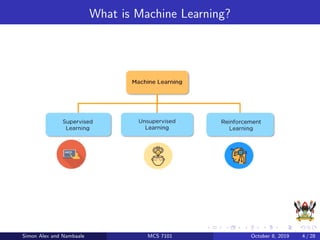
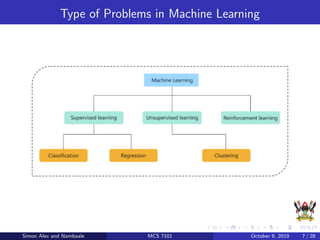
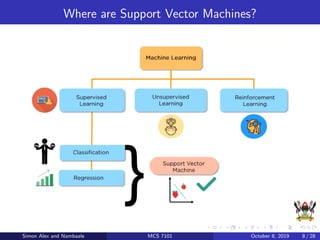
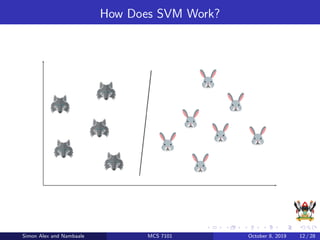
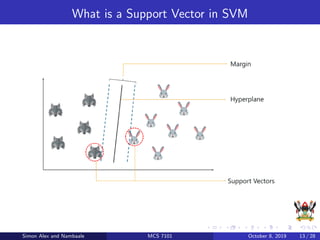
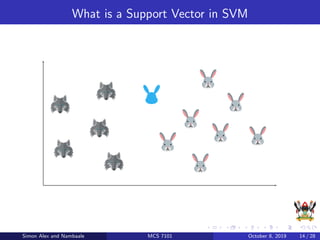
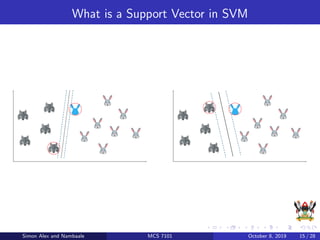
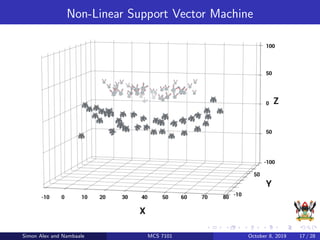
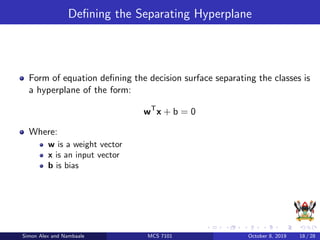
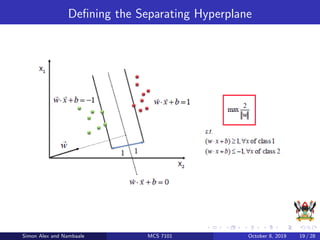
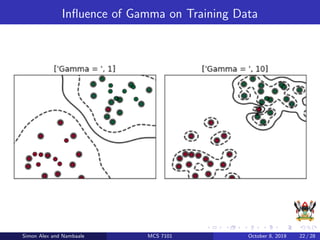
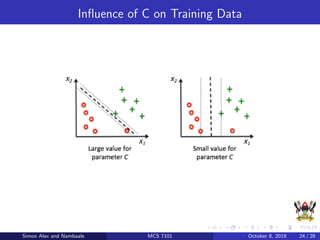
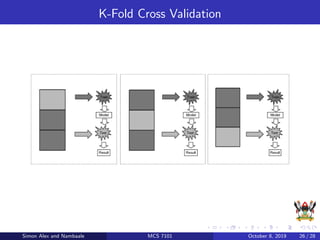
The document discusses support vector machines (SVM), a supervised machine learning algorithm. SVM can be used for both classification and regression problems by finding a hyperplane that separates classes with the maximum margin. It explains key SVM concepts like support vectors, kernels, hyperparameters like gamma and C, and evaluation techniques like cross-validation. Applications mentioned include text categorization, bioinformatics, face recognition and image classification.