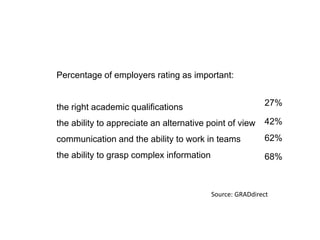
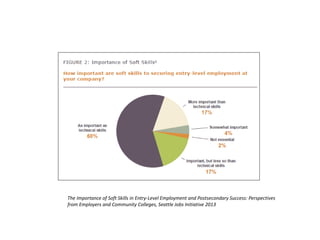
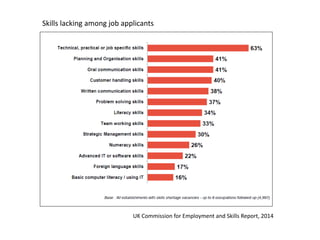
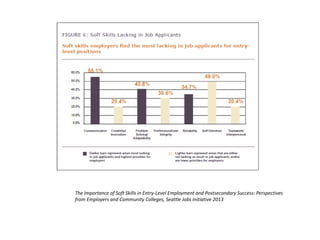
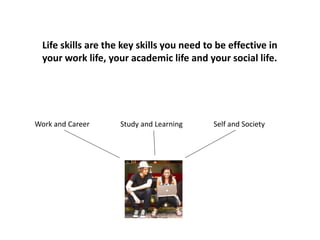
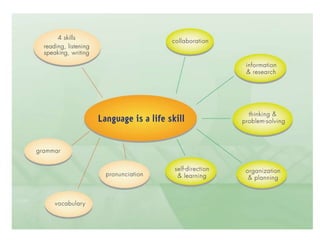
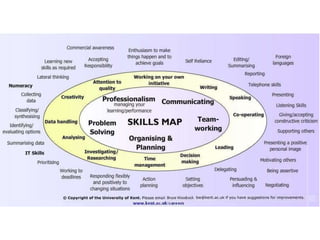
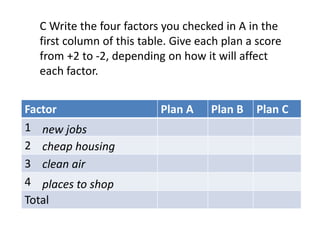
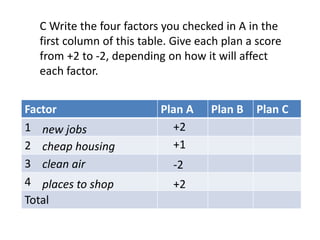
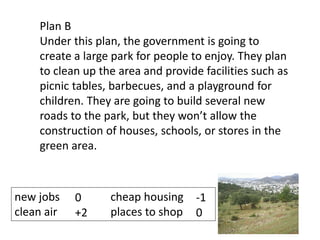
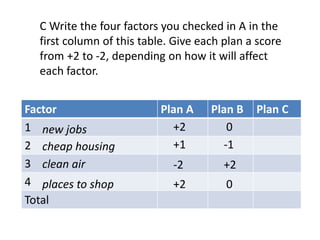
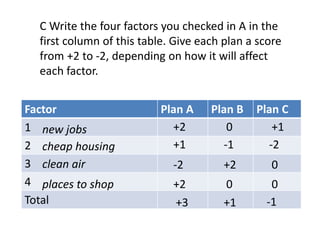
This document discusses the importance of developing life skills and transferable skills across different domains like study, work and life. It notes that while employers value "soft skills" like communication, teamwork and problem solving, many graduates lack these skills. The document also examines definitions of life skills from various organizations and advocates for teaching life skills through subjects like English class. It provides some sample classroom activities focused on developing skills like evaluating plans, analyzing assumptions and critical thinking.