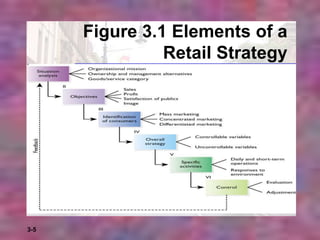
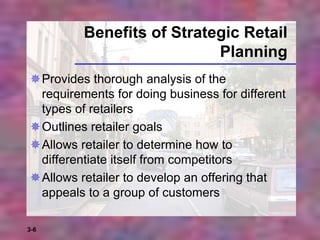
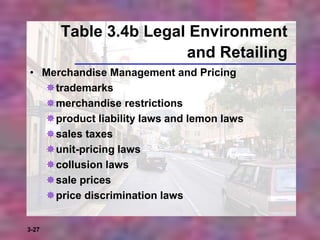
This chapter discusses strategic planning for retailers. It outlines the steps in strategic planning, including situation analysis, objectives, identifying consumers, developing an overall strategy and specific activities, and implementing controls and feedback. A retail strategy is a one-year plan that guides a retailer's mission, goals, target market, and activities. Strategic planning benefits retailers by analyzing business requirements, outlining goals, allowing differentiation from competitors, and appealing to customer groups.