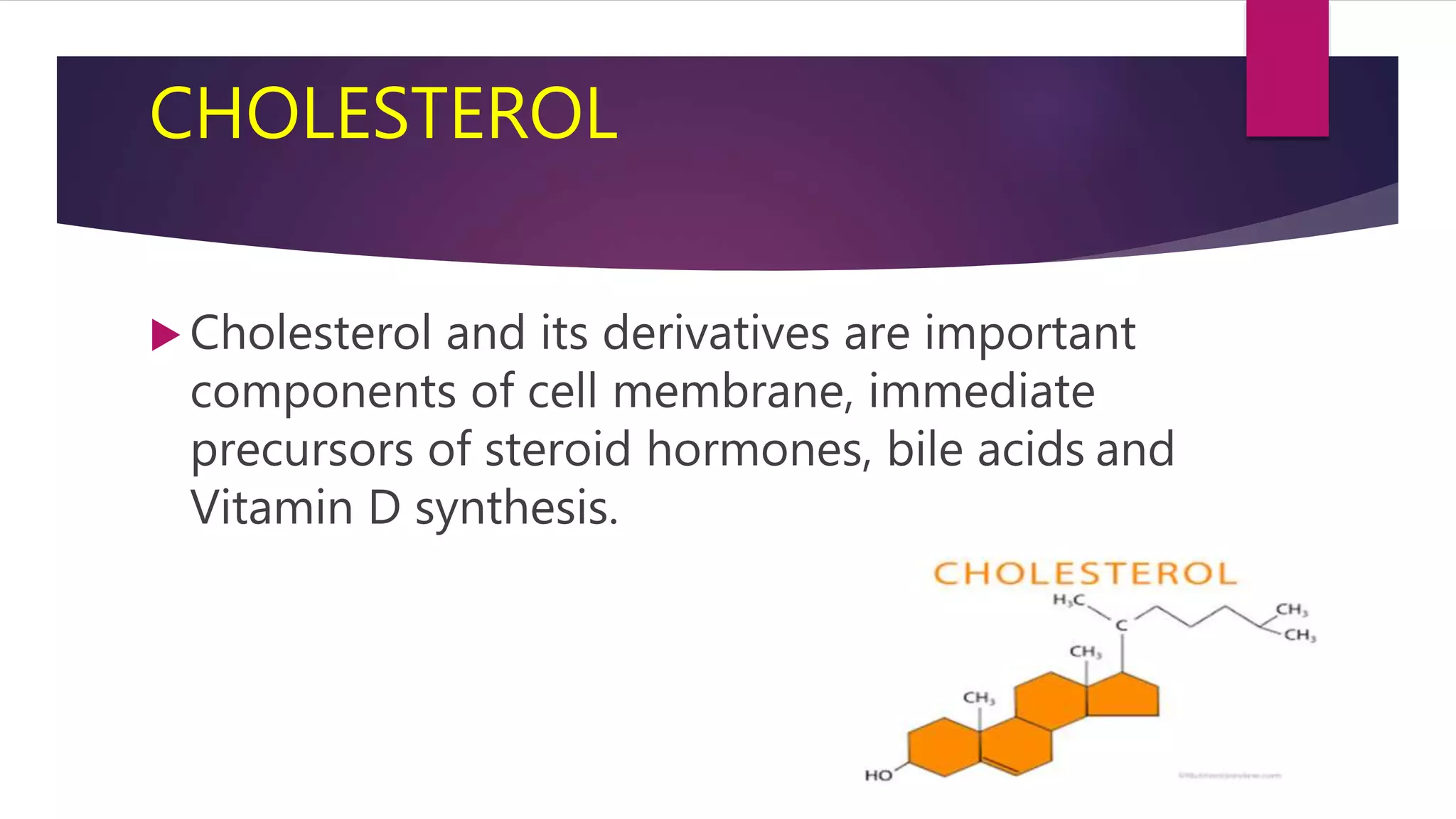
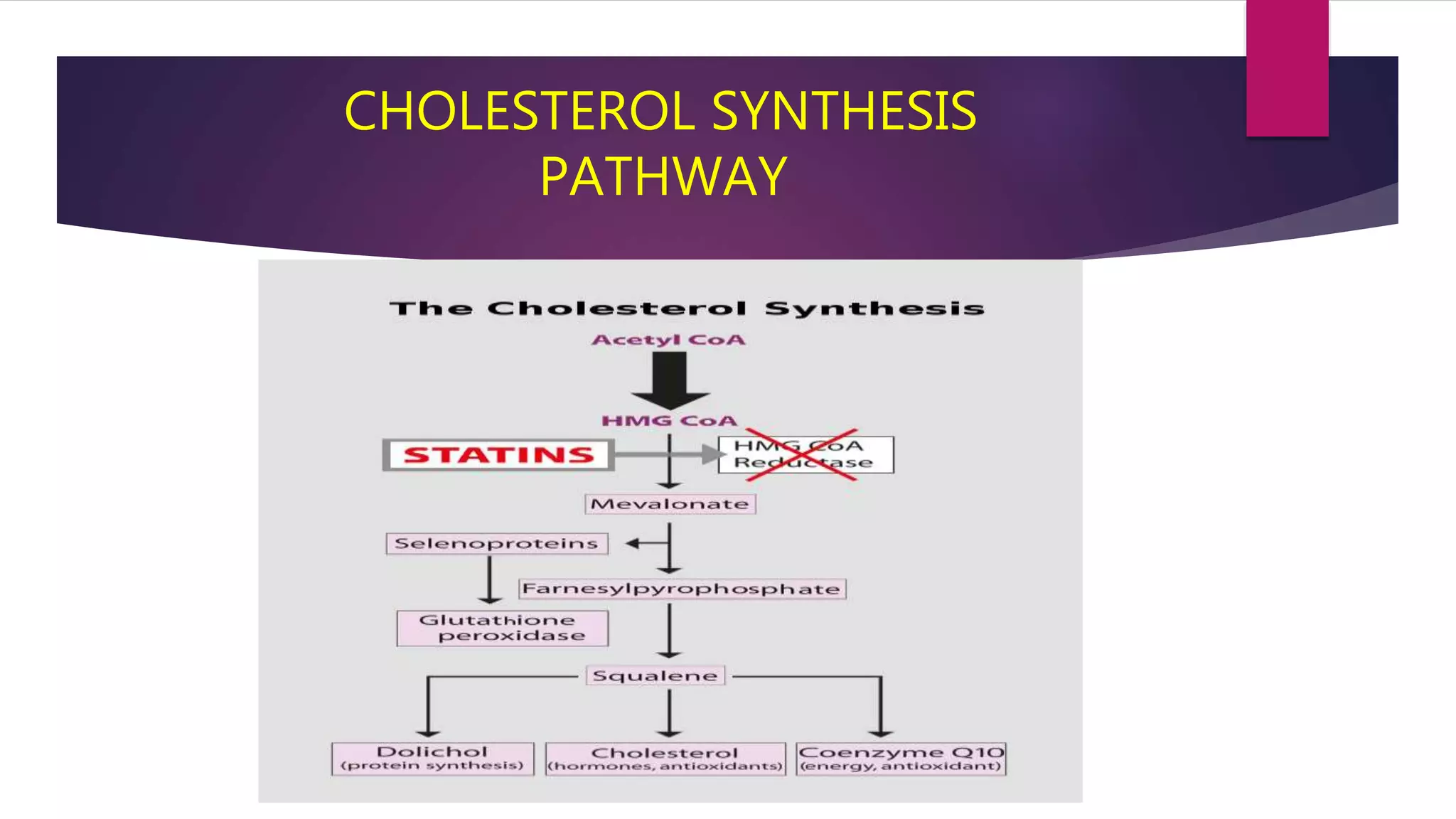
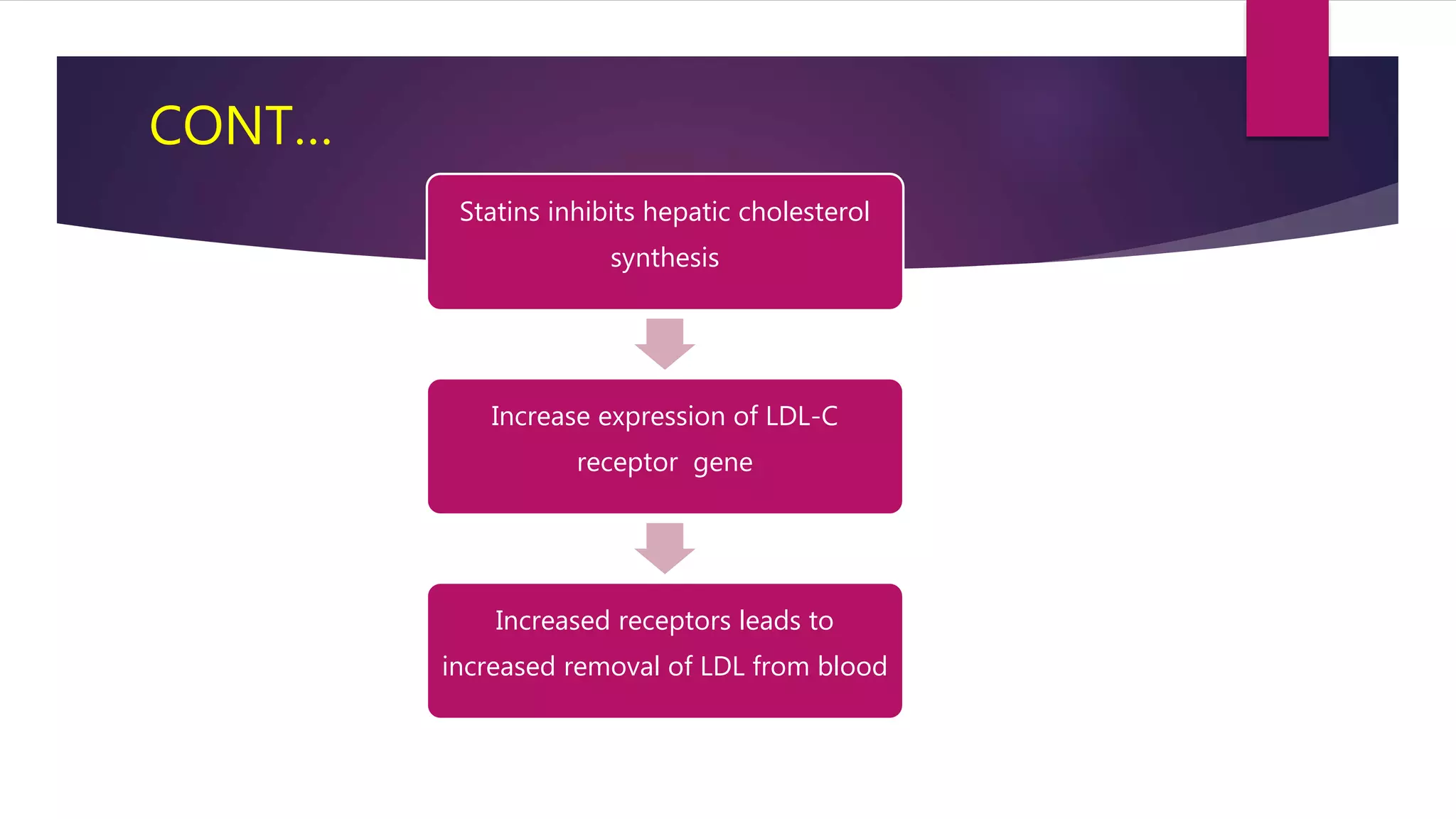
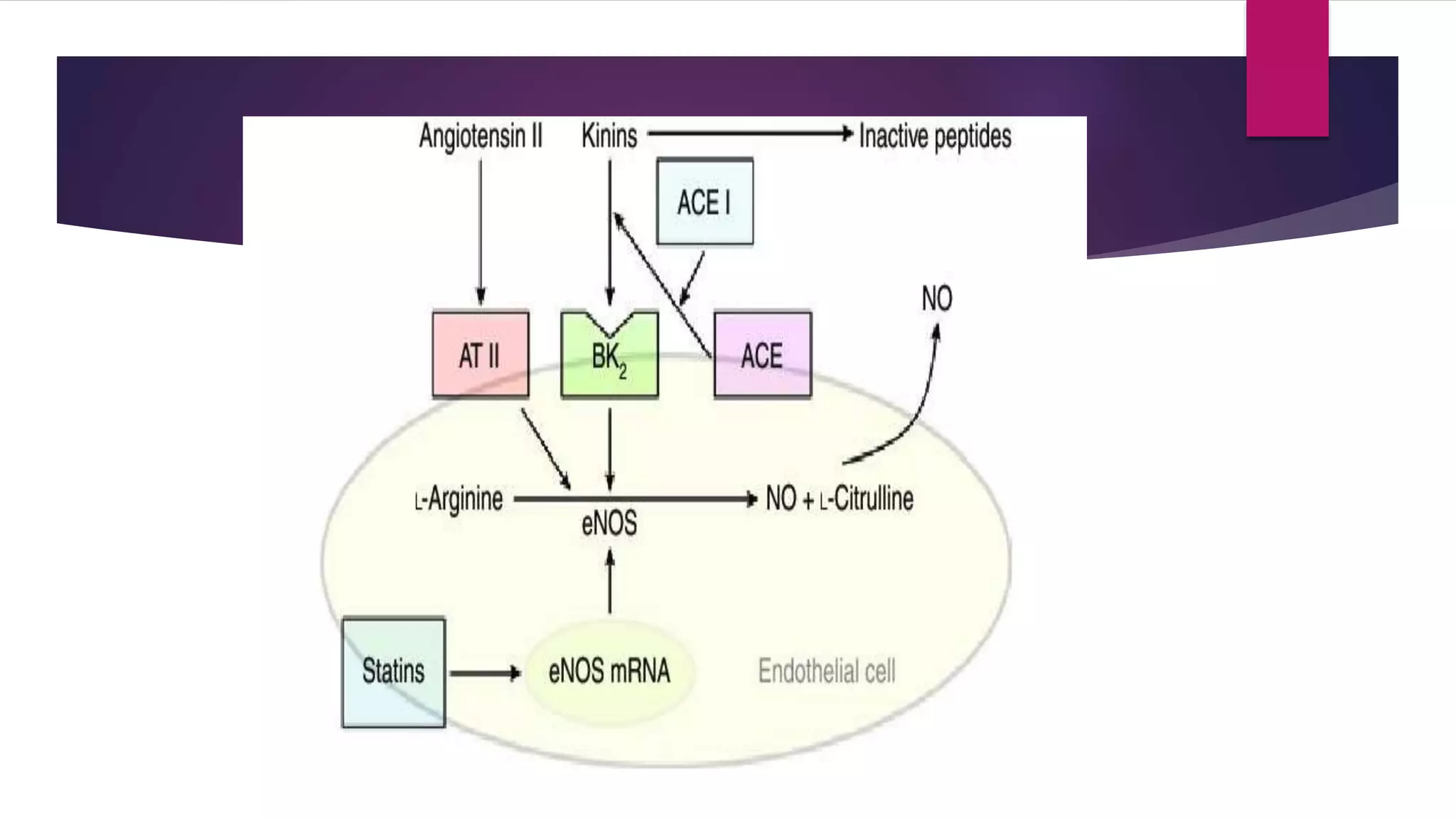
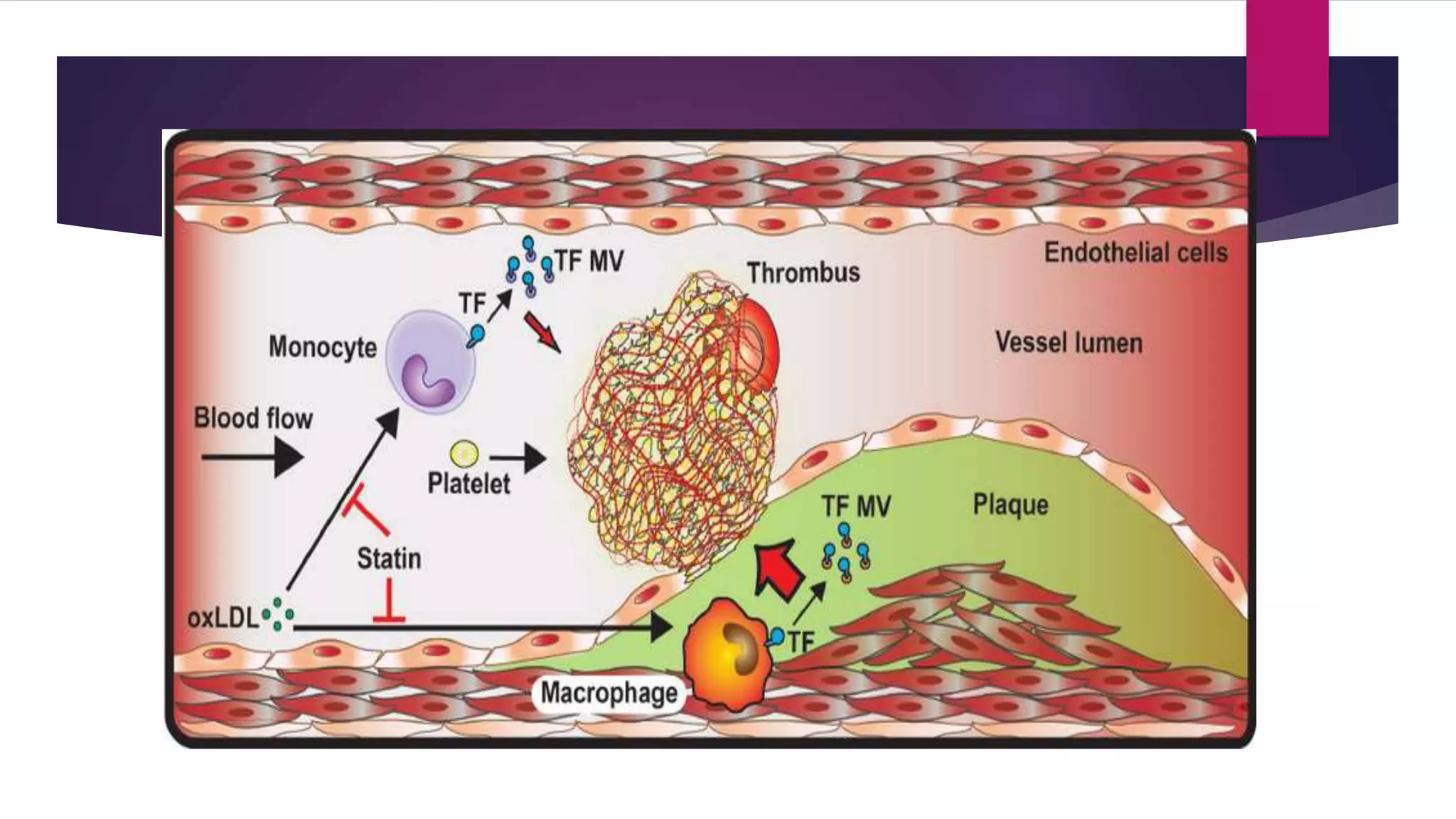
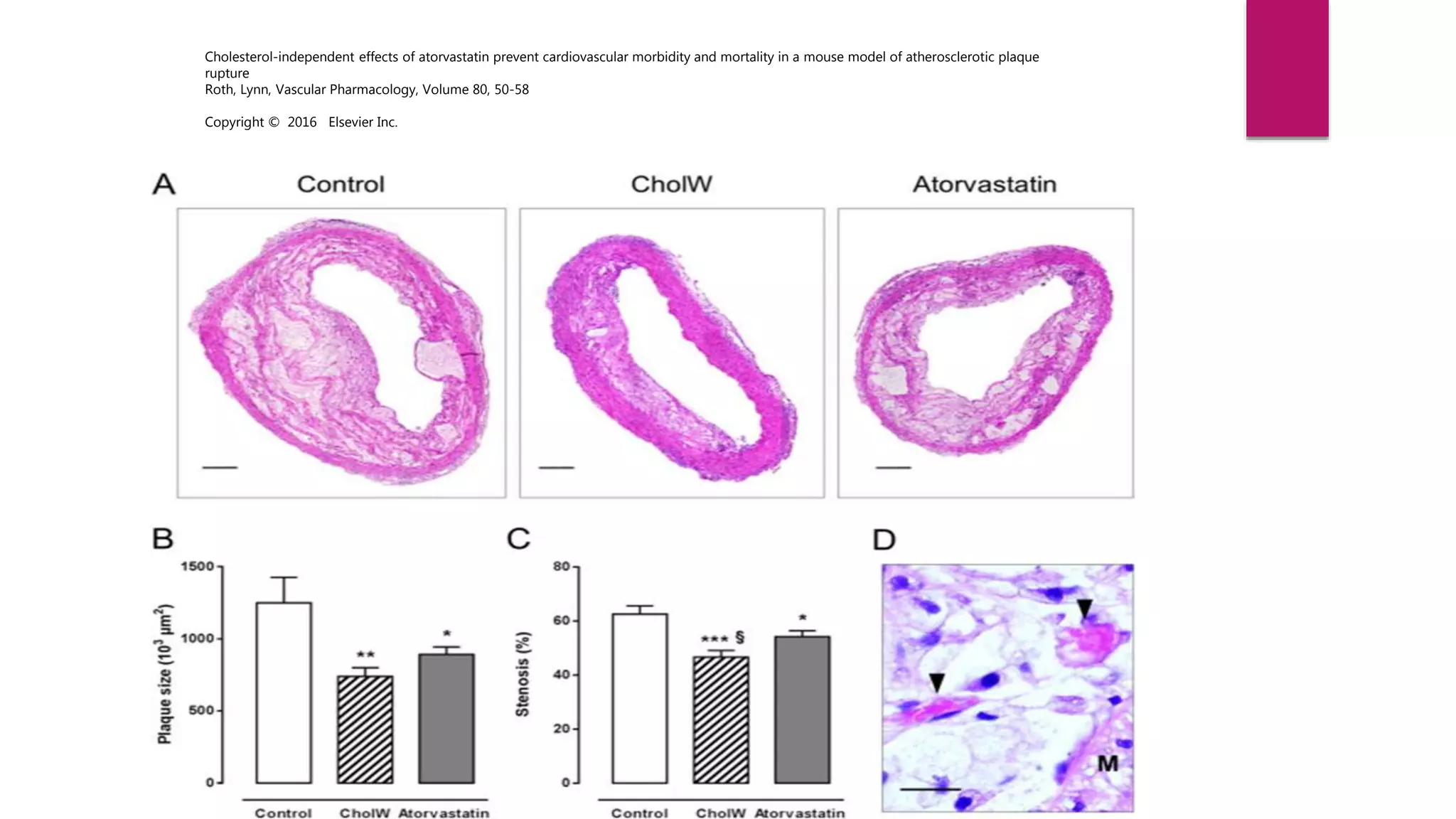
