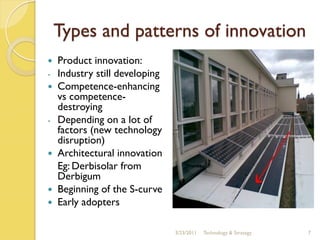
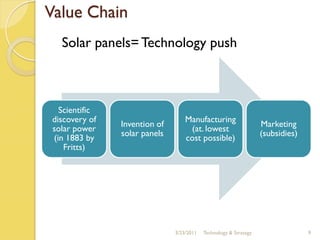
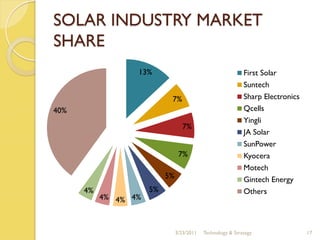
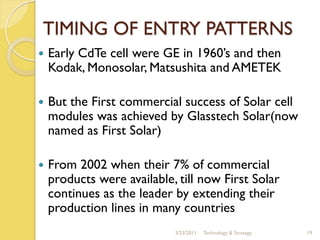
The document discusses the history and evolution of solar technology and the company First Solar. It summarizes that solar power has grown 48% annually since 2002 but still only accounts for 0.04% of global energy consumption. First Solar is the world's leading solar panel manufacturer, using cadmium telluride to produce panels at a lower cost than competitors. However, the solar industry remains dependent on government subsidies and is still in its infancy with opportunities for new market entrants.