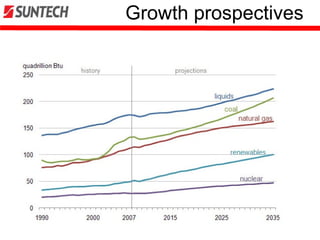
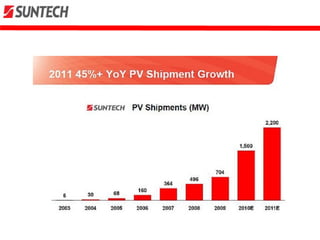
This document provides an overview of the solar panel manufacturer Suntech. Some key details:
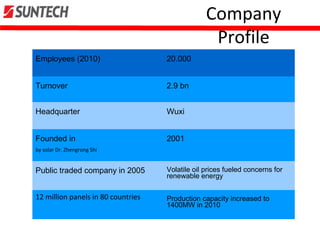
- Founded in 2001 and went public in 2005, Suntech had 20,000 employees and $2.9 billion in turnover by 2010.
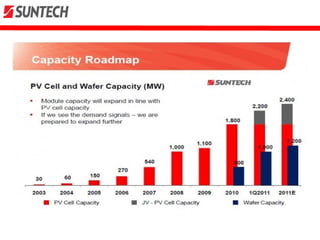
- It is headquartered in Wuxi, China and has manufactured over 12 million solar panels across 80 countries.
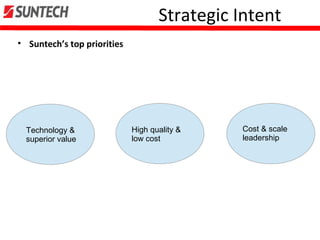
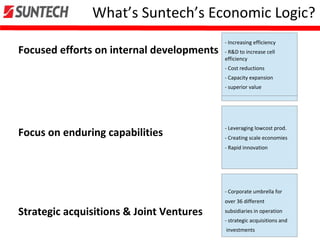
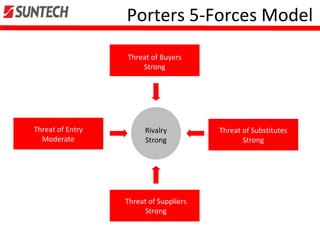
- Suntech focuses on technology leadership, high quality, and cost leadership through R&D, efficiency gains, and scale.
- It uses acquisitions and partnerships to strengthen its core business and supply chain.
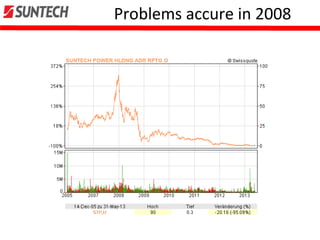
- However, Suntech declared insolvency in 2013 due to high competition, price dumping accusations, and financial issues