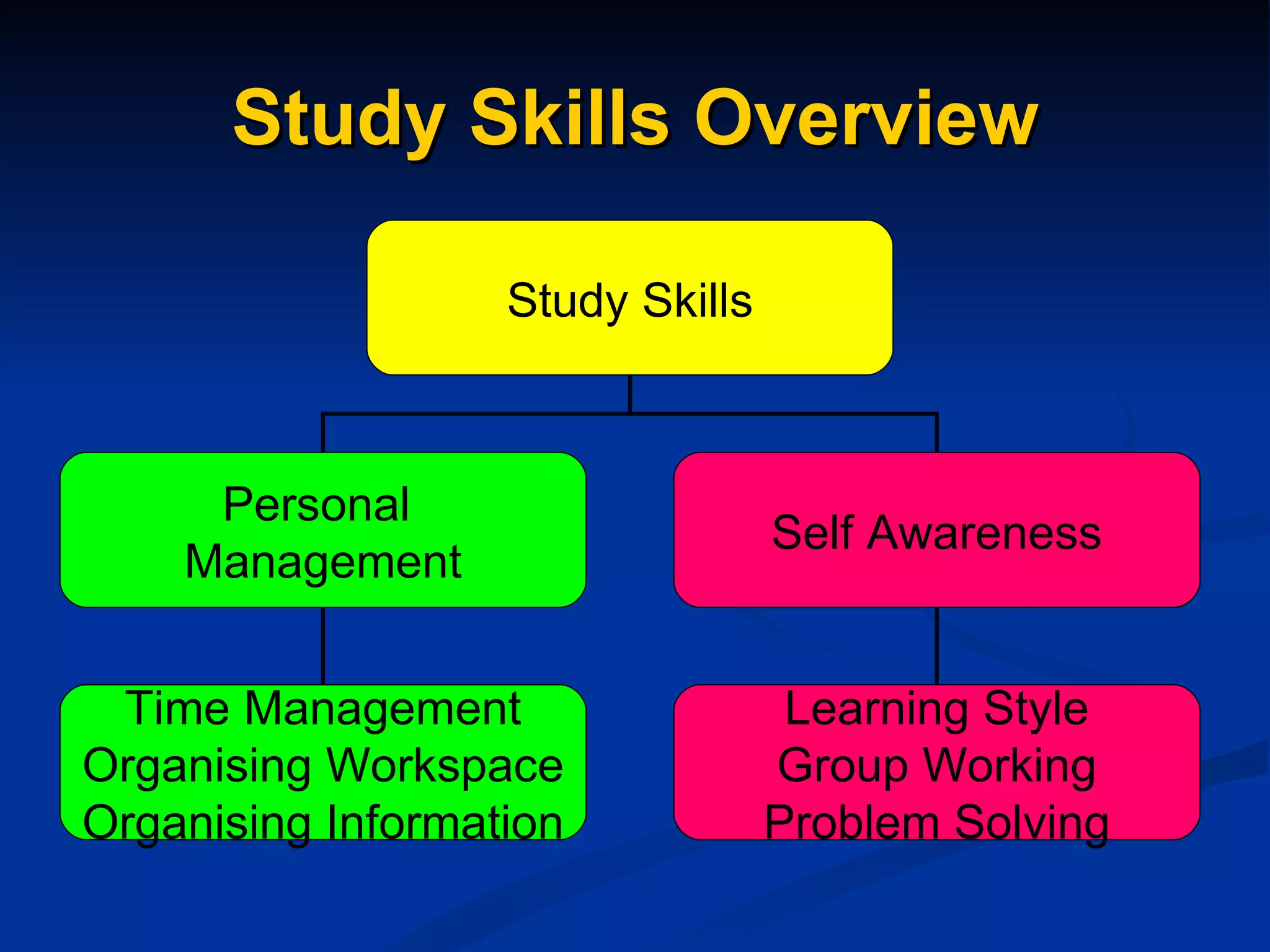
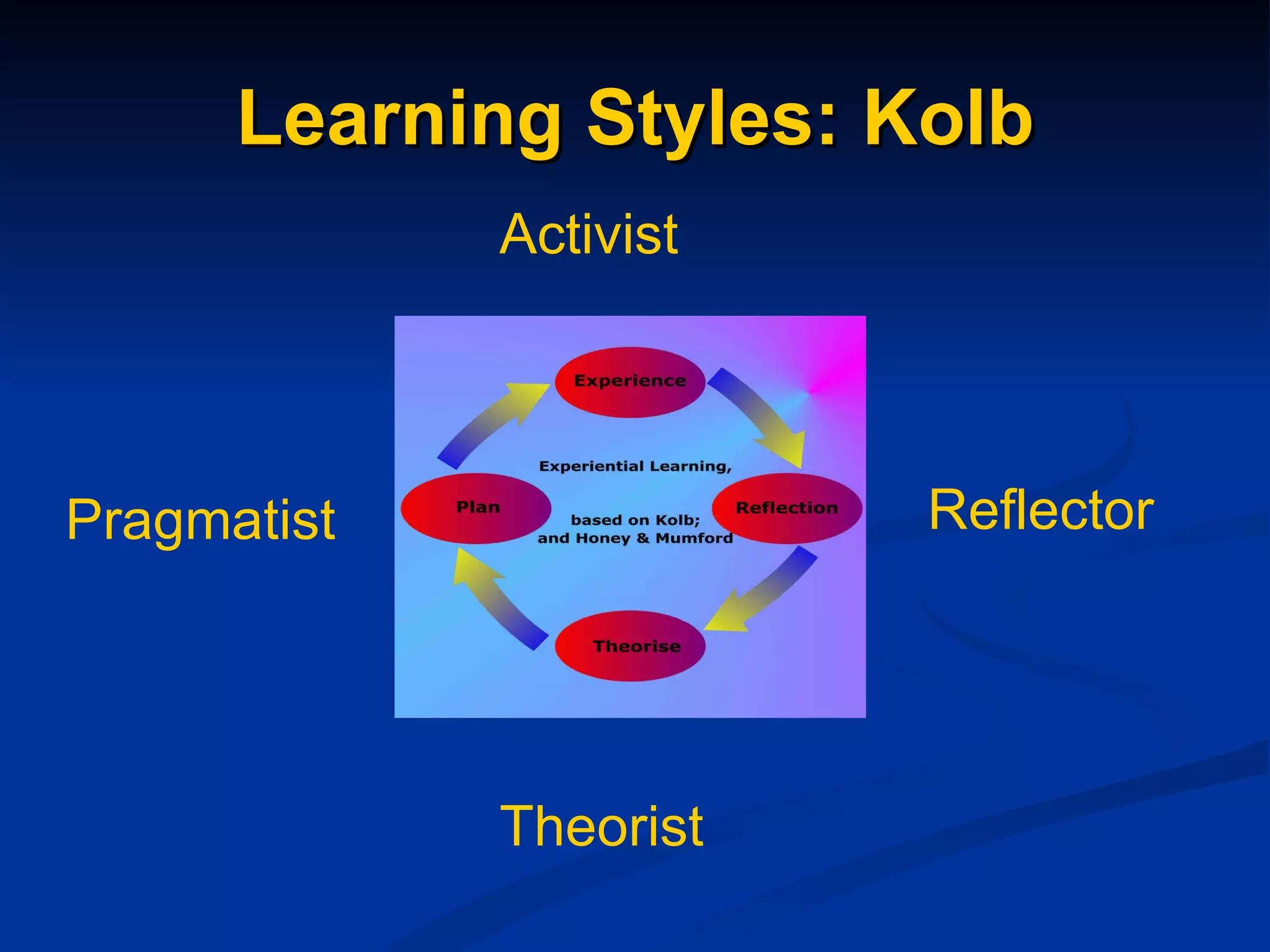
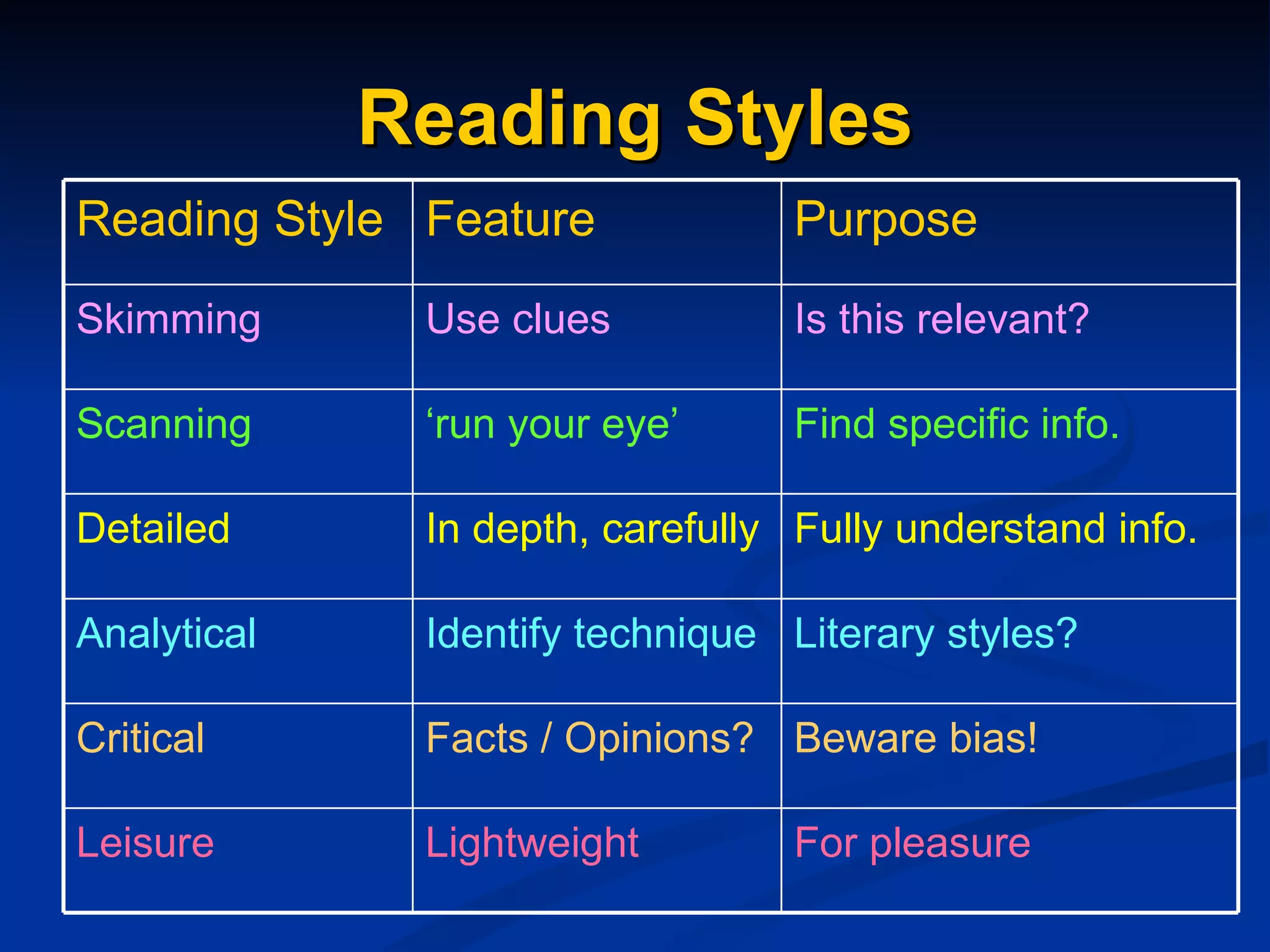
