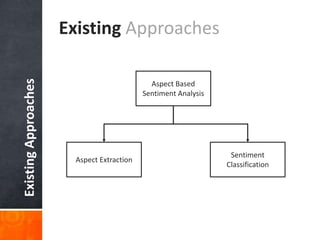
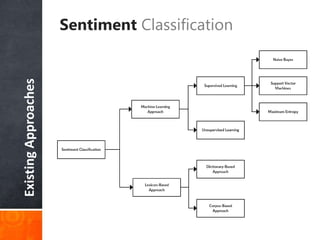
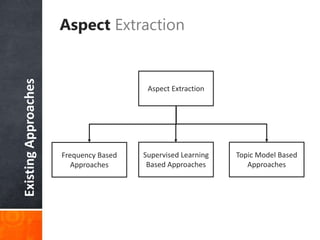
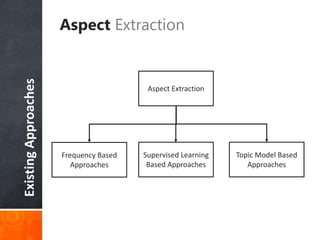
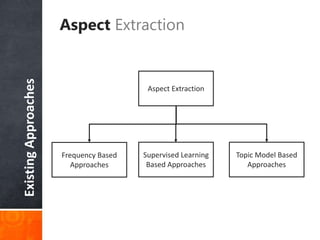
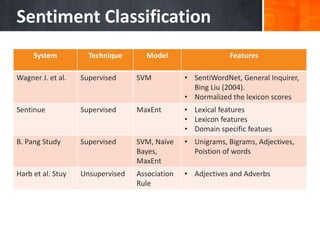
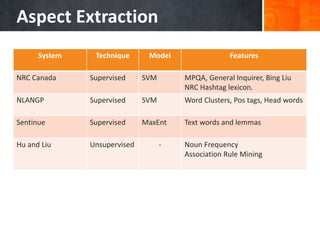
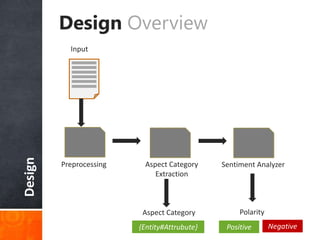
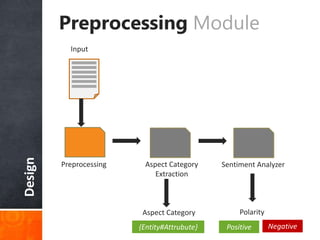
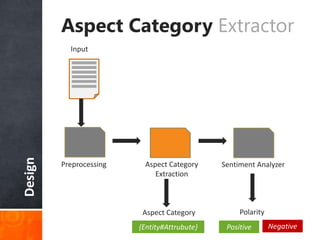
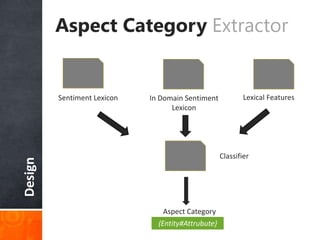
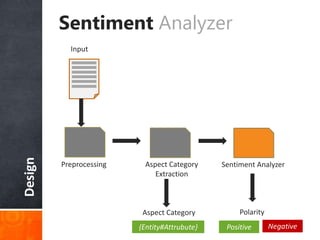
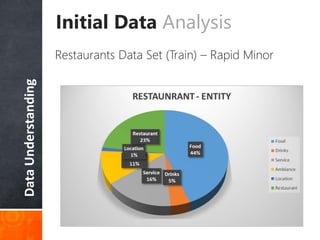
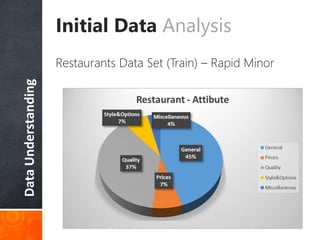
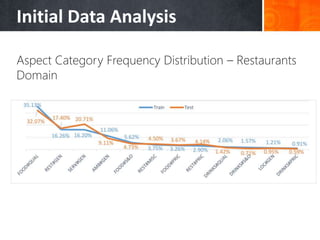
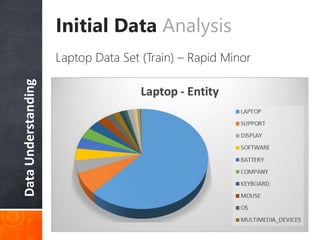
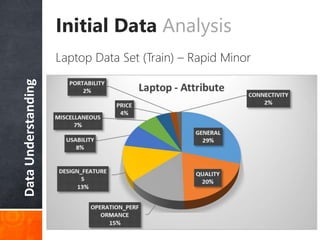
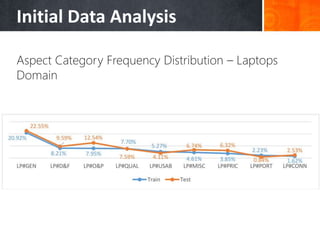
The document discusses a supervised learning approach to aspect-based sentiment analysis, outlining the importance of identifying sentiments linked to specific aspects of entities. It includes a thorough literature review, research aims, and the proposed methodology for extracting aspect categories and determining sentiment polarity. Current progress includes dataset collection and annotation, with plans for implementation and evaluation.