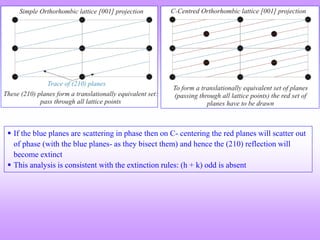
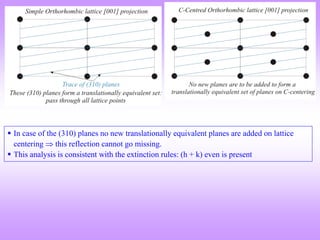
The document discusses structure factor calculations for different crystal lattices, including simple cubic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered cubic lattices. It outlines the extinction rules associated with various atomic arrangements and their effects on observable reflections in X-ray scattering. The analysis emphasizes how different lattice structures and atom positions impact the presence or absence of specific diffraction peaks.
![n
ni
e )
1
(
)
(
2
Cos
e
e i
i
Structure factor calculations
A Atom at (0,0,0) and equivalent positions
[2 ( )]
j j j j
i i h x k y l z
j j
F f e f e
[2 ( 0 0 0)] 0
i h k l
F f e f e f
2
2
f
F F is independent of the scattering plane (h k l)
ni
ni
e
e
Simple Cubic
1
)
(
i
n
odd
e
1
)
(
i
n
even
e
All reflections are
present](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurefactorcalculations-240611024808-02c63c1d/85/structure-factor-calculations-for-x-ray-diffraction-pattern-pptx-1-320.jpg)
![B Atom at (0,0,0) & (½, ½, 0) and equivalent positions
[2 ( )]
j j j j
i i h x k y l z
j j
F f e f e
1 1
[2 ( 0)]
[2 ( 0 0 0)] 2 2
[ 2 ( )]
0 ( )
2
[1 ]
i h k l
i h k l
h k
i
i h k
F f e f e
f e f e f e
F is independent of the ‘l’index
C- centred Orthorhombic
Real
]
1
[ )
( k
h
i
e
f
F
f
F 2
0
F
2
2
4 f
F
0
2
F
e.g. (001), (110), (112); (021), (022), (023)
e.g. (100), (101), (102); (031), (032), (033)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurefactorcalculations-240611024808-02c63c1d/85/structure-factor-calculations-for-x-ray-diffraction-pattern-pptx-2-320.jpg)
![C Atom at (0,0,0) & (½, ½, ½) and equivalent positions
[2 ( )]
j j j j
i i h x k y l z
j j
F f e f e
1 1 1
[2 ( )]
[2 ( 0 0 0)] 2 2 2
[ 2 ( )]
0 ( )
2
[1 ]
i h k l
i h k l
h k l
i
i h k l
F f e f e
f e f e f e
Body centred
Orthorhombic
Real
]
1
[ )
( l
k
h
i
e
f
F
f
F 2
0
F
2
2
4 f
F
0
2
F
e.g. (110), (200), (211); (220), (022), (310)
e.g. (100), (001), (111); (210), (032), (133)
This implies that (h+k+l) even reflections are only present.
The situation is identical in BCC crystals as well.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurefactorcalculations-240611024808-02c63c1d/85/structure-factor-calculations-for-x-ray-diffraction-pattern-pptx-5-320.jpg)
![D Atom at (0,0,0) & (½, ½, 0) and equivalent positions
[2 ( )]
j j j j
i i h x k y l z
j j
F f e f e
]
1
[ )
(
)
(
)
(
)]
2
(
2
[
)]
2
(
2
[
)]
2
(
2
[
)]
0
(
2
[
h
l
i
l
k
i
k
h
i
h
l
i
l
k
i
k
h
i
i
e
e
e
f
e
e
e
e
f
F
Face Centred Cubic
Real
f
F 4
0
F
2
2
16 f
F
0
2
F
(h, k, l) unmixed
(h, k, l) mixed
e.g. (111), (200), (220), (333), (420)
e.g. (100), (211); (210), (032), (033)
(½, ½, 0), (½, 0, ½), (0, ½, ½)
]
1
[ )
(
)
(
)
( h
l
i
l
k
i
k
h
i
e
e
e
f
F
Two odd and one even (e.g. 112); two even and one odd (e.g. 122)
h,k,l → all even or all odd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurefactorcalculations-240611024808-02c63c1d/85/structure-factor-calculations-for-x-ray-diffraction-pattern-pptx-6-320.jpg)
![Mixed indices CASE h k l
A o o e
B o e e
( ) ( ) ( )
CASE A: [1 ] [1 1 1 1] 0
i e i o i o
e e e
( ) ( ) ( )
CASE B: [1 ] [1 1 1 1] 0
i o i e i o
e e e
0
F 0
2
F
(h, k, l) mixed e.g. (100), (211); (210), (032), (033)
Mixed indices Two odd and one even (e.g. 112); two even and one odd (e.g. 122)
Unmixed indices CASE h k l
A o o o
B e e e
Unmixed indices
f
F 4
2
2
16 f
F
(h, k, l) unmixed
e.g. (111), (200), (220), (333), (420)
All odd (e.g. 111); all even (e.g. 222)
( ) ( ) ( )
CASE A: [1 ] [1 1 1 1] 4
i e i e i e
e e e
( ) ( ) ( )
CASE B: [1 ] [1 1 1 1] 4
i e i e i e
e e e
This implies that in FCConly
h,k,l ‘unmixed’ reflections are
