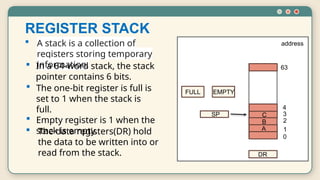
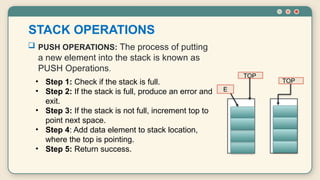
The document discusses stack organization, a data structure that follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle, detailing its operations (push and pop) and implementation methods (register and memory stacks). It describes how stack pointers work and outlines the procedural steps for the push and pop operations. Additionally, it explains the use of stacks in evaluating arithmetic expressions using Reverse Polish Notation (postfix notation).