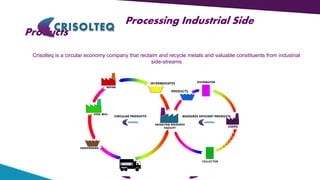
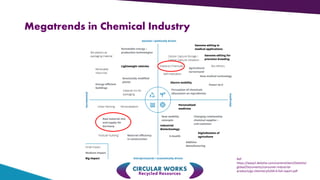
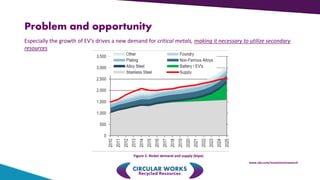
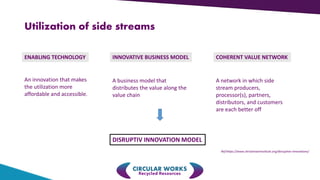
Crisolteq is a circular economy company that reclaims and recycles metals and valuable constituents from industrial side-streams. It has locations in Harjavalta, Nornick, Raisio, and Tornio where it processes side-streams from various industries. Crisolteq utilizes disruptive innovation through novel combinations of existing technologies and business models to make side-stream utilization more affordable and distribute value across networks of producers, processors, and customers. It has invested over 5 million euros since 2005 to develop projects and transition them to commercial operations. Crisolteq's circular economy model creates new products from residues through separation and processing, forming linkages between various industries like steel, pulp, and others.