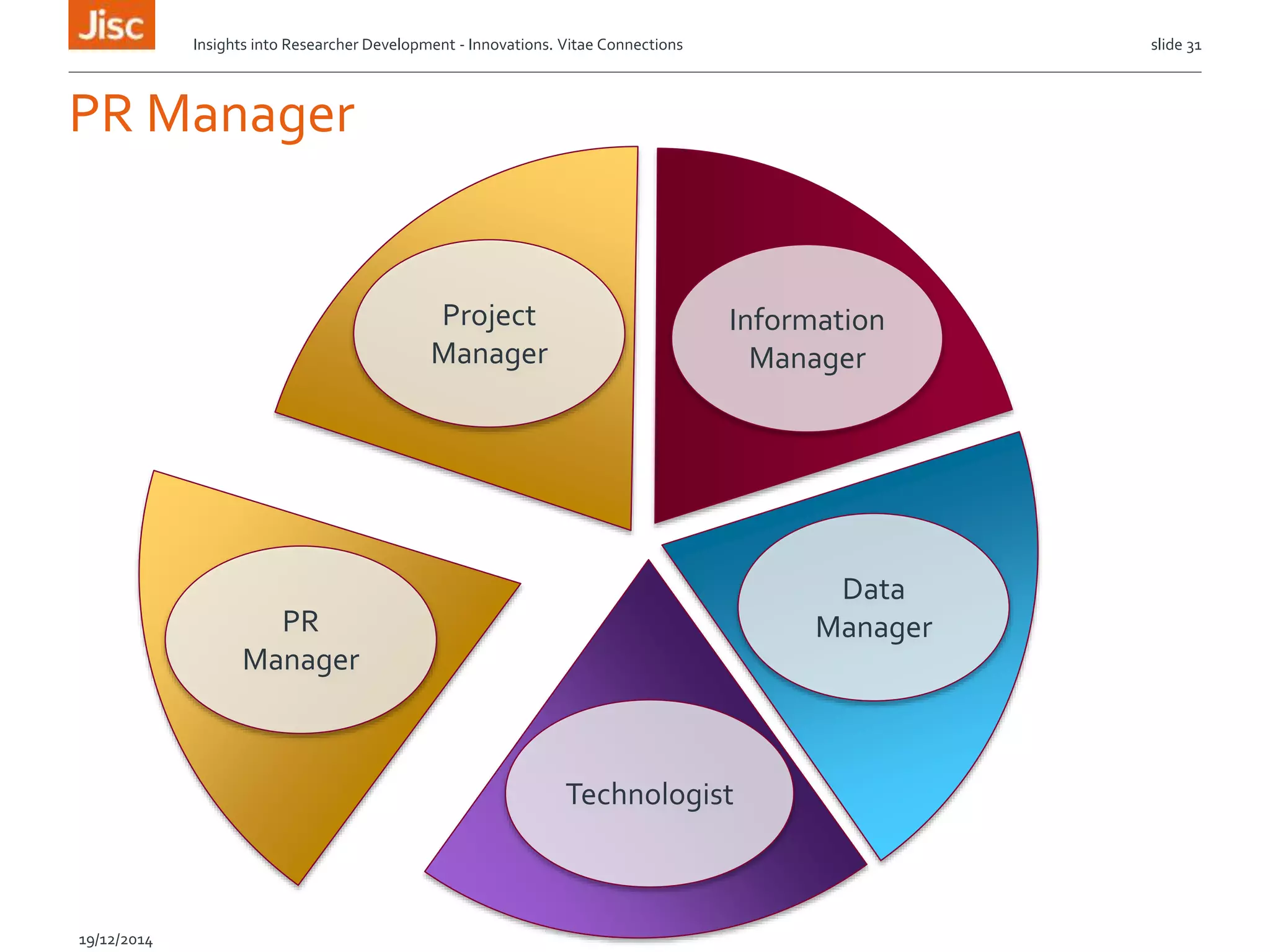
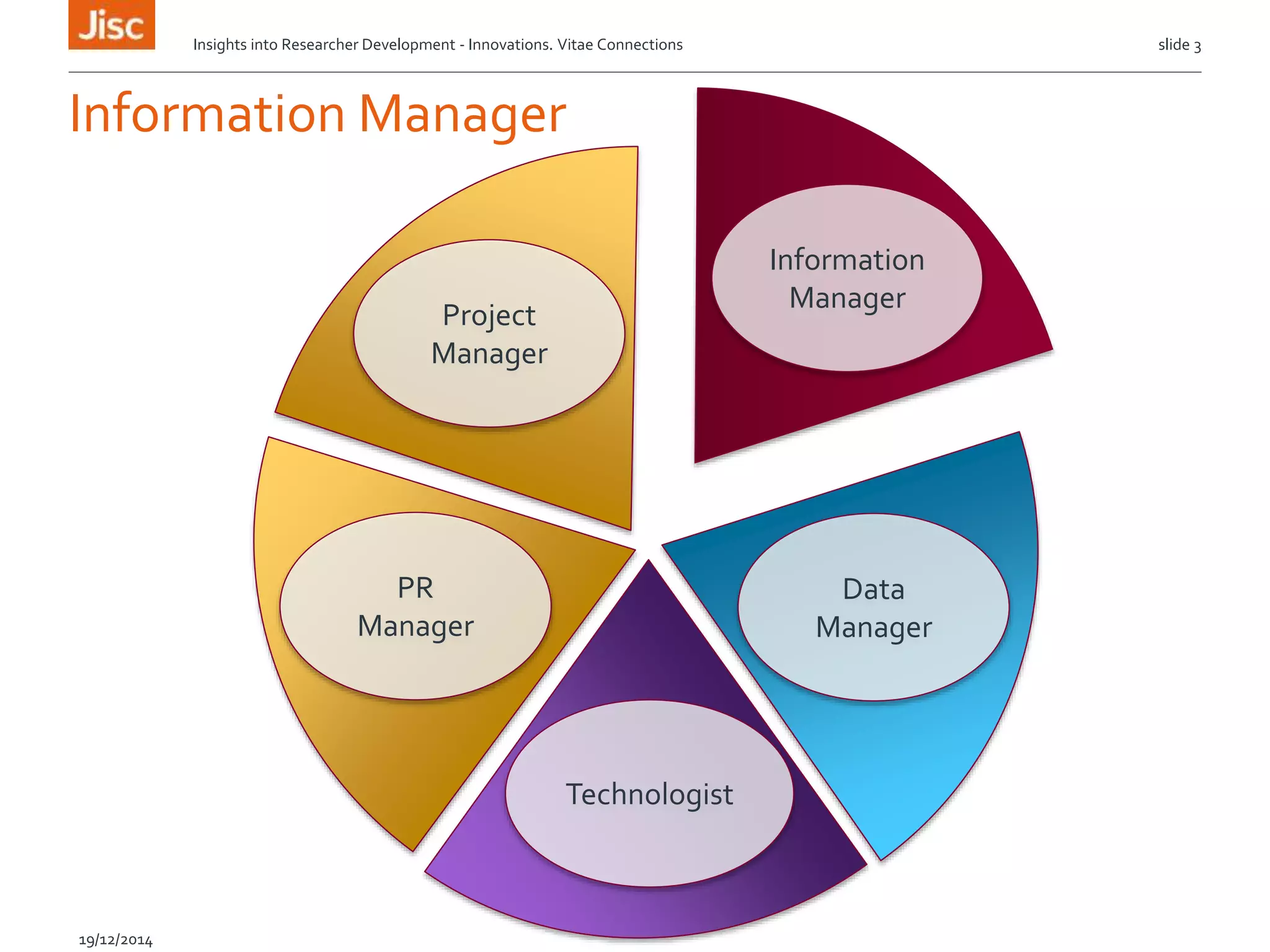
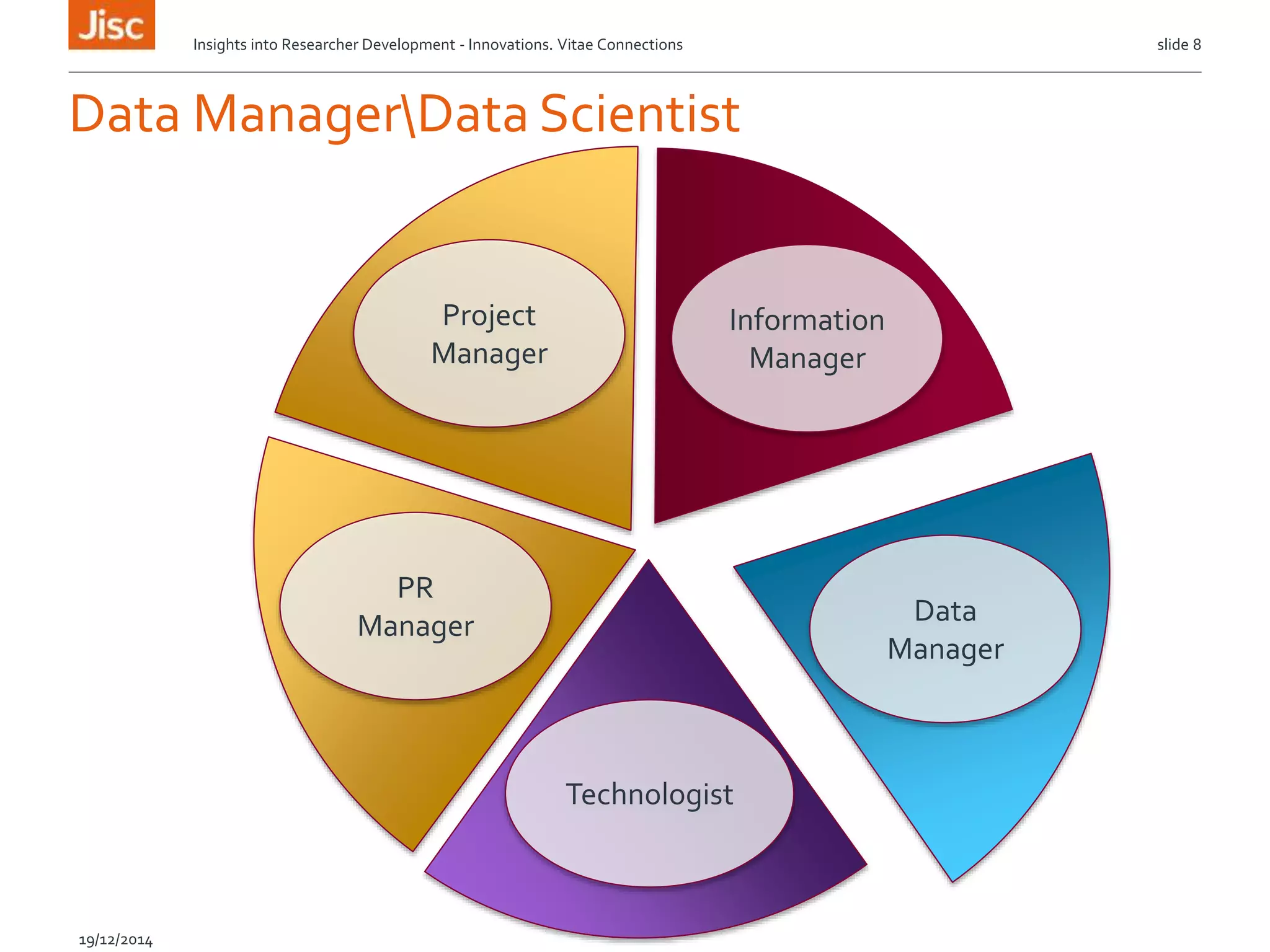
The document discusses the skills needed for researchers to adapt to the future demands of digital research. It outlines several roles that may be important for future researchers, including information manager, data manager, technologist, PR manager, and project manager. It also summarizes findings from a study on the research behaviors of doctoral students and barriers they face. Key needs identified include training researchers in research data management and data skills to help address issues around data sharing, reproducibility, and making the most of digital tools and resources.












![Need forTraining in RDM and Data Skills
‘data skills should be made a core academic competency’
‘data handling [should be] embedded in the curriculum’
‘There is a need to go beyond the workshop and the short
training course, and embed preparation for a professional
(and personal) lifetime of digital data curation within the
academic curriculum.’
Graham Pryor and Martin Donnelly (2009), ‘Skilling up to do data: whose role, whose
responsibility, whose career? IJDC, Issue 2,Volume 4, pp.158-170.
slide 16
19/12/2014
Insights into Researcher Development - Innovations. Vitae Connections](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vitae-tomorrows-researchers-141219015040-conversion-gate01/75/Vitae-tomorrows-researchers-16-2048.jpg)