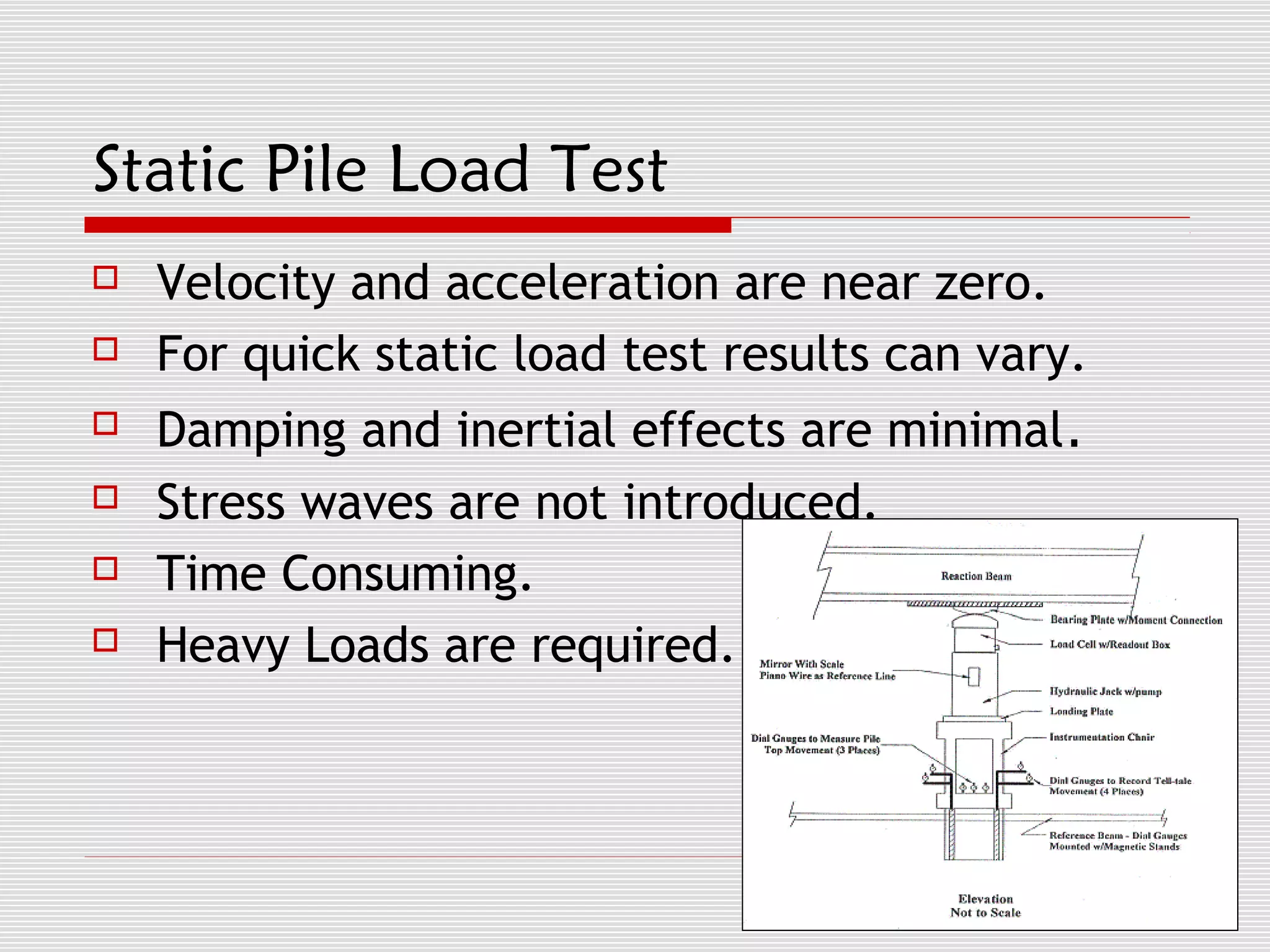
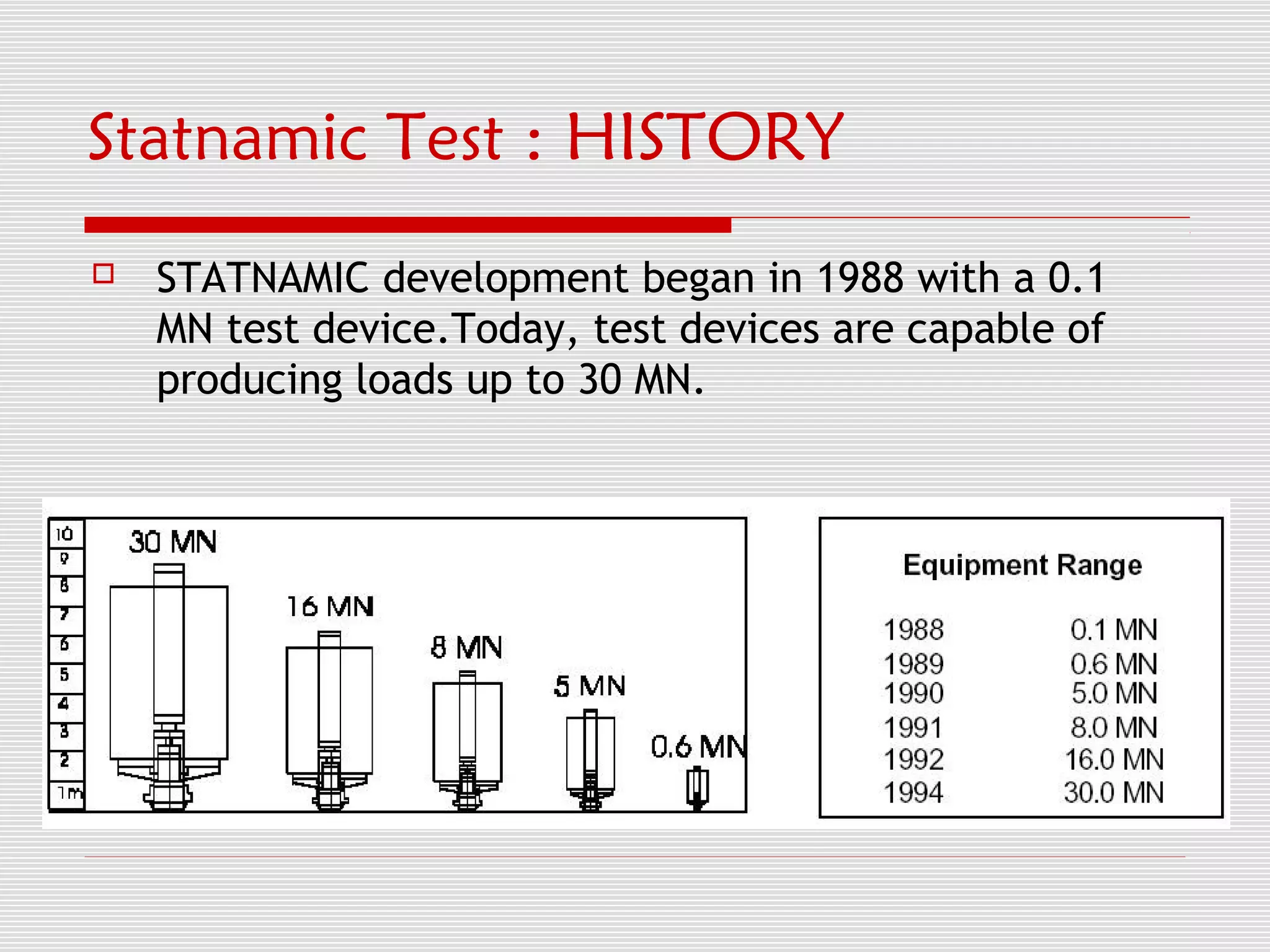
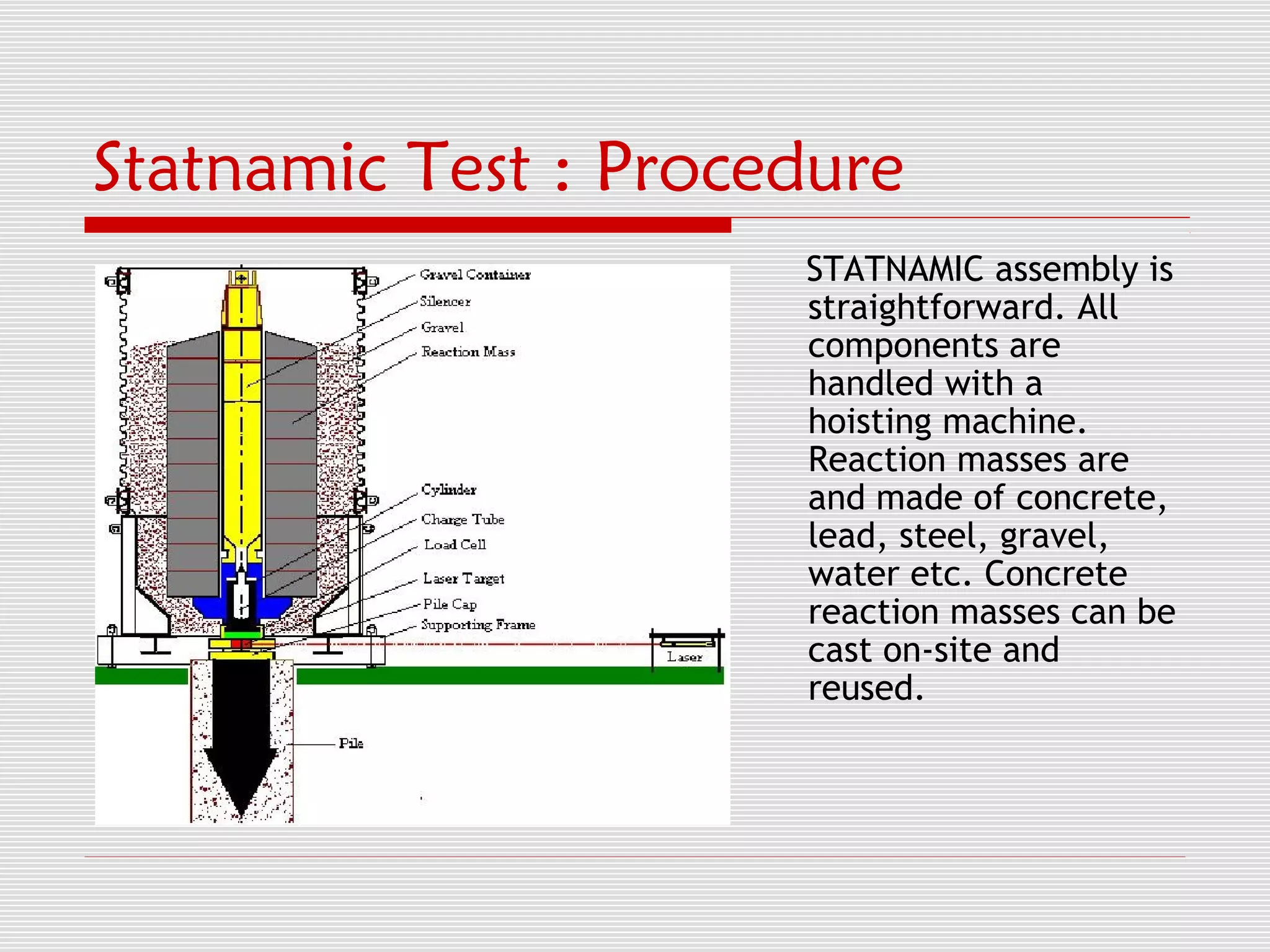
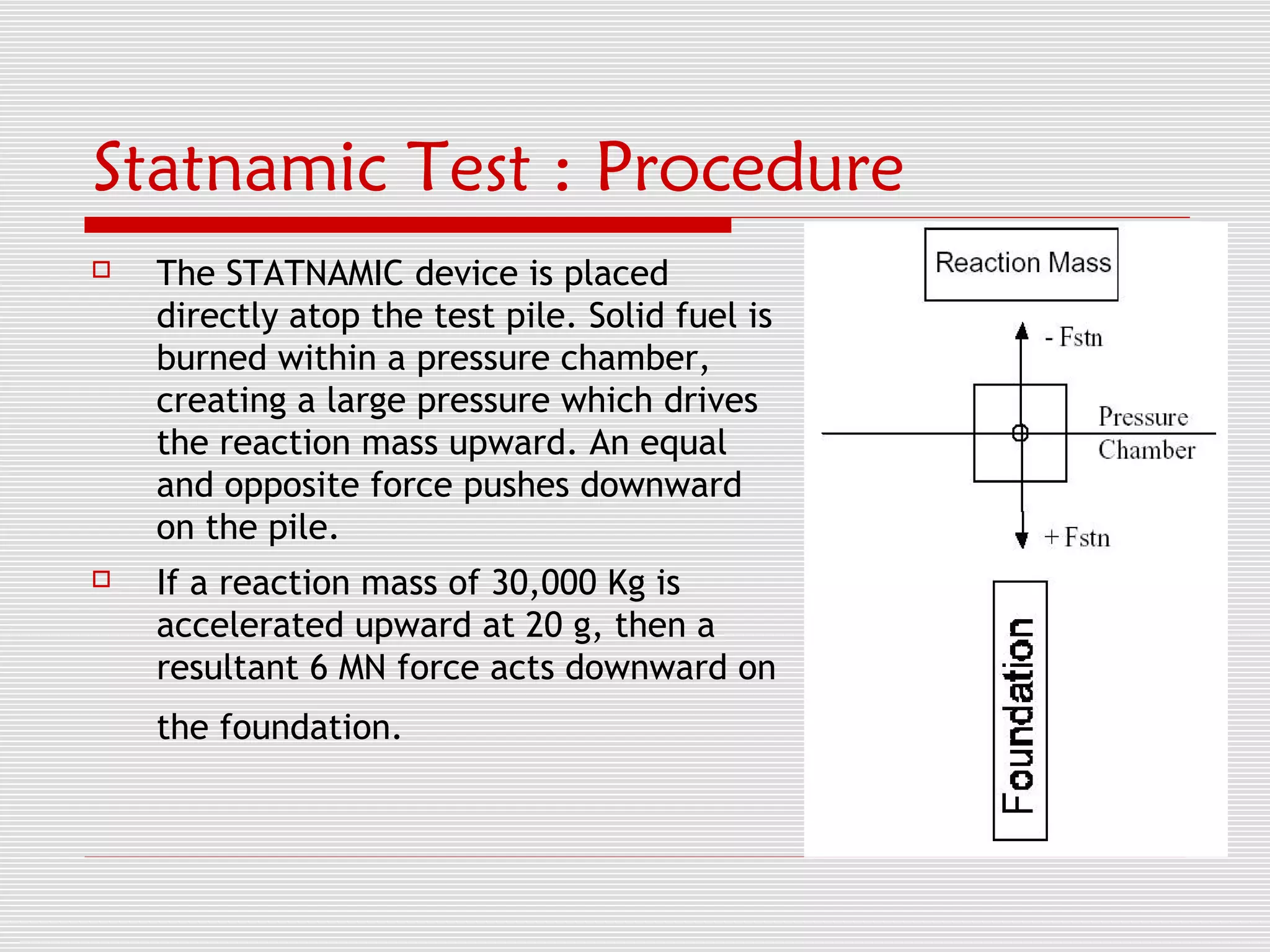
The document discusses Statnamic testing for piles. Statnamic testing loads piles using controlled explosions that induce stress waves into the pile over 120 milliseconds, allowing the pile and soil to be loaded together. It is faster and less expensive than static pile load testing. Statnamic testing can test piles, pile groups, and other deep foundations up to loads of 30 MN. It provides immediate load-displacement results on site.