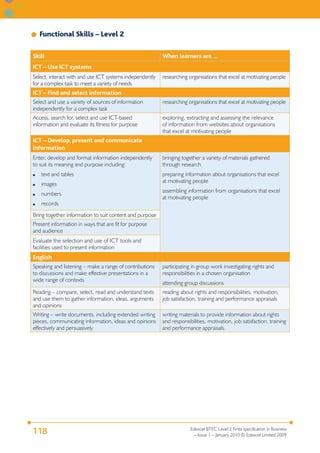
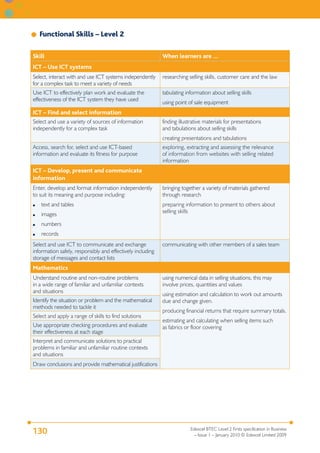
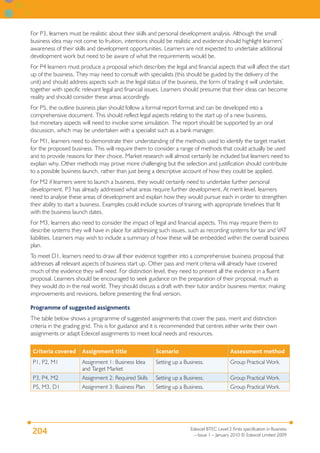
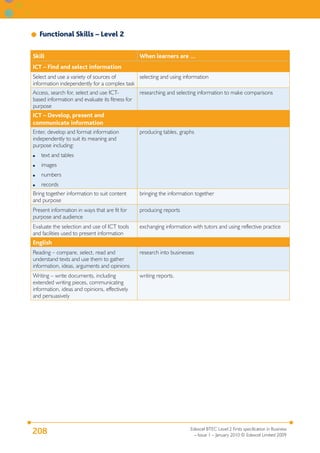
This document provides the specification for Edexcel BTEC qualifications in Business at Level 2, including the Certificate (15 credits), Extended Certificate (30 credits) and Diploma (60 credits). It outlines the purpose and structure of the qualifications, including their equivalence to GCSEs. The qualifications focus on developing knowledge and skills relevant to employment in business-related jobs. Units cover topics such as business purposes, organizations, finance, communication, customer relations, and business ethics. Assessment is through assignments designed to provide evidence for meeting the grading criteria.




























![Unit content
1 Understand the purpose and ownership of business
Purpose: supply of goods and services eg at a profit, free, at cost, for sale below cost
Ownership: sole trader; partnership; limited companies (private [ltd], public [plc]); charity; voluntary
organisations; co-operatives; government
Size: small; medium; large
Scale: local; regional; national; European and global organisations
Classification: primary (eg farming, forestry, fishing, extraction/mining); secondary (eg manufacturing,
engineering, construction); tertiary (eg private service industries, local and national public services,
voluntary/not-for-profit services)
2 Understand the business context in which organisations operate
Role of government: European; national; local; growth, full employment; inflation/deflation; surpluses;
competitiveness; equality
Business environment characteristics: markets; trends (employment, income, growth); relative growth/decline
by sector: decline of primary and secondary industries; growth of tertiary service industries; legal framework
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
24 – Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-30-320.jpg)
![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 identify the purpose of M1 contrast the ownership and D1 evaluate how a business
four different business purposes of two different organisation has responded
organisations business organisations to changes in the business
[IE] environment.
P2 describe the different types
of business ownership, linking
this to the size and scale of
four different organisations
P3 explain how businesses are M2 compare areas of growth
classified using local and or decline in the primary,
national examples secondary and tertiary
classifications of business
activities.
P4 outline the role of
government in creating the
business climate
[IE]
P5 explain the characteristics
of the local business
environment.
[IE, RL]
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-31-320.jpg)










