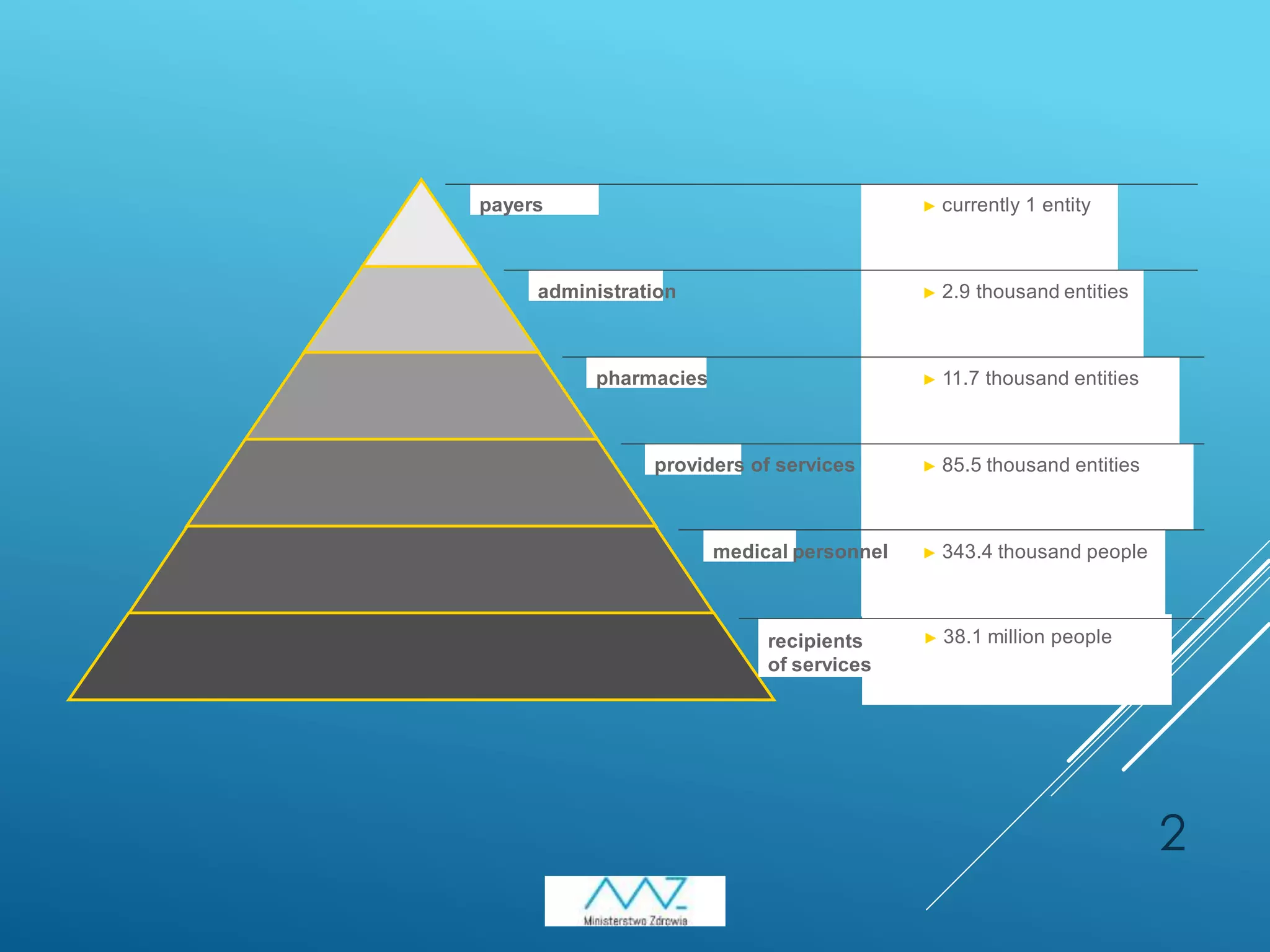
