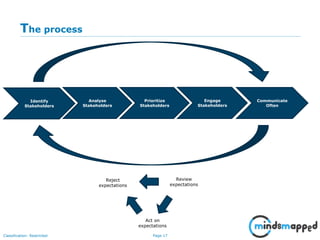
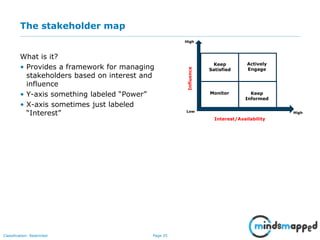
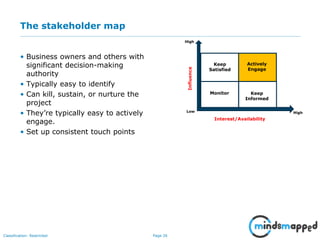
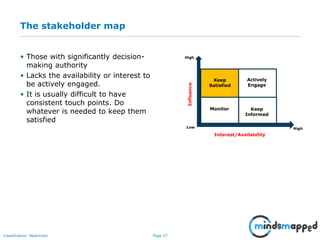
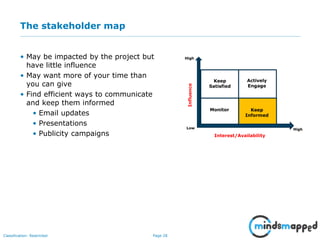
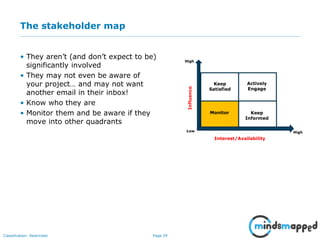
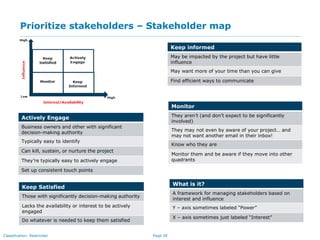
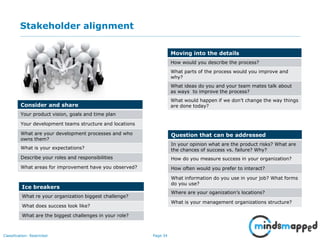
The document outlines the importance of effective stakeholder management within organizations, emphasizing the need to identify, analyze, and engage stakeholders throughout the product development cycle. It provides guidelines for prioritizing stakeholders based on their influence and interest while also addressing challenges such as unclear or unreasonable expectations. The main goal is to align stakeholder needs with organizational objectives, ensuring successful collaboration and communication.