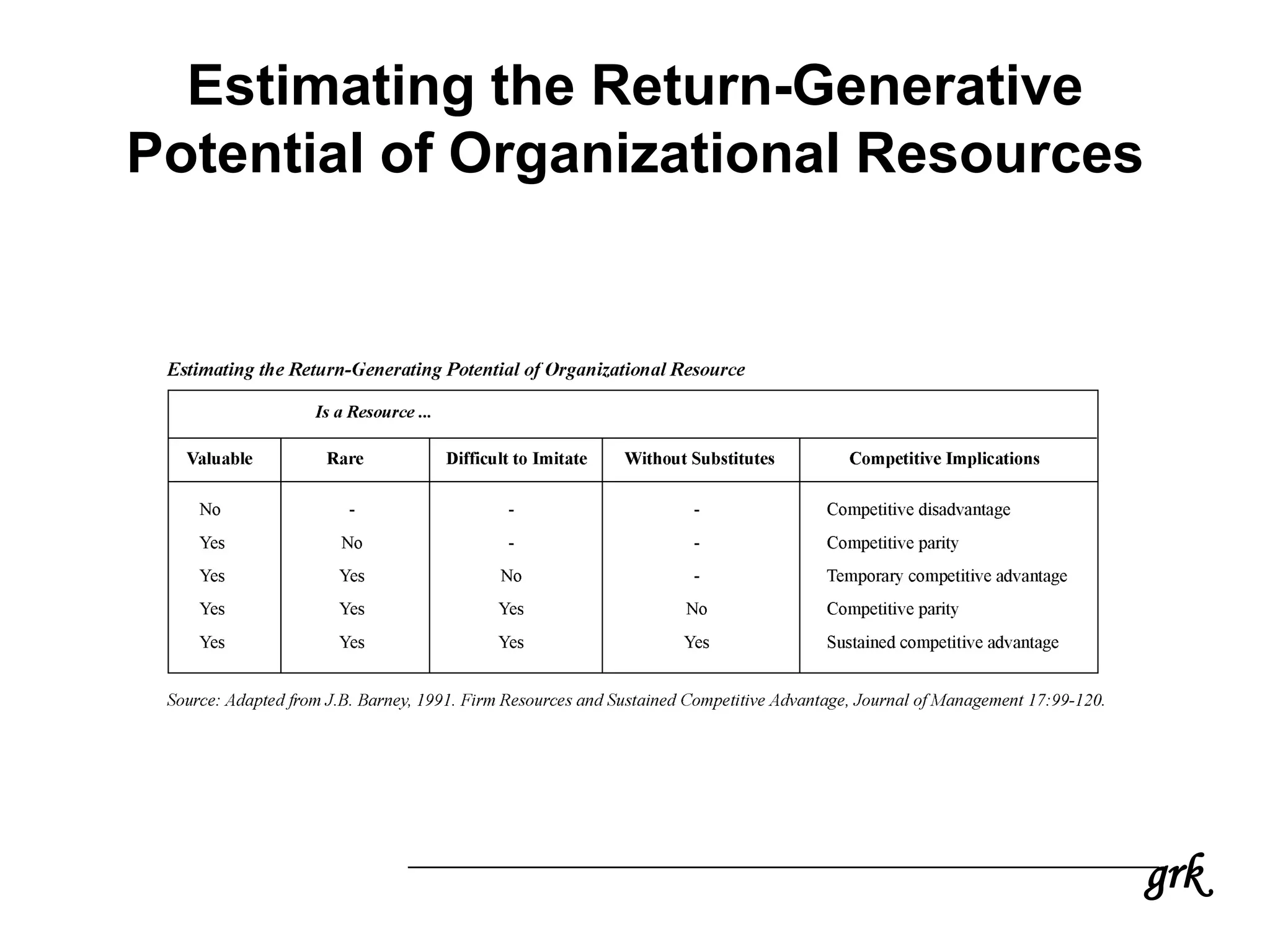
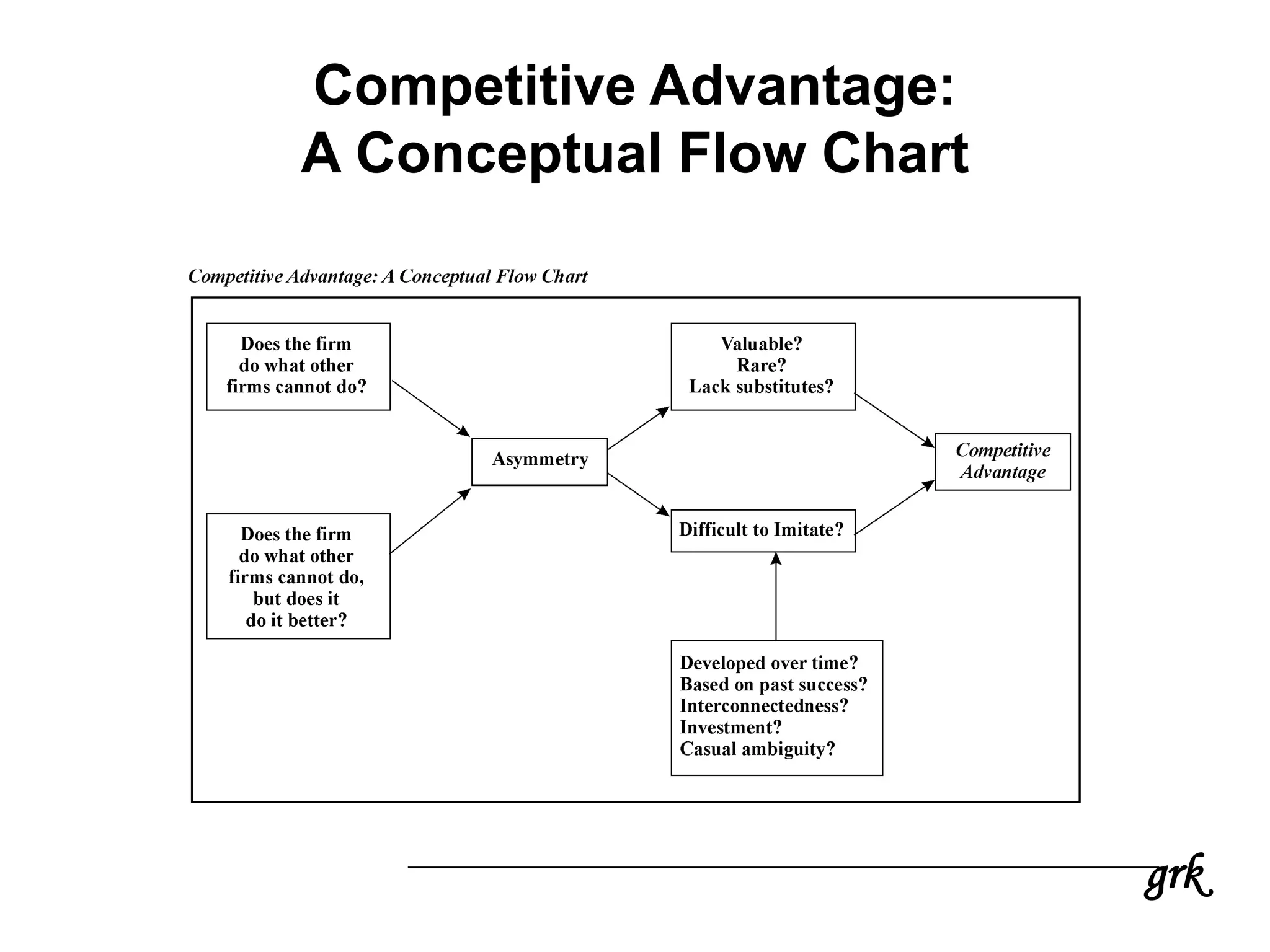
This document provides an overview of strategic financial management. It discusses key objectives of financial management like maximizing shareholder value. It also covers strategy formulation, Porter's five forces model for industry analysis, competitive advantage, and various aspects of strategic financial management like mergers and acquisitions, financial risk management, and linking financial performance to corporate strategy. The document emphasizes analyzing a company's financial structure from the perspectives of investors, competitors, and internal stakeholders to identify opportunities to improve.


























![grk
From an Internal Perspective
• Financial Flexibility
– Excess cash + (Debt at minimum rating – Current
Debt outstanding)
• Sustainability
– ROE x (1-DPO)
• De Pont system of ratios
– ROE = P/S x S/A x A/E
• Financial-leverage equation
– ROE = [ROTC + (ROTC – Ka) x (D/E)]
• Feasibility](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elementsoffinancialpolicy-210416071551/75/Strategic-Financial-Management-30-2048.jpg)

