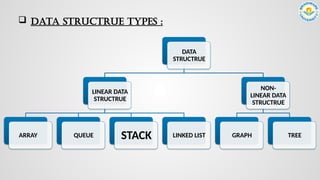
The document provides an overview of stacks, a linear data structure that operates on a last-in-first-out principle, allowing insertion and deletion at a single end called the top. It includes descriptions of stack operations such as push, pop, peek, and checks for stack conditions, as well as the distinction between fixed size and dynamic size stacks. Algorithms for these operations are also outlined along with potential overflow and underflow conditions.





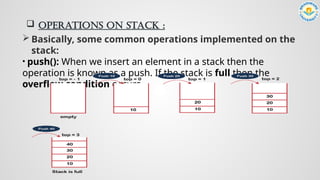
![ALGORITHM OF PUSH AND POP OPERATIONS IN STACK :
Step-1 : Start
Step-2 : if stack is
“full”
print(“OVERFLOW”)
Endif.
Exit
Step-3 : else
top=top+1
Step-4 : stack[top]=item
Step-5 : End else
Step-6 : Exit
Step-1 : Start
Step-2 : if stack is “empty”
print(“UNDERFLOW”)
Endif.
Exit
Step-3 : else
item=stack[top]
Step-4 : top=top-1
return value
Step-5 : End else
Step-6 : Exit
push() operation pop() operation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ocjxq97otp2bdfye2nie-ds-presentation-582-241104081156-5a6f3cc6/85/STACK_IN_DATA-STRUCTURE-AND-ALGORITHMS-pptx-9-320.jpg)
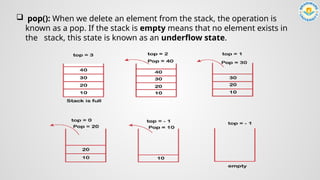
![ peek()/top() : It returns the element at the given position or
tops element.
E
R
A
W
N
I
A
R
B
0
1
2
3
6
9
7
8
4
5
TOP
STACK
Algorithm of top() operations
Step-1 : Start
Step-2 : return
stack[top]
Step-3 : Exit
INDEXING](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ocjxq97otp2bdfye2nie-ds-presentation-582-241104081156-5a6f3cc6/85/STACK_IN_DATA-STRUCTURE-AND-ALGORITHMS-pptx-10-320.jpg)
![• isEmpty(): This operation is determines whether the stack is
empty or not.
• isFull(): In this operation determines whether the stack is full or
not.'
Algorithm of isEmpty() operations Algorithm of isFull() operations
Step-1 : Start
Step-2 : if
stack[i]=top[i]
print(“FULL”)
Endif
Exit
Step-3 : else
return 0 or
False
Step-4 : End else
Step-5 : Exit
Step-1 : Start
Step-2 : if stack top < 1
print(“EMPTY”)
return 1 or true
Endif
Exit
Step-3 : else
return 0 or
False
Step-4 : End else
Step-5 : Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ocjxq97otp2bdfye2nie-ds-presentation-582-241104081156-5a6f3cc6/85/STACK_IN_DATA-STRUCTURE-AND-ALGORITHMS-pptx-11-320.jpg)