![Unit content
1 Be able to set business aims and objectives
Aims and objectives: mission; aims (the long-term visions or goals of a business); objectives (specific,
measurable, achievable, realistic, time-constrained [SMART] targets to help achieve the overall aims of a
business); purpose of objectives in providing a business focus (eg break even, growth, profit maximisation,
survival, market share, sales, service provision); relationship with other businesses; failing to meet aims
and objectives; business consequences
Sector: government; private; public; not-for-profit; voluntary
2 Understand the main functional areas in business organisations
Functional areas: sales, production, purchasing; administration, customer service, distribution, finance,
human resources, ICT, marketing, research and development (R and D); purposes of functional areas
in supporting business aims and objectives; developing new markets; developing new products; using
information technology to integrate functional areas
Links: relationships and interactions with other functional areas; external links (eg suppliers, customers,
banks, government agencies); information flows; flows of goods and services
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
36 – Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-42-320.jpg)
![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 define aims and objectives M1 compare the aims and D1 assess whether a selected
objectives of different business meets its aims and
businesses objectives.
P2 describe the purpose for
a business in setting aims
and objectives
[IE]
P3 write aims and objectives
for a selected business
P4 describe the functional areas M2 compare the interaction
in two contrasting business of functional areas and how
organisations they relate to each other
[CT] in two selected businesses
to support the business
objectives.
P5 explain how these functional
areas link in one of these
organisations.
[CT, RL]
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-43-320.jpg)











![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 identify the difference M1 explain the importance of D1 evaluate the importance of
between start up and costs, revenue and profit for cash flow and break even for
operating costs, variable a business organisation the effective management
and fixed costs of business finance.
[TW] [IE]
P2 identify the different types
of revenue
[TW, CT]
P3 outline the differences
between gross and net profit
P4 calculate break even using
given data to show the level
at which income equals
expenditure
P5 present the break even as M2 demonstrate the impact of
an annotated graph showing changing cost and revenue
breakeven data on the break even point
of a selected business
P6 prepare an annual cash flow M3 analyse the implications
forecast using monthly data. of regular and irregular cash
[IE] inflows and outflows for
a business organisation.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-55-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 describe the main job M1 compare the main job D1 analyse the relationship
roles and functions in an roles and functions in two between job roles, functions
organisation organisations and explain how and an organisation’s structure,
[IE] they may differ in different using appropriate illustrative
organisational structures examples
[IE]
P2 identify different
organisational structures used
within business organisations
[IE]
P3 produce a basic job M2 produce a detailed and D2 analyse how effective
description and person relevant job description recruitment contributes
specification for a specific job and person specification to an organisation’s success.
for a specific job. [IE]
P4 complete an application and
interview for a specific job
[RL]
P5 match current knowledge
and skills to possible
job opportunities using
appropriate sources of
information and advice
[RL]
P6 produce a personal career
development plan.
[CT, RL, SM]
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
59](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-65-320.jpg)











![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
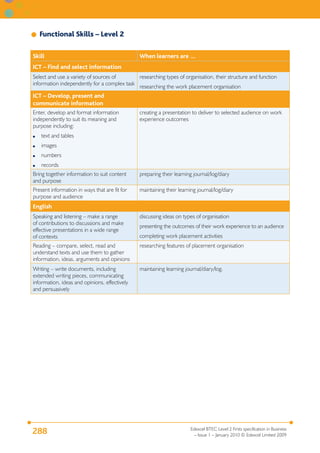
P1 outline different office M1 explain procedures for using D1 assess the importance of
equipment and systems office equipment and systems having procedures for using
office equipment and systems
when providing business and
administration support.
[RL]
P2 describe the function of
different office equipment
P3 demonstrate the procedures
needed to process, retrieve
and archive information
P4 operate an electronic diary M2 compare and contrast paper
system for business purposes and electronic diary systems.
[SM]
P5 safely carry out administrative
tasks using office equipment.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
71](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-77-320.jpg)








