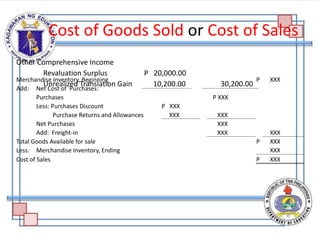
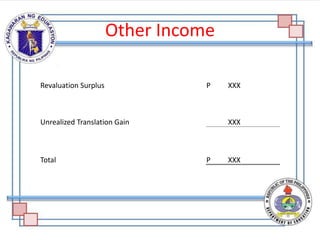
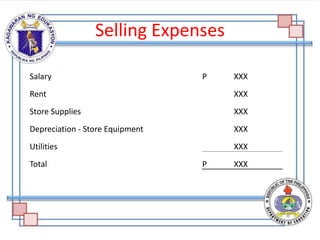
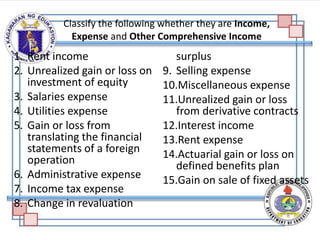
The document discusses the components and purpose of an income statement and the statement of comprehensive income, outlining key elements for both service and merchandising businesses. It covers the structure of the income statement including income, expenses, and various account classifications, emphasizing differences between service and merchandising concerns. Additionally, it provides exercises for classifying financial elements into categories such as assets, liabilities, capital, income, and expenses.