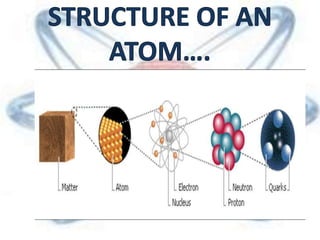
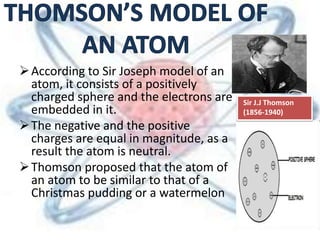
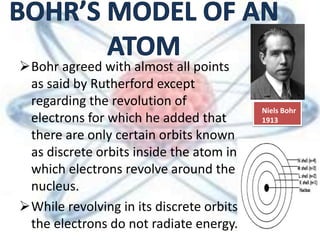
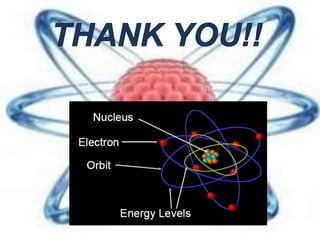
The document discusses the history and structure of the atomic model, beginning with Dalton's atomic theory and including Thomson's "plum pudding" model, Rutherford's discovery of the nucleus through alpha particle scattering experiments, and Bohr's improvement adding discrete electron orbits. It explains that atoms are the smallest particles that make up elements, consisting of a tiny, dense nucleus of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons in shells or orbits. The key parts of an atom - the nucleus, protons, neutrons, and electrons - are defined along with the scientists who discovered them.