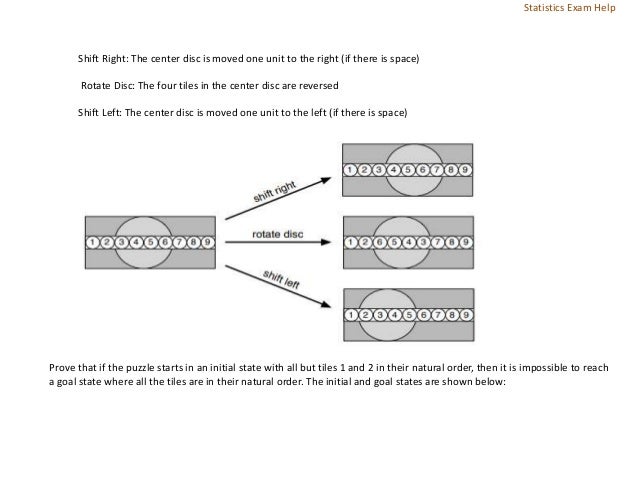
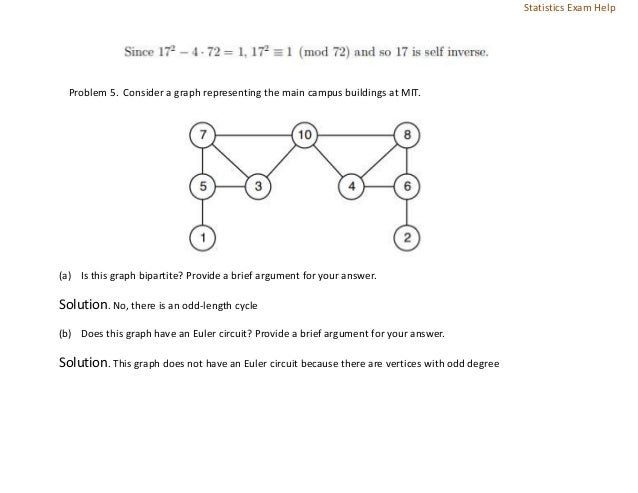
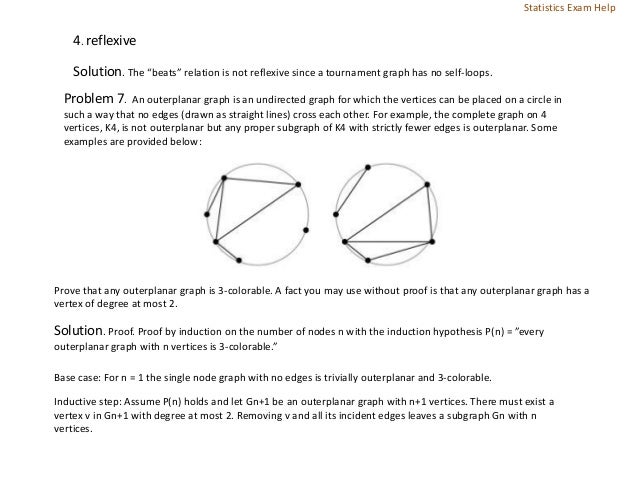
The document consists of several mathematical problems and solutions related to boolean logical operators, modular arithmetic, graph theory, tournament graphs, and outerplanar graphs. Key topics include the proof of universality of NOR, induction in proving congruences, properties of tournament graphs, and colorability of outerplanar graphs. Various problem-solving techniques, such as induction and graph properties, are demonstrated throughout the document.