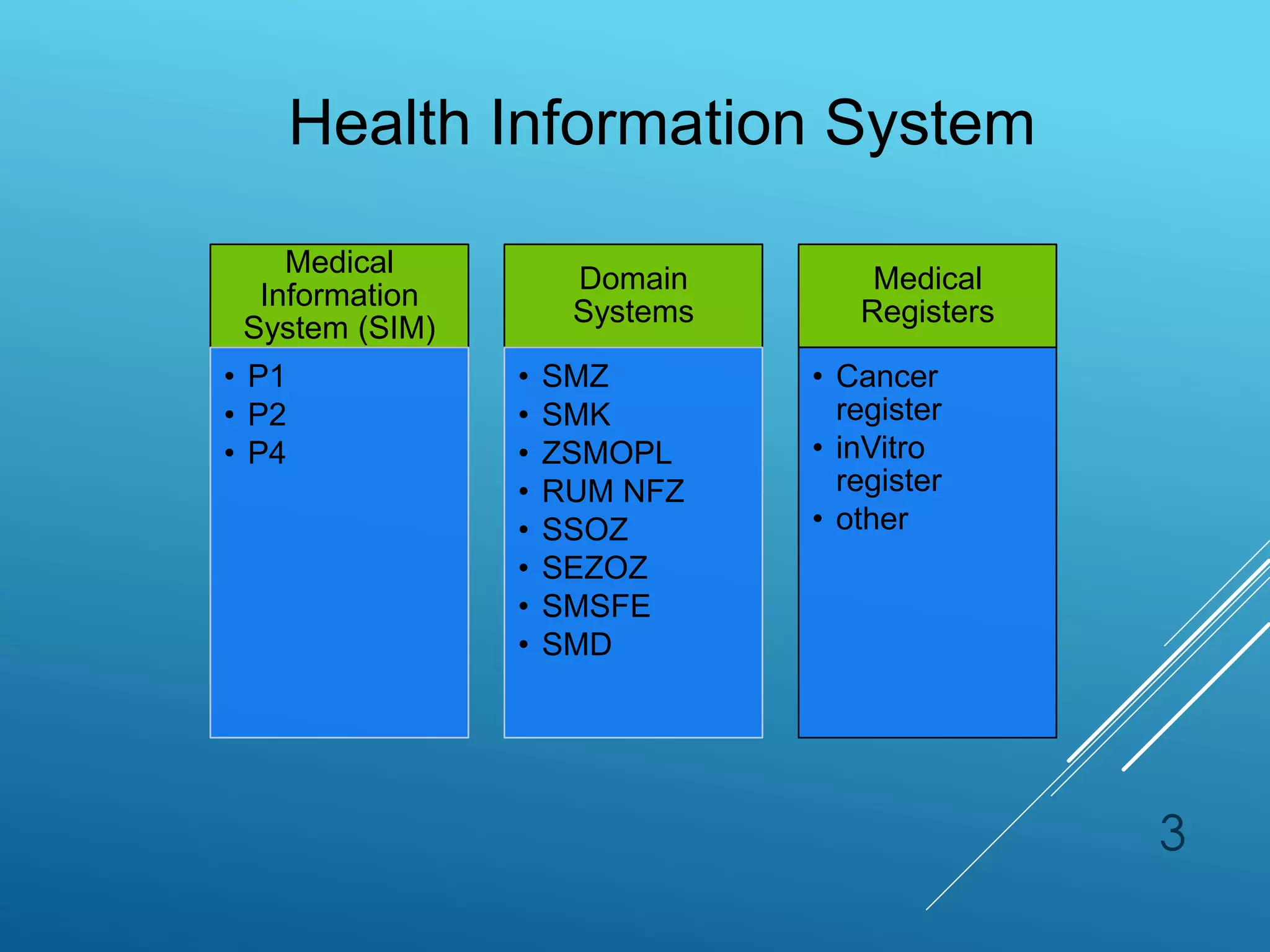
