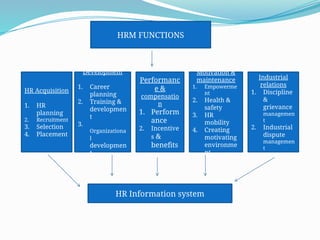
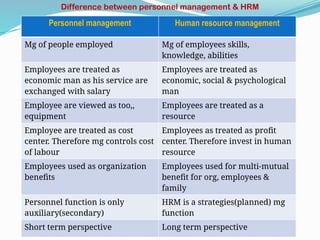
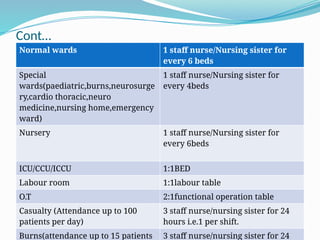
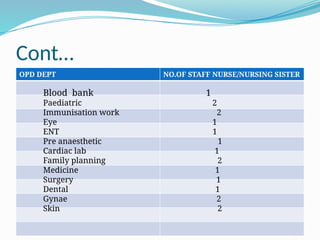
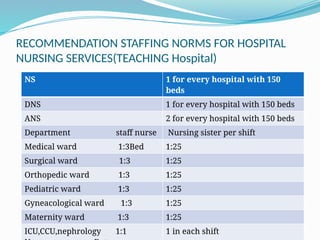
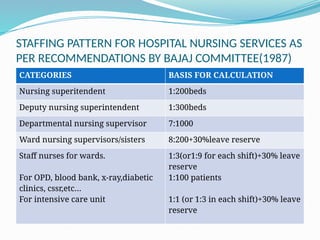
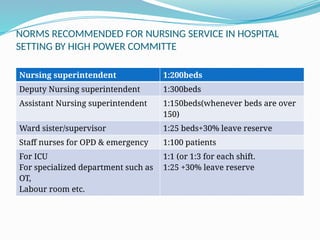
Human Resource Management (HRM) is focused on the effective management of an organization's workforce, encompassing recruitment, training, development, and employee relations. Staffing is a critical HRM process involving the planning, selection, and development of human resources to meet organizational needs. The document outlines various HRM functions, staffing importance, factors affecting staffing, and provides recommendations for staffing norms in healthcare settings.