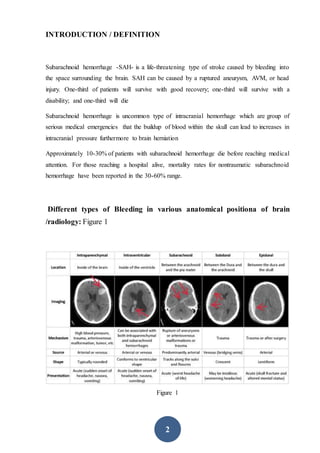
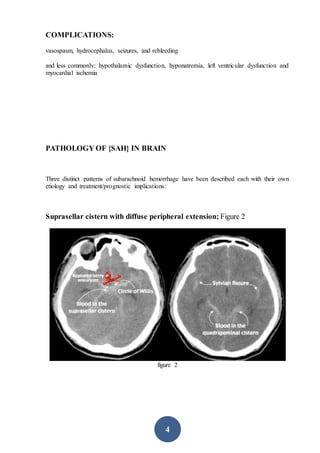
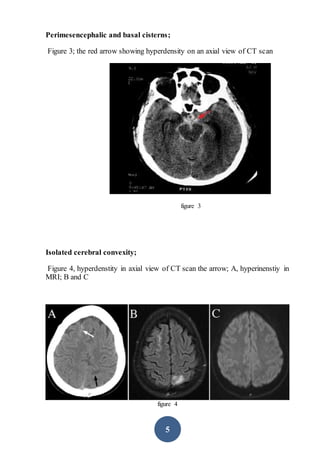
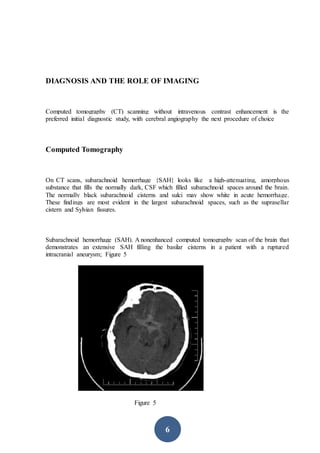
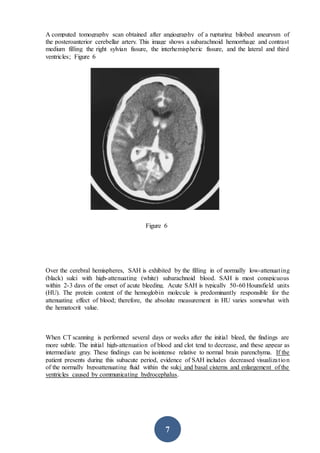
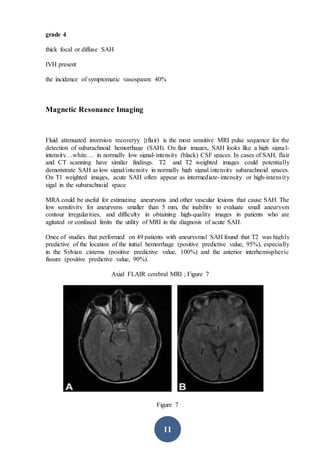
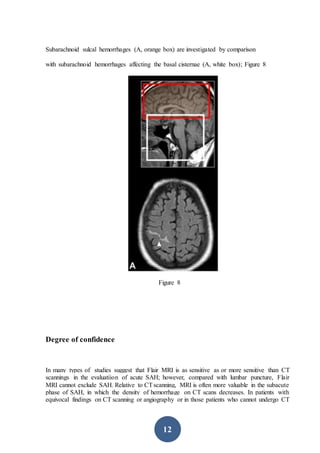
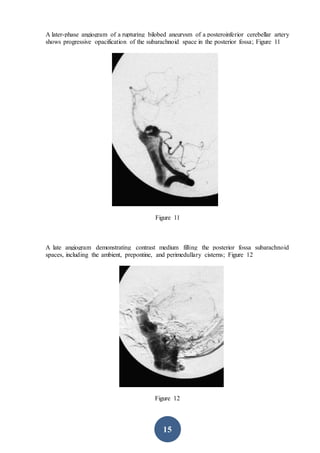
CT scanning is the preferred initial imaging study for diagnosing subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). CT scans can detect blood in the subarachnoid spaces around the brain and have a sensitivity of 93-100% within 24 hours. The amount of blood seen on CT scans correlates with risk of developing vasospasm and can help prognosticate. While CT is very accurate for diagnosing acute SAH, its sensitivity decreases after 5-7 days. If CT is negative but clinical suspicion remains, lumbar puncture should be performed.