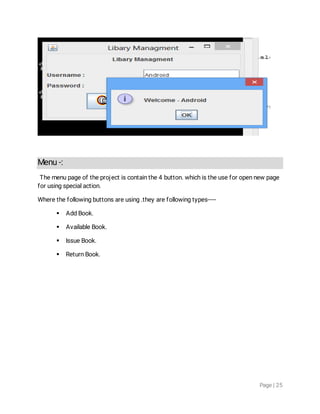
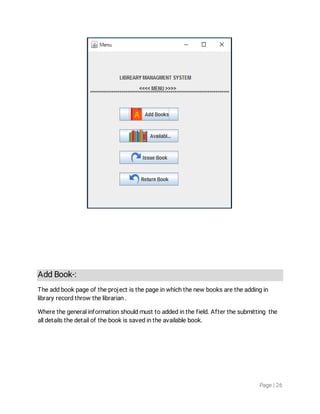
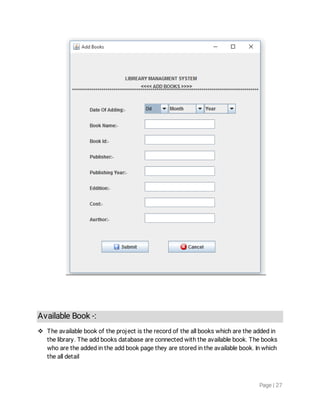
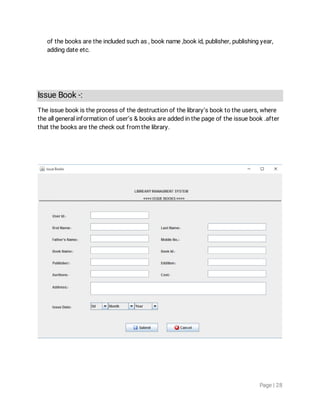
1. The document discusses object-oriented programming concepts in Java like inheritance, abstraction, encapsulation, polymorphism etc. It provides examples and definitions for classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism etc.
2. It discusses different types of constructors in Java like default, parameterized constructors and constructor overloading.
3. It explains static keyword in Java for static variables, static methods and static blocks. It provides memory management advantages of static keyword.





![Page|7
object.
Javaconstructoris invokedatthetimeofobjectcreation.Itconstructsthe
valuesi.e.providesdatafortheobjectthatiswhyitisknownasconstructor.
Rulesforcreatingjavaconstructor
Therearebasicallytworulesdefinedfortheconstructor.
1. Constructornamemustbesameasitsclassname
2. Constructormusthavenoexplicitreturntype
Typesofjavaconstructors
Therearetwotypesofconstructors:
1. Defaultconstructor(no-arguementconstructor)
2. Parameterizedconstructor
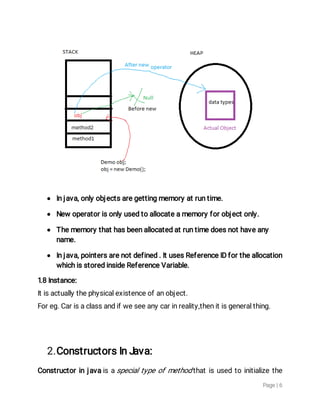
2.1DefaultConstructor:
Eg.
classBike1{
Bike1(){
System.out.println("Bikeiscreated");
}
publicstaticvoidmain(Stringargs[]){](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appintechreport1-170925204513/85/summer-training-report-on-java-7-320.jpg)







![Page|16
Voidget(intx,inty){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;}
publicstaticvoidmain(Stringargs[])
{
Childc1=newChild();
C1.get(1,2);
C1.show();
}
}
Output:
1
2
7.2Interfaces:
Interfacesaretheblueprintofaclass.
Itisareferencetypeinjava.Itisacollectionofabstractmethods.
Aclassimplementsaaninterface,therebyinheritinganabstract
methodsftheinterface.
Alongwiththeabstractmethods,italsocontainconstants,default
methods,staticmethods,andnestedmethods.
Interfacecontainsthebehaviorthataclassimplements.
Interfacecan’tbeinstanciated.
Interfacedoesnotcontainanyconstructors.
Allthemethodsofinterfaceareabstract.
Aninterfaceisnotextendedbyaclass.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appintechreport1-170925204513/85/summer-training-report-on-java-16-320.jpg)
![Page|17
Aninterfacecanextendmultipleinterfaces.
Interfacekeywordisusedtodeclareinterface.
Foreg.
InterfaceMy{
voidshow();}
classChildimplementsMy{
publicvoidshow()
{System.out.println(“show”);}
Publicstaticvoidmain(Stringargs[]){
Mym=newMy();
m.show();}
output:
show
7.3ExtendindInterfaces:
Eg.
publicinterfaceSports{
publicvoidshow();
}
PublicinterfaceFootballextendsSports{
Publicvoidscore();
}
7.4Extendingmultipleinterfaces
Eg.PublicinterfacehockeyextendsSports,Football{}
8.StringHandling:
Creatingstringbymostdirectway:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appintechreport1-170925204513/85/summer-training-report-on-java-17-320.jpg)
![Page|18
Stringg=“Helloworld”;
Stringclassisimmutablesoonceobjectiscreateditcan’tbechanged.
ImportantmethodsofStringclass:
1.byteb[]=g.getBytes();
2.charch[]=g.toCharArray();
3.charc=g.charAt(2);
4.Strings1=g.toUpperCase();
5.Strings2=g.toLowerCase();
6.Strings1=g.subString(10);
7.Strings2=g.subString(0,4);
8.Strings=String.valueOf(10);
9.intI=Integer.parseInt(“10”);etc.
StringConcatenation:
Strings=“good”;
S=s+“morning”;
StringComparision:
1.Booleanb=s1.equals(s2);
Italwayscomparesthecontentofreferencevariable,ifsamethenreturns
true;
2.booleanb=s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2);
3.intx=s1.CompareTo(s2);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appintechreport1-170925204513/85/summer-training-report-on-java-18-320.jpg)