![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 explain the types and purposes M1 explain the appropriate uses D1 analyse the contribution
of business support of office equipment types, that office equipment
[IE] features and functions to suit makes to the provision
different business purposes of business support
P2 describe the use of office
equipment to meet different
business requirements
P3 demonstrate using office
equipment safely in
accordance with health
and safety legislation
P4 draw up a checklist for M2 produce all post-meeting
a meeting documentation
P5 produce documents needed M3 explain the organisation D2 analyse the organisation
for a meeting. and support provided and documents and materials
for meetings. provided for a meeting,
making recommendations
for any improvements.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
81](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-87-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 demonstrate interpersonal M1 explain how interpersonal D1 assess the importance
interactions in a business interaction skills are used of effective interpersonal
context to support business interaction skills in a given
communication business situation
P2 explain, using examples, the M2 discuss how verbal
purpose of verbal business communications can be
communications in four used effectively in business
different business contexts situations
[IE]
P3 demonstrate speaking and
listening skills in a one to one
business context
[RF]
P4 demonstrate speaking and M3 carry out a review of their D2 assess the effectiveness
listening skills in a business speaking and listening skills of speaking and listening
group context. in both a one-to-one, and skills in supporting business
[RF, TW] group context, identifying operations in a given
their strengths and business context.
weaknesses. [TW]
[TW]
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
91](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-97-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 identify, using examples the M1 describe appropriate methods D1 explain the importance
purposes of written business of written communication in of written communication
communications in four different business contexts in an organisation in specific
different business contexts business contexts
[IE]
P2 produce three documents M2 compare your choice D2 justify your choice of internal
of different types to support of internal and external and external documents
straightforward business tasks documents explaining why each
for internal communication document is appropriate
in an organisation for its intended audience
P3 produce three documents
of different types for external
communication by an
organisation
[RL]
P4 identify appropriate methods M3 describe appropriate methods D3 explain appropriate methods
of communication to different of written communication to of written communication
audiences. different audiences. to different audiences.
[TW]
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
101](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-107-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 outline the rights and M1 explain the rights and D1 compare the rights and
responsibilities of employers responsibilities of employers responsibilities of employers
in a chosen organisation and employees and employees
[IE]
P2 outline the rights and
responsibilities of employees
in a chosen organisation
P3 explain the importance of job M2 explain the relationship D2 analyse the relationship
satisfaction and teamwork between motivation, between motivation,
in the workplace teamwork and job teamwork and job satisfaction
satisfaction. and how they contribute
to organisational success.
P4 examine how employees
can be motivated in the
workplace
[RL]
P5 describe the importance of
training to an organisation
P6 explain the benefits of
performance appraisal.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
111](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-117-320.jpg)








![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 describe the role of sales staff M1 explain the role of sales D1 demonstrate the confident
[CT] staff and the sales techniques use of personal selling skills
they use when making sales
P2 identify the techniques used M2 compare the selling skills D2 evaluate the preparation,
when making personal sales and processes used in skills and processes used
different situations. in different situations.
P3 explain the knowledge and
skills used when making
personal sales
P4 prepare to make personal
sales
P5 use selling skills and processes
to make sales.
[TW, SM, RL]
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
121](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-127-320.jpg)












![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 describe three different types M1 explain how different
of customers and their needs customers’ needs and
and expectations expectations can differ
P2 outline the benefits of
good customer service
in a selected organisation
P3 demonstrate presentation, M2 display confident D1 anticipate and meet the
communication and presentation, communication needs of different customers
interpersonal skills in different and interpersonal skills when in three contrasting situations
customer service situations demonstrating customer [T4/5]
[TW] service in a range of
customer service situations
P4 explain what contributes M3 analyse the importance of
to consistent and reliable customer service to different
customer service businesses
[IE]
P5 describe how customer M4 explain how monitoring D2 analyse how monitoring
service can be monitored and evaluating can improve and evaluating can improve
and evaluated customer service for the customer service for the
customer, the organisation customer, the organisation
and the employee. and the employee.
P6 outline how improvements
to the customer service in an
organisation could be made.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
135](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-141-320.jpg)













![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 describe three different M1 compare the features of D1 make recommendations
business organisations which three business organisations for a business organisation
operate online operating online considering going online
[IE]
P2 explain how they operate
their activities online
[RL]
P3 explain the issues a business
organisation would need to
consider to go online
[CT]
P4 explain the operational risks M2 analyse the benefits to D2 suggest ways in which a
for a business organisation businesses and customers business could deal with the
operating online of conducting business online operational risks associated
with an online presence
P5 create web-pages to meet M3 explain how the website D3 justify the use of different
a user need assists in achieving the construction features in
[CT, SM, TW, EP] aims and objectives the design of a website
of the business user
P6 describe the benefits to a
business organisation of
marketing a product or
service online
P7 outline the impact of online M4 analyse the consequences D4 evaluate the benefits and
business on society. on society of an increase drawbacks to society of
in online business. increasing business online.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
149](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-155-320.jpg)











