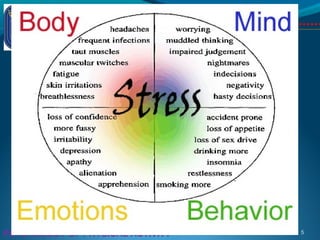
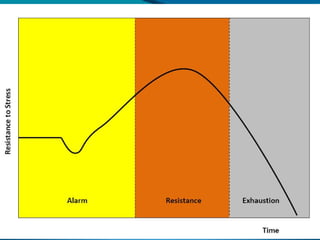
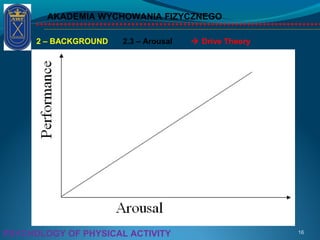
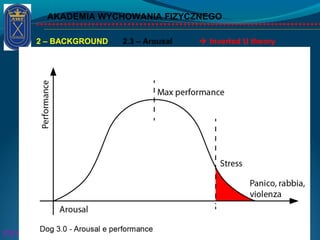
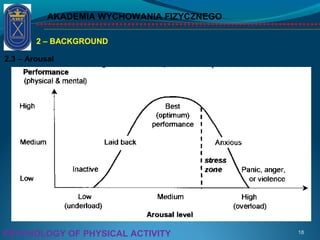
This document discusses the psychology of physical activity and sport. It begins with definitions of key terms like psychology, sport psychology, stress, and arousal. It then discusses background topics such as the relationship between stress and activation, the inverted-U theory of arousal, and whether the body or mind is more important for success. Triggers of stress and examples of athletes dealing with stress are provided. The document emphasizes the importance of controlling stress and arousal, avoiding burnout, using rituals and motivation, and working with a coach and psychologist.