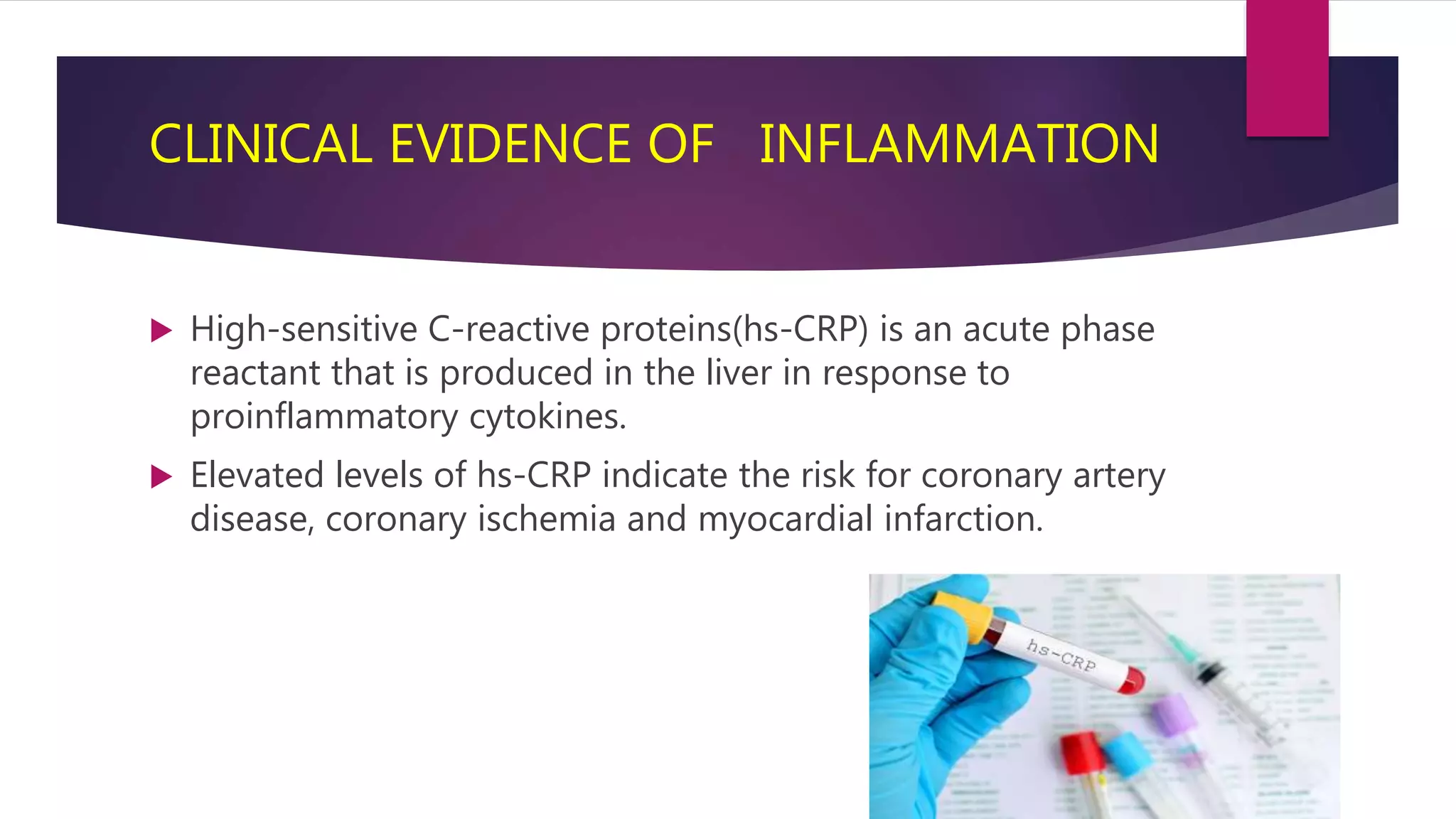
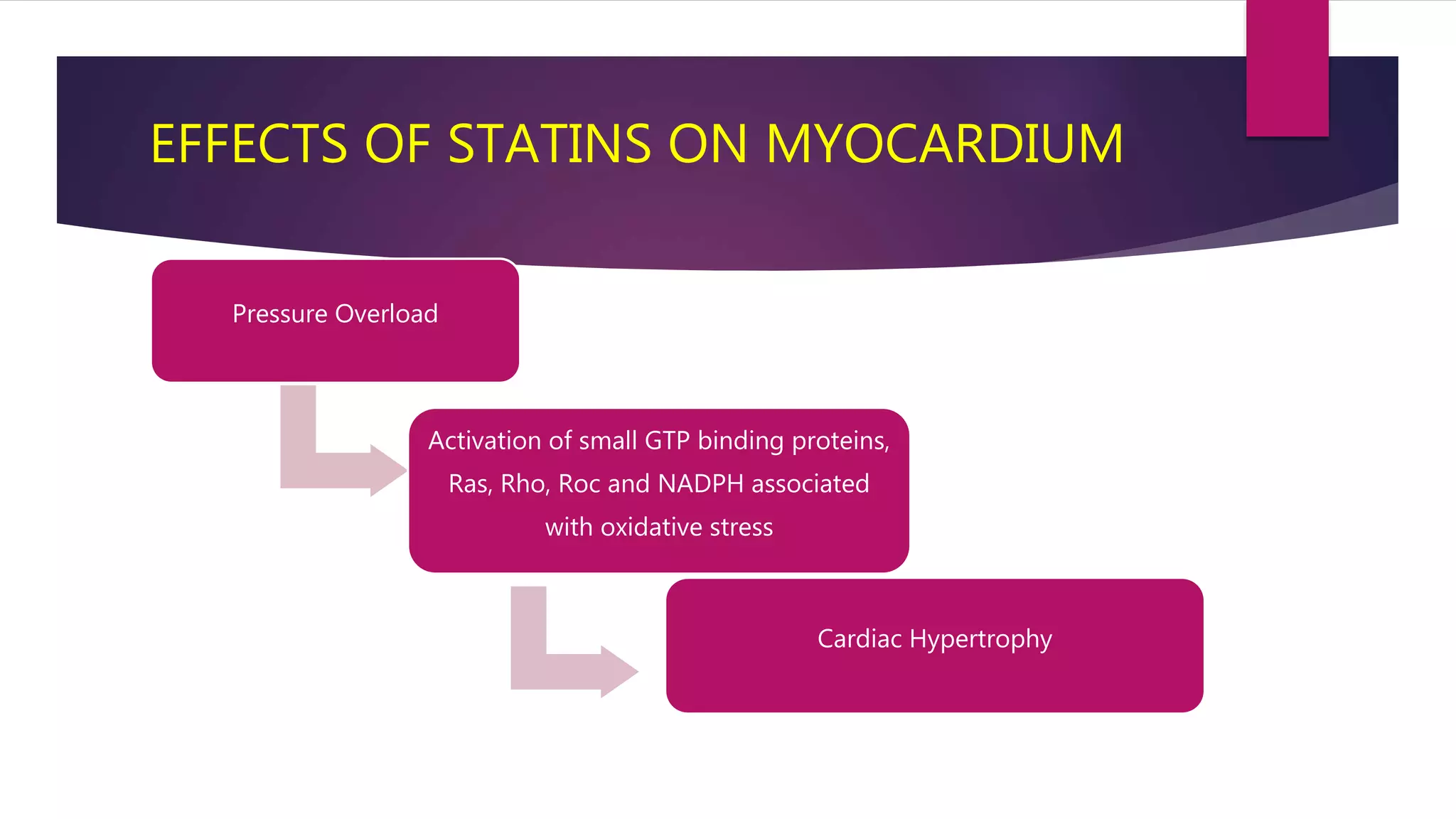
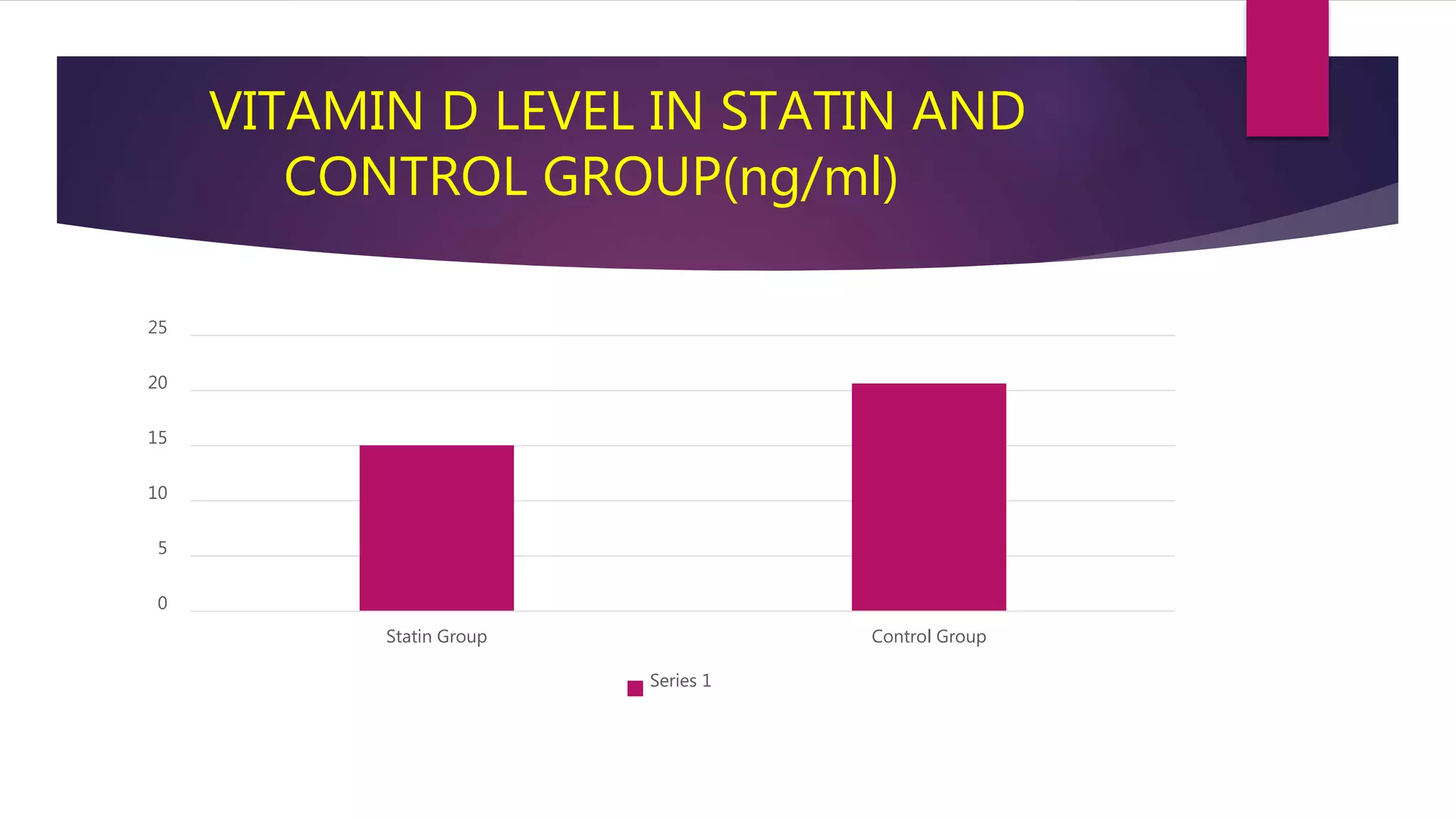
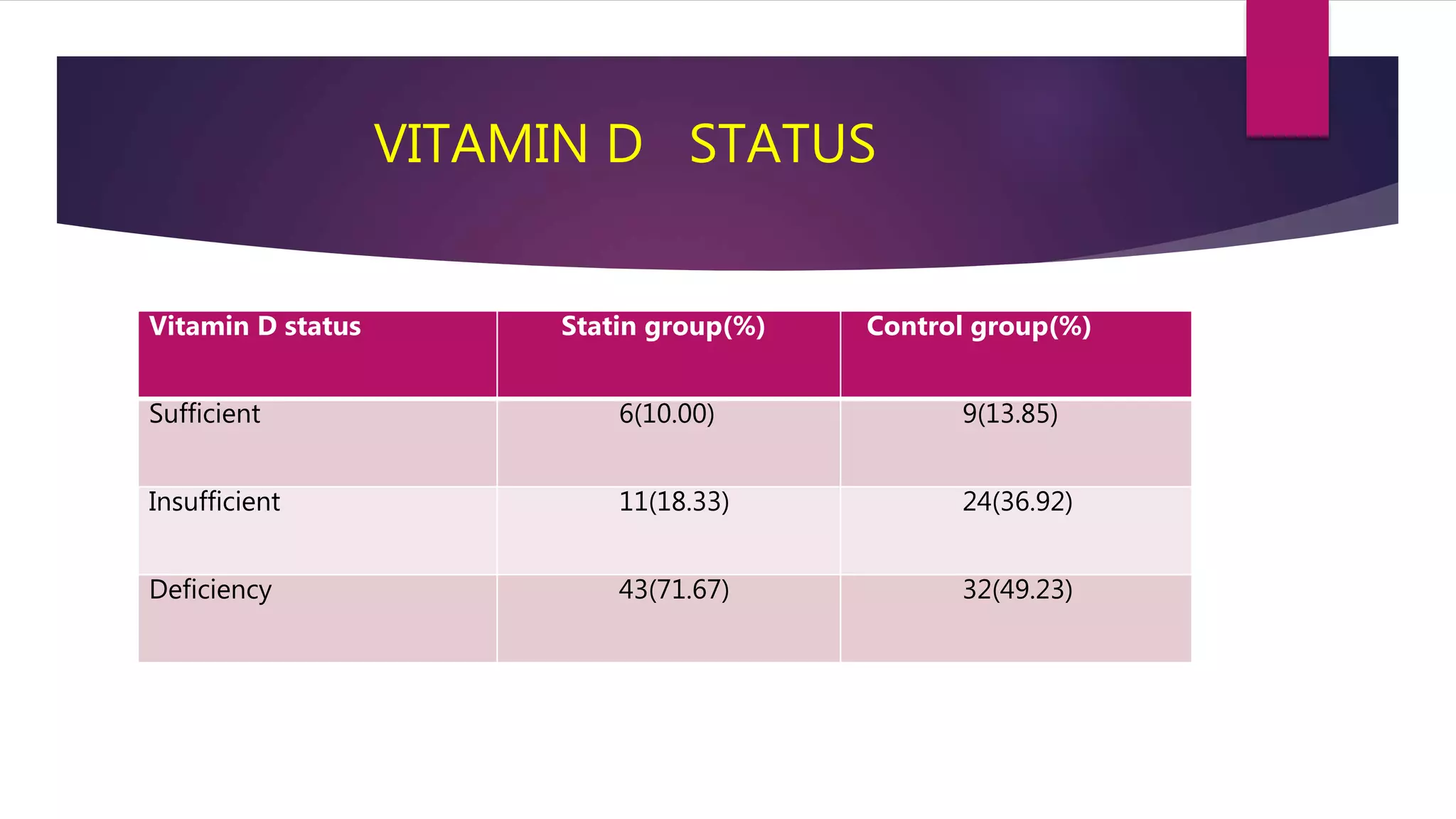
This document summarizes a presentation on statins and their pleiotropic effects. It begins with an overview and introduction on statins. It then discusses cholesterol synthesis and statins' mechanism of action in inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase to lower cholesterol. The document outlines various pleiotropic effects of statins including improving endothelial function, providing plaque stability, anti-inflammatory effects, and effects on other organs. It summarizes several research articles on topics like statins' effect on CRP and the association between statins and vitamin D.


![INTRODUCTION
Cardiovascular diseases (coronary heart disease) principal cause of
morbidity and mortality in developing as well as developed countries.
Atherosclerosis is the main underlying cause of disorders in CVDs.
An association has been established between Elevated levels of plasma
Cholesterol and increased atherosclerotic diseases.
Several landmark clinical trials Eg: Scandinavian simvastatin survival study,
cholesterol and Recurrent Events, Heart Protection study etc have
demonstrated the benefit of lipid lowering with 3-hydroxy-3-
methylglutaryl coenzyme A[HMG CoA] reductase enzyme inhibitors
/statins for primary and secondary of CHDs.
Statins also exerts many pleiotropic effects too.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/statinsanditspleiotropiceffects2-191025161209/75/Statins-and-its-pleiotropic-effects-2-3-2048.jpg)