![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 explain how the law M1 apply the law accurately D1 apply the legal principles of
protects purchasers in given consumer dispute the main areas of consumer
of goods and services scenarios analysing protection by reference to
[IE] how legislation protects statutes and decided cases
consumers in the purchase in given consumer dispute
of both goods and services scenarios including defective
goods and services.
P2 identify how the law protects
consumers against negligence
P3 identify the meaning and M2 explain the meaning and
effect of terms in consumer effect of terms in a consumer
contracts contract.
[IE]
P4 identify how the law
protects consumers against
the imposition of exclusion
clauses
P5 apply the appropriate
remedy in a given consumer
protection situation.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
161](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-167-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 explain the meaning M1 assess the values of a chosen D1 analyse the business and
of ‘business values’ business and consider ethical values of a chosen
[IE] whether they are ethical business and discuss how
well these meet their legal
responsibilities
P2 explain the meaning
of ‘ethical values’
[IE]
P3 describe how ethics go
beyond the requirements
of the law
P4 discuss the current ethical
issues affecting specified
businesses
P5 apply a test to make sure
a business decision is ethical
P6 create an ethical policy for M2 discuss the effectiveness D2 justify an ethical policy.
a chosen business. of a selected ethical policy.
[CT]
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
171](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-177-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 identify the documents
used to record financial
transactions
[IE]
P2 outline the sequence in which
these documents are used
P3 complete documents to
record financial transactions
P4 create trading, profit and M1 explain the importance D1 evaluate how financial
loss accounts from a given of a profit and loss and recording systems can
set of data balance sheet for a business contribute to managing
organisation when making business finances.
strategic financial decisions [IE]
P5 create a balance sheet from
a given set of data
P6 identify how ways M2 explain how ways
of recording financial of recording financial
transactions help prevent transactions help prevent
fraud in a business fraud in a business
organisation. organisation.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
181](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-187-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 explain how knowledge M1 explain, using examples, the D1 evaluate the issues that need
of personal strengths and benefits of starting a business to be considered when
weaknesses can be applied to starting a business
preparing for and contributing
to a business
P2 identify how regulations and M2 analyse the different aspects
laws for small businesses can that will affect preparation
affect preparation for business for business.
P3 describe how small
businesses prepare to market
and sell products or services
P4 describe the financial issues
that can affect preparation
for business
P5 outline the contents of D2 justify recommendations
a business plan for starting made for starting a business.
and running a business
[EP TW]
,
P6 explain the sources of advice
and support available when
preparing for business.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
191](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-197-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner is
able to:
P1 present the initial business M1 explain methods used to D1 present a comprehensive
idea using relevant criteria identify the target market for business proposal that
the proposed business addresses all relevant aspects
of business start up.
P2 explain how to identify the
target market
P3 describe the skills needed to M2 analyse the personal
run the business successfully development needed to run
and what areas require the business successfully
further personal development
[TW, EP]
P4 describe the legal and
financial aspects that will affect
the start-up of the business
P5 produce a proposal M3 assess the implications of the
containing the essential legal and financial aspects that
information for the start up of will affect the start up of the
a business. business.
[TW, EP]
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills which are embedded in the assessment of this unit. By achieving the criteria,
learners will have demonstrated effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
201](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-207-320.jpg)







![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 describe the characteristics
of an effective team
P2 describe, giving examples,
different types of team
structure
P3 explain the benefits of M1 assess the benefits of team
team working working for the organisation
and individual team member
P4 demonstrate working
effectively as a team
member and team leader
dealing with any conflict
or difficult situations
[TW]
P5 review the team’s overall D1 evaluate the team’s overall
effectiveness and own effectiveness in meeting goals,
contribution to achieving making recommendations
goals for improvements.
[RL]
P6 describe the attributes M2 explain how motivation
needed by a team leader theories are used in the
workplace.
P7 identify ways a leader can
motivate team members.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
211](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-217-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate
that they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The criteria for a pass grade describe the level
of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner is
able to:
P1 assess own business
proposition using marketing
concepts
[CT3]
P2 justify types of promotion
for a micro start-up business
drawing on evidence of
success or failure in the
marketplace
P3 plan marketing for a micro M1 explain how marketing D1 develop a cost-effective,
start-up business that is principles have been used to coordinated marketing mix
relevant to customer needs develop a marketing mix for a and promotion plan to meet
[SM2/SM3] micro start-up business the needs of a defined target
market.
P4 plan costed promotional M2 produce a cost-effective
activity for a micro start-up promotion plan that
business that is appropriate communicates consistent
for customer groups messages to prospective
[SM2/SM3]. customers.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills which are embedded in the assessment of this unit. By achieving the criteria,
learners will have demonstrated effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
221](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-227-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate
that they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The criteria for a pass grade describe the level of
achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner is
able to:
P1 outline ways of managing M1 explain the reasons for D1 justify reasons for financial
personal financial planning budgetary decisions planning decisions.
and accurate record keeping
[IE3]
P2 identify sources of advice for M2 analyse the different features
ways of managing financial of financial products and
products and services services relating to current
and savings accounts.
P3 describe financial products
and services appropriate
to self
P4 construct a personal budget
that takes account of
personal remuneration and
expenditure.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills which are embedded in the assessment of this unit. By achieving the criteria,
learners will have demonstrated effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
231](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-237-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 identify the various M1 compare how two different D1 evaluate the choice
sub-sectors, channels, chosen businesses operate in of channels for a
formats, business models and terms of channel, sub-sector, selected business
locations of retail businesses location and support
P2 explain how other businesses
support the retail sector
P3 identify the importance M2 compare the branding
of branding and promotion and promotion of two
to retail channels different businesses/products
P4 assess the marketing mix
for a product
P5 generate ideas and explore M3 compare and contrast D2 justify brand idea in terms
possibilities for branding brand ideas. of customer need
a product
[EP]
P6 produce promotional D3 evaluate promotional
materials taking into materials.
account ethical and
cultural considerations.
[CT, TW]
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
241](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-247-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 describe how the size, M1 analyse the different D1 evaluate the success
location and nature of a merchandising and display of various displays and
retail outlet affect the way it techniques in the chosen merchandising and display
merchandises and displays outlet and how they influence techniques used by different
products customers buying outlets and those in their
own designs.
P2 explain the merchandising
and display techniques used
in a chosen retail outlet
and how they influence
customers to buy
P3 use a variety of sketches, M2 analyse how their designs
diagrams and/or photographs for layout and a display are
to redesign how the space is effective in the chosen outlet.
used in a retail outlet
P4 plan a positive, display, using
a variety of goods
[TW, EP]
P5 carry out a health and safety
assessment on at least
two displays.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
251](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-257-320.jpg)