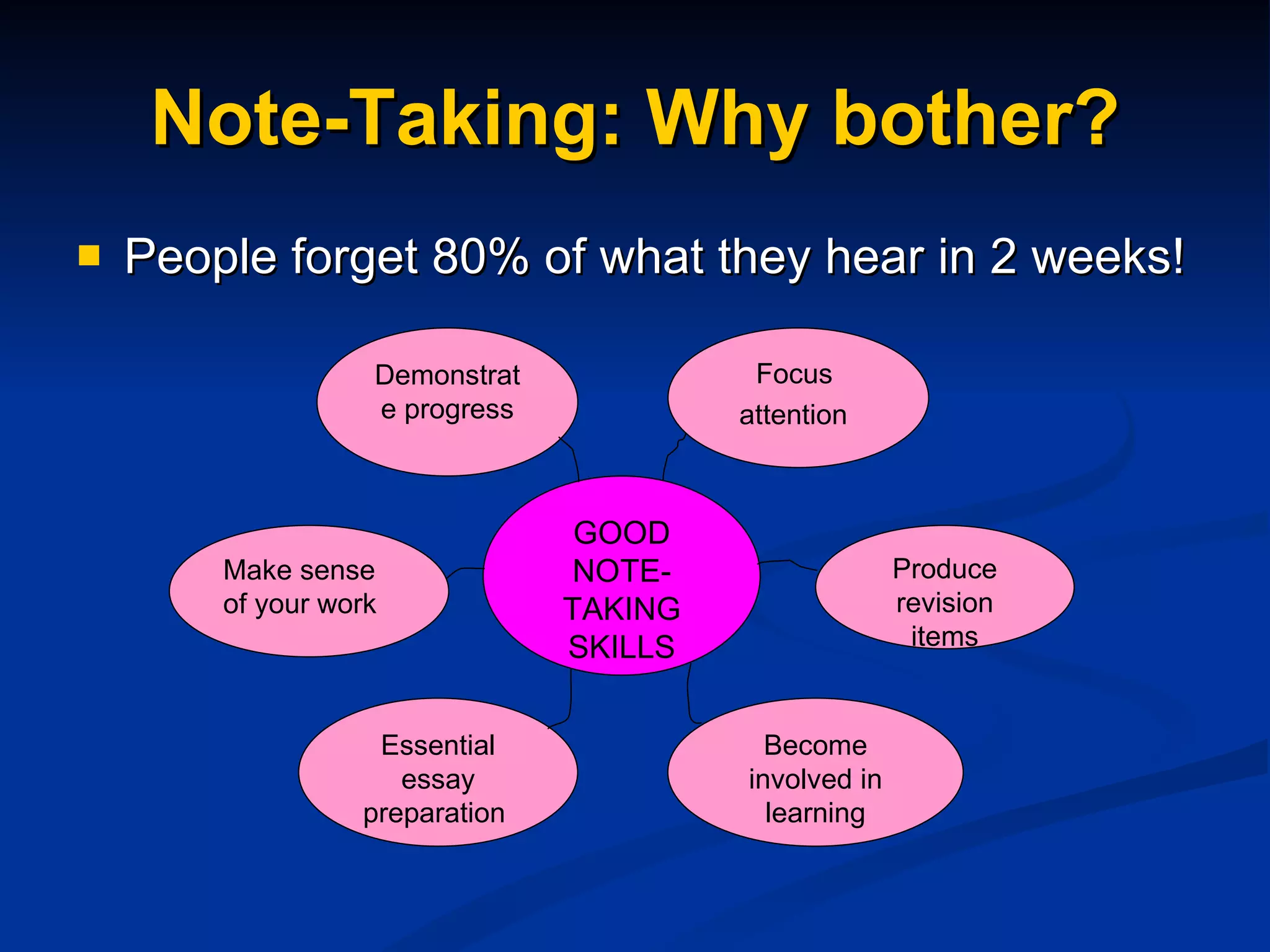
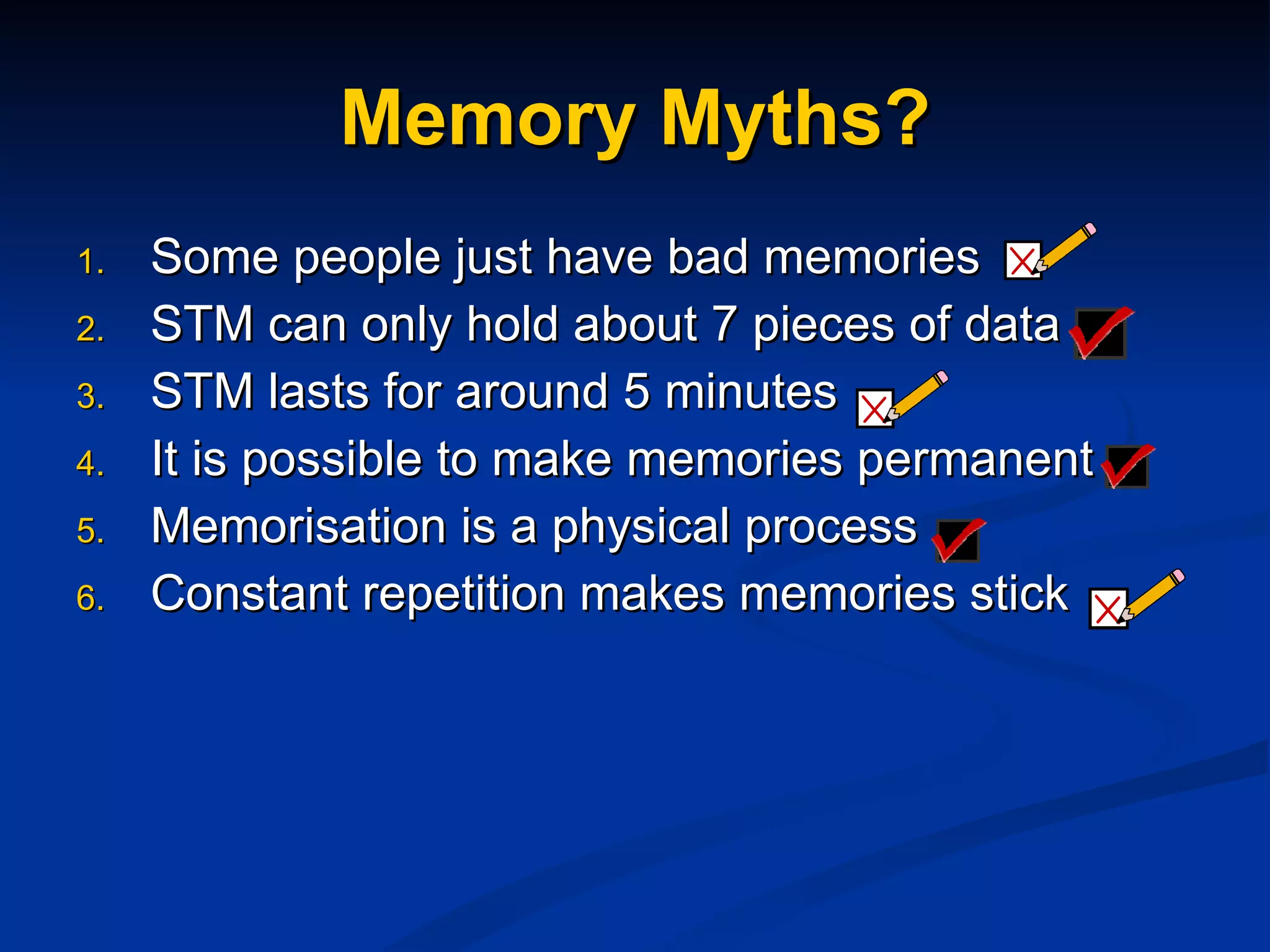
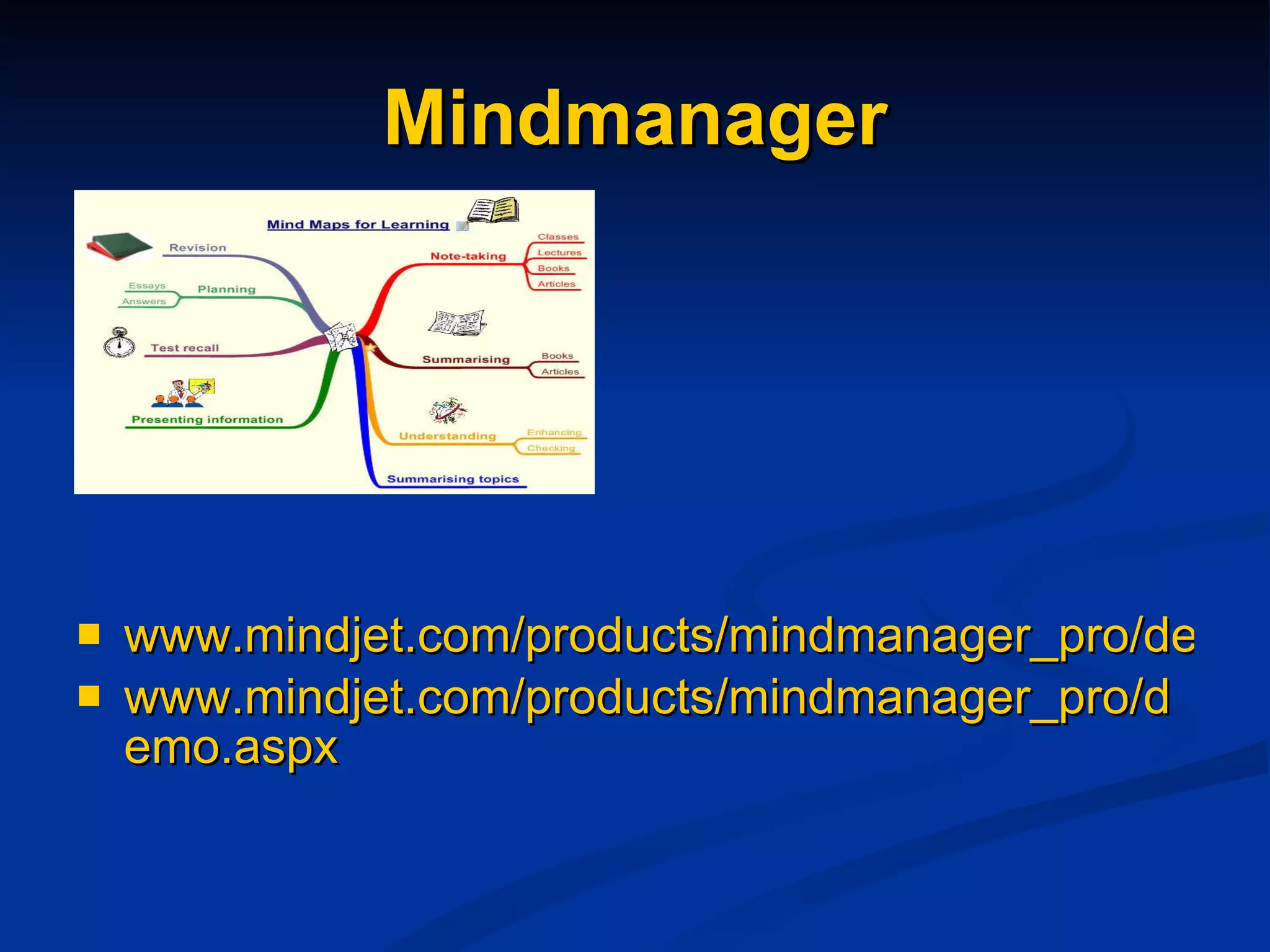
The document discusses study skills and provides an overview of various topics related to developing effective study habits. It defines study skills and highlights their importance for students and staff. It also identifies three major learning styles and explores study skills resources available at the college. Some key study skills covered include time management, note-taking, reading strategies, essay writing, memory techniques, and mind mapping.