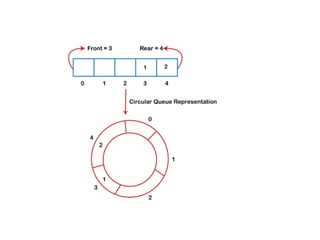
The document discusses abstract data types related to stacks and queues, highlighting their structures and operations. A stack follows a last in, first out (LIFO) approach, while a circular queue functions on a first in, first out (FIFO) principle and efficiently utilizes memory by forming a continuous loop. Additionally, it mentions priority queues which allow for the servicing of elements based on their priority level.


















![• Toper form the insertion of an element to the
queue, the position of the element is
calculated by the relation as
• Rear = (Rear + 1) % Maxsize.
then set
• Queue [Rear] = value.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitii-250109140308-d4d36687/85/STACK-AND-QUEUES-APPLICATIONS-INFIX-TO-POST-FIX-24-320.jpg)





