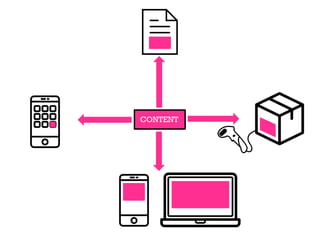
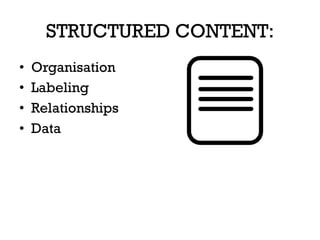
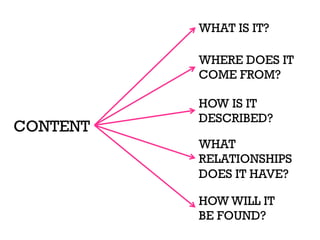
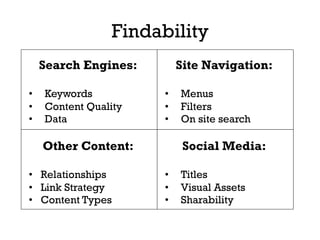
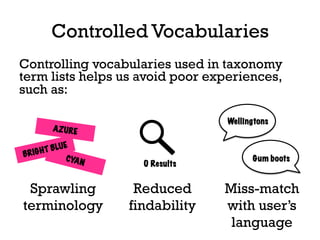
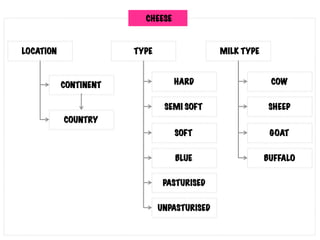
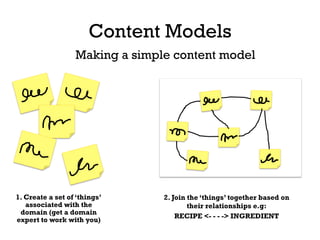
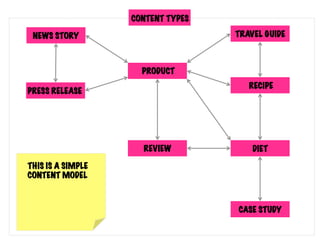
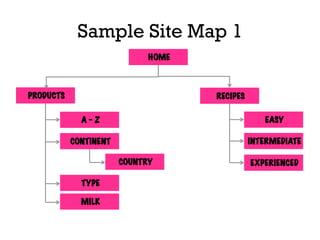
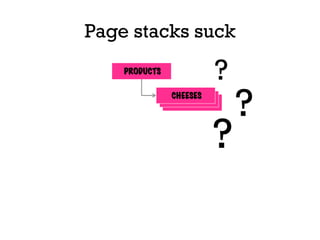
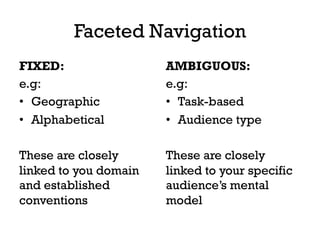
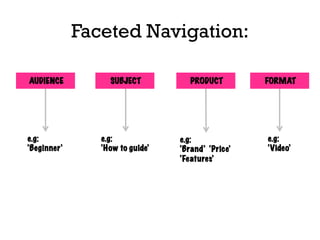
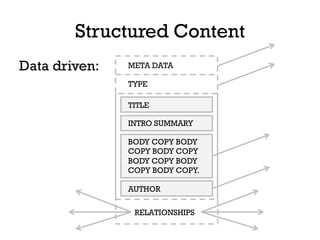
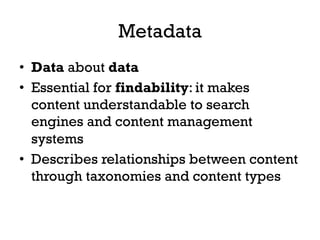
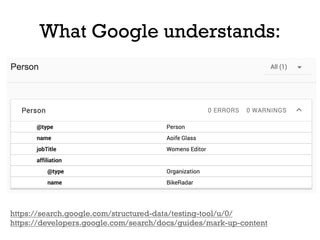
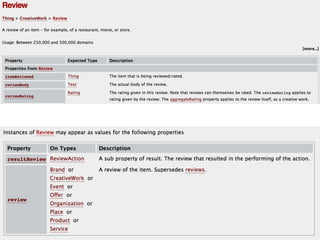
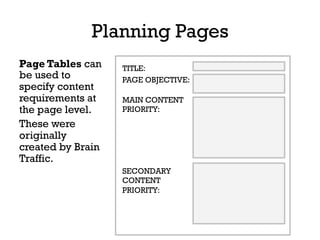
The document presents insights into structured content and its significance in user experience (UX) and content strategy, emphasizing that high-quality, findable content is crucial for effective digital services. It discusses the importance of content modeling, navigation, metadata, and microdata in enhancing content findability and user interaction. Additionally, it outlines various activities related to content creation, organization, and management, utilizing controlled vocabularies and taxonomies for better user experiences.