![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 describe the principles of lean M1 explain the benefits of lean D1 analyse the benefits of lean
organisation techniques organisation techniques organisation techniques.
P2 explain the benefits of a lean
environment
P3 describe the process for
conducting a productivity
needs analysis
P4 undertake a productivity M2 identify improvements and
needs analysis in a selected draw up an action plan for
organisation their implementation.
[TW, EP]
P5 produce a process map
using appropriate symbols
and terminology for an
identified process.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
261](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-267-320.jpg)








![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner
is able to:
P1 identify the main Kaizen M1 explain the main Kaizen D1 evaluate Kaizen and
principles and their techniques and their workplace organisation
application application in a given techniques in a given
organisation organisation.
P2 explain areas of weakness
in workplace organisation
and suggest improvements
P3 identify elements that
contribute to good visual
management in the
workplace
[TW, EP]
P4 prepare appropriate visual M2 suggest visual management
indicators improvements to workplace.
P5 describe the benefits of
standard working methods
and prepare a standardised
work document suggesting
how to eliminate variance
to process.
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills applicable in the pass criteria. It identifies opportunities for learners to demonstrate
effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
– Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009
271](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-277-320.jpg)










![Assessment and grading criteria
In order to pass this unit, the evidence that the learner presents for assessment needs to demonstrate that
they can meet all the learning outcomes for the unit. The assessment criteria for a pass grade describe the
level of achievement required to pass this unit.
Assessment and grading criteria
To achieve a pass grade the To achieve a merit grade the To achieve a distinction grade
evidence must show that the evidence must show that, in the evidence must show that,
learner is able to: addition to the pass criteria, in addition to the pass and
the learner is able to: merit criteria, the learner is
able to:
P1 describe the type, structure M1 explain how structure
and function of the host supports the functioning
organisations of the host organisations
P2 identify the competitors
of the host organisations
P3 prepare a plan showing M2 assess progress against the
agreed objectives and targets aims, objectives and targets
for one activity in each of two
work placements
[RL2, TW1, SM3]
P4 demonstrate problem-solving
skills in carrying out the plans
P5 maintain a reflective log M3 explain how the development D1 evaluate how the work
to monitor the progress of skills and behaviours experience supported
of activity and development improved effectiveness in the the development of
of own skills and behaviours workplace. entrepreneurial skills
[RL3, SM2]
P6 Present results of activities in D2 evaluate the contribution
a suitable format describing of own skills and abilities
own contribution in the to the performance of
workplaces the businesses.
[RL6].
PLTS: This summary references where applicable, in the square brackets, the elements of the personal,
learning and thinking skills which are embedded in the assessment of this unit. By achieving the criteria,
learners will have demonstrated effective application of the referenced elements of the skills.
Key IE – independent enquirers RL – reflective learners SM – self-managers
CT – creative thinkers TW – team workers EP – effective participators
Edexcel BTEC Level 2 Firsts specification in Business
282 – Issue 1 – January 2010 © Edexcel Limited 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newlevel2specificationsept2010-100406045947-phpapp02/85/Student-Workbook-Example-288-320.jpg)