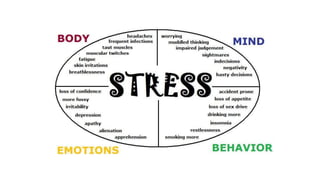
This document discusses stress, anxiety, and strategies for managing them. It defines stress as the body's normal response to threatening events. There are different types of stress like acute, episodic, and chronic stress. The document also defines anxiety as feelings of worry and unease about an uncertain outcome. It notes that stress and negative thoughts can trigger anxiety. Finally, the document provides strategies for managing stress and anxiety, such as exercise, meditation, saying no, altering situations when possible, and accepting things that cannot be changed.