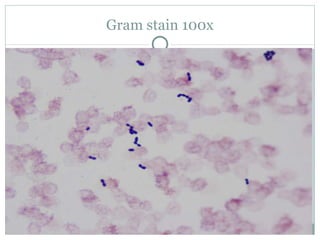
A 71-year-old male with a history of coronary artery disease and autoimmune hepatitis was admitted with fever. Blood cultures grew Streptococcus salivarius. S. salivarius bacteremia can represent a serious underlying illness. The patient's treatment plan includes 2 weeks of intravenous ceftriaxone and gentamicin, followed by surveillance blood cultures and endocarditis prophylaxis for dental procedures.