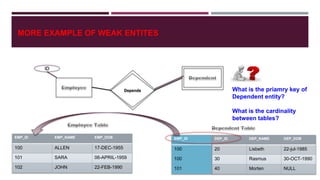
The document discusses entity relationship diagrams (ERD), subqueries, and views. It covers concepts such as weak entities, derived attributes, multi-valued attributes, composite attributes, and examples of how to represent these in an ERD. It also provides examples of subqueries used in SELECT statements and how to create views in SQL along with exercises for practicing views.


![SUBQUERY
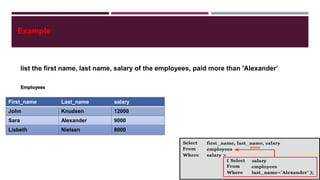
◼A subquery/Inner query/Nested query is a SQL query within another SQL query and embedded within the
WHERE clause.
◼Subqueries are most frequently used with the SELECT statement. The basic syntax is as follows:
SELECT column_name FROM table
WHERE column_name OPERATOR
(SELECT column_name FROM
table
[WHERE] )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subqueryview-190604085620/85/Subquery-view-11-320.jpg)
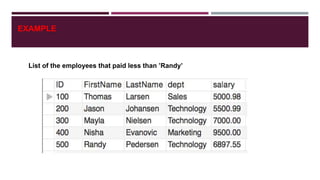




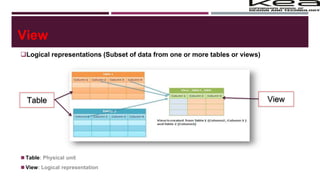

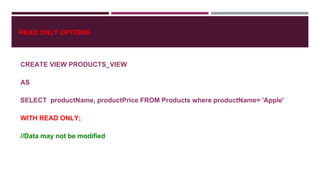
![Creating a View
CREATE [OR REPLACE] VIEW //REPLACE if view already exists
VIEW_NAME
AS
SELECT COLUMN1, COLUMN2,…
FROM TABLE_NAME
WHERE CONDITION;
EXAMPLE 1
EXAMPLE 2
CREATE VIEW [List of Chair] AS
SELECT ProductID, ProductName, productprice
FROM Products
WHERE productName = ‘Chair’;
CREATE VIEW [List of products more than 1000] AS
SELECT ProductID, ProductName
FROM Products
WHERE productprice > 1000’;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subqueryview-190604085620/85/Subquery-view-20-320.jpg)