This document provides an overview of various training programs offered by SSDN Technologies, including courses in Java, C++, and Android. It details the fundamentals of object-oriented programming (OOP), including the key concepts of encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism in Java. Additionally, it outlines the history of Java development, its features, performance characteristics, and the phases involved in compiling and executing Java programs.


















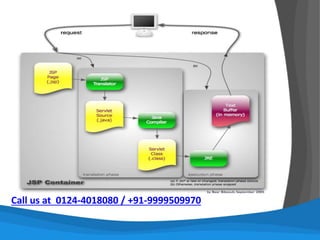

![This program prints Welcome to Java!
public class Welcome
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Welcome to Java!");
}
}
Call us at 0124-4018080 / +91-9999509970](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-weeks-summer-training-java-140520232015-phpapp02/85/6-Weeks-Summer-Training-on-Java-By-SSDN-Technologies-21-320.jpg)
