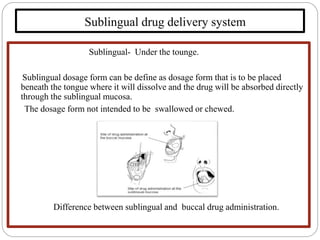
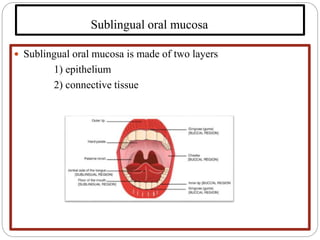
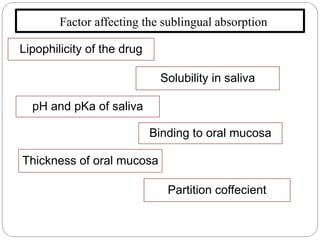
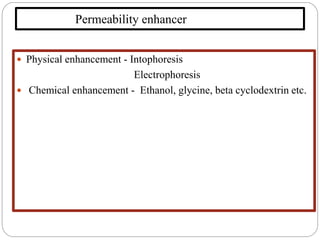
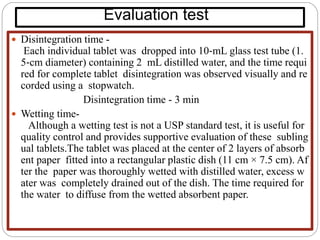
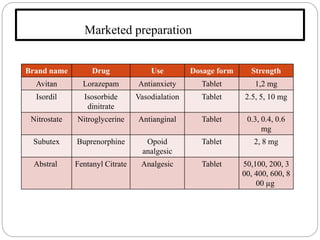
This document discusses sublingual drug delivery systems. Sublingual dosage forms are placed under the tongue to dissolve and be absorbed through the sublingual mucosa without being swallowed. This bypasses first-pass liver metabolism, allows for rapid drug absorption due to high vascularization of the sublingual region, and can be used for emergency medications. Common sublingual dosage forms include tablets, films, sprays and semi-solid forms. Evaluation tests include disintegration time, wetting time, and pharmacokinetic studies in animals. Several marketed sublingual drugs are also listed.