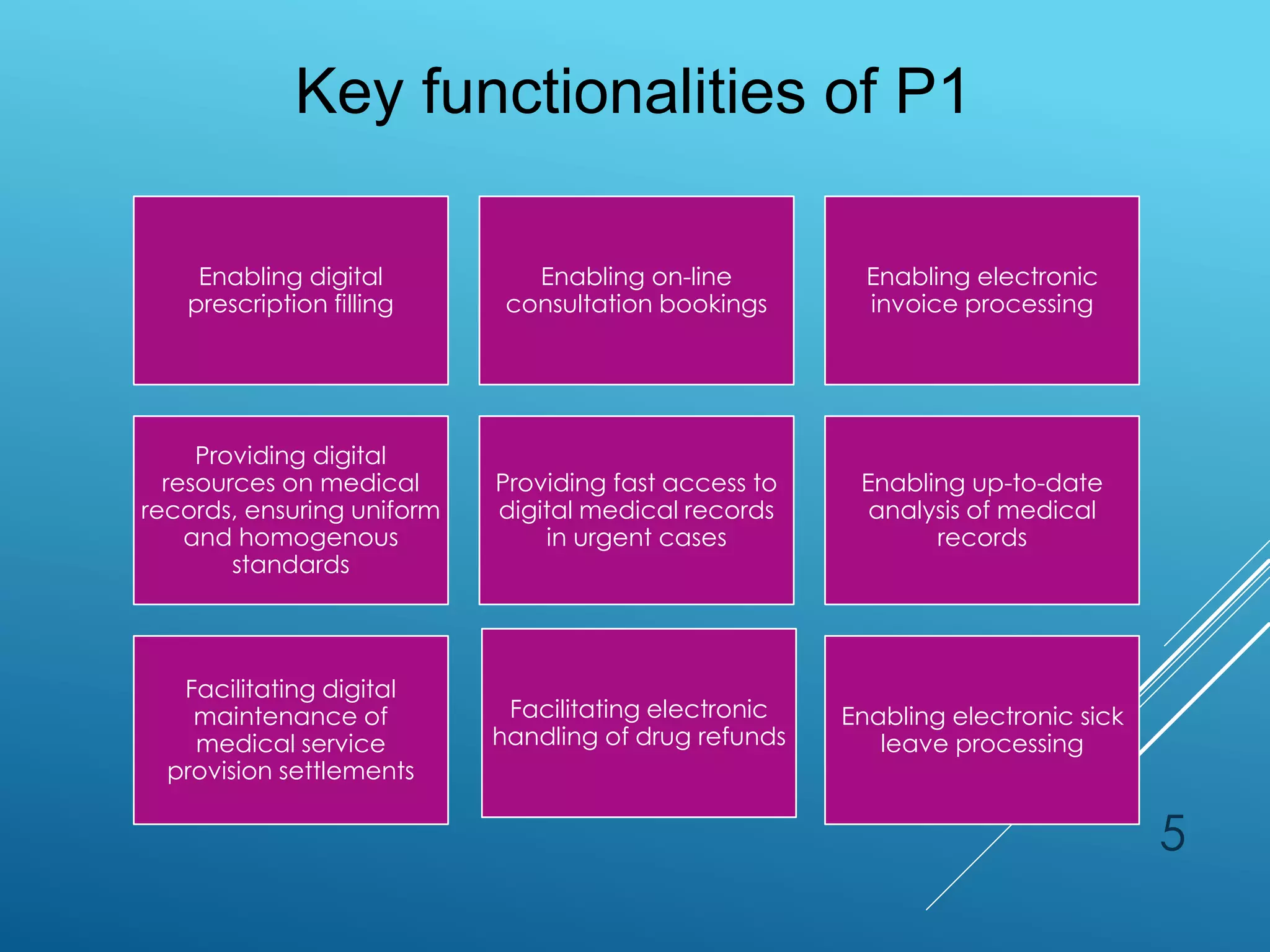
