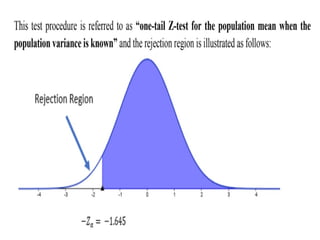
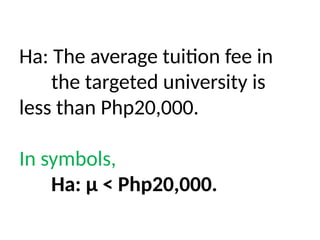The document discusses hypothesis testing, specifically focusing on identifying the rejection region and applying it to a real-life scenario involving a father's concerns about university tuition fees. It outlines the steps of hypothesis testing and includes examples with null and alternative hypotheses, emphasizing the use of z-tests and t-tests depending on sample size and variance. The summary concludes with instructions on how to establish a decision rule based on significance levels.