present.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurefactorcalculations-240611024808-02c63c1d/85/structure-factor-calculations-for-x-ray-diffraction-pattern-pptx-7-320.jpg)
![E
Na+ at (0,0,0) + Face Centering Translations (½, ½, 0), (½, 0, ½), (0, ½, ½)
Cl− at (½, 0, 0) + FCT (0, ½, 0), (0, 0, ½), (½, ½, ½)
)]
2
(
2
[
)]
2
(
2
[
)]
2
(
2
[
)]
2
(
2
[
)]
2
(
2
[
)]
2
(
2
[
)]
2
(
2
[
)]
0
(
2
[
l
k
h
i
l
i
k
i
h
i
Cl
h
l
i
l
k
i
k
h
i
i
Na
e
e
e
e
f
e
e
e
e
f
F
]
[
]
1
[
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
l
k
h
i
l
i
k
i
h
i
Cl
h
l
i
l
k
i
k
h
i
Na
e
e
e
e
f
e
e
e
f
F
]
1
[
]
1
[
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
k
h
i
h
l
i
l
k
i
l
k
h
i
Cl
h
l
i
l
k
i
k
h
i
Na
e
e
e
e
f
e
e
e
f
F
]
1
][
[ )
(
)
(
)
(
)
( h
l
i
l
k
i
k
h
i
l
k
h
i
Cl
Na
e
e
e
e
f
f
F
NaCl:
Face Centred Cubic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurefactorcalculations-240611024808-02c63c1d/85/structure-factor-calculations-for-x-ray-diffraction-pattern-pptx-8-320.jpg)
![]
1
][
[ )
(
)
(
)
(
)
( h
l
i
l
k
i
k
h
i
l
k
h
i
Cl
Na
e
e
e
e
f
f
F
Zero for mixed indices
Mixed indices CASE h k l
A o o e
B o e e
]
2
][
1
[
Term
Term
F
0
]
1
1
1
1
[
]
1
[
2
:
A
CASE )
(
)
(
)
(
o
i
o
i
e
i
e
e
e
Term
0
]
1
1
1
1
[
]
1
[
2
:
B
CASE )
(
)
(
)
(
o
i
e
i
o
i
e
e
e
Term
0
F 0
2
F
(h, k, l) mixed e.g. (100), (211); (210), (032), (033)
Mixed indices](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurefactorcalculations-240611024808-02c63c1d/85/structure-factor-calculations-for-x-ray-diffraction-pattern-pptx-9-320.jpg)
![(h, k, l) unmixed ]
[
4 )
( l
k
h
i
Cl
Na
e
f
f
F
]
[
4
Cl
Na
f
f
F If (h + k + l) is even
2
2
]
[
16
Cl
Na
f
f
F
]
[
4
Cl
Na
f
f
F If (h + k + l) is odd
2
2
]
[
16
Cl
Na
f
f
F
e.g. (111), (222); (133), (244)
e.g. (222),(244)
e.g. (111), (133)
Unmixed indices CASE h k l
A o o o
B e e e
4
]
1
1
1
1
[
]
1
[
2
:
A
CASE )
(
)
(
)
(
e
i
e
i
e
i
e
e
e
Term
4
]
1
1
1
1
[
]
1
[
2
:
B
CASE )
(
)
(
)
(
e
i
e
i
e
i
e
e
e
Term
Unmixed indices
h,k,l → all even or all odd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurefactorcalculations-240611024808-02c63c1d/85/structure-factor-calculations-for-x-ray-diffraction-pattern-pptx-10-320.jpg)
![F
Al at (0, 0, 0)
Ni at (½, ½, ½)
NiAl: Simple Cubic (B2- ordered structure)
SC
1 1 1
[2 ( )]
[2 ( 0 0 0)] 2 2 2
[ 2 ( )]
0 [ ]
2
i h k l
i h k l
Al Ni
h k l
i
i h k l
Al Ni Al Ni
F f e f e
f e f e f f e
Real
Al Ni
F f f
e.g. (110), (200), (211); (220), (310)
e.g. (100), (111); (210), (032), (133)
[ ]
i h k l
Al Ni
F f f e
2 2
( )
Al Ni
F f f
Al Ni
F f f
2 2
( )
Al Ni
F f f
Click here to know more about ordered structures
When the central atom is identical to the corner ones we have the BCC case.
This implies that (h+k+l) even reflections are only present in BCC.
This term is zero for BCC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurefactorcalculations-240611024808-02c63c1d/85/structure-factor-calculations-for-x-ray-diffraction-pattern-pptx-11-320.jpg)

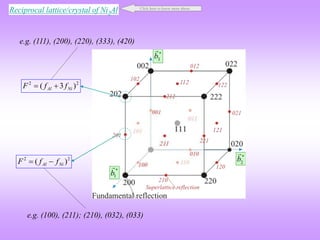
![G
Al Atom at (0,0,0)
Ni atom at (½, ½, 0) and equivalent positions
[2 ( )] [2 ( )] [2 ( )]
[2 ( 0)] 2 2 2
( ) ( ) ( )
[ ]
h k k l l h
i i i
i
Al Ni
i h k i k l i l h
Al Ni
F f e f e e e
f f e e e
Simple Cubic (L12 ordered structure)
Real
(h, k, l) unmixed
(h, k, l) mixed
e.g. (111), (200), (220), (333), (420)
e.g. (100), (211); (210), (032), (033)
(½, ½, 0), (½, 0, ½), (0, ½, ½)
Two odd and one even (e.g. 112); two even and one odd (e.g. 122)
Ni
Al
( ) ( ) ( )
[ ]
i h k i k l i l h
Al Ni
F f f e e e
3
Al Ni
F f f
2 2
( 3 )
Al Ni
F f f
Al Ni
F f f
2 2
( )
Al Ni
F f f
h,k,l → all even or all odd
Click here to know more about ordered structures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structurefactorcalculations-240611024808-02c63c1d/85/structure-factor-calculations-for-x-ray-diffraction-pattern-pptx-13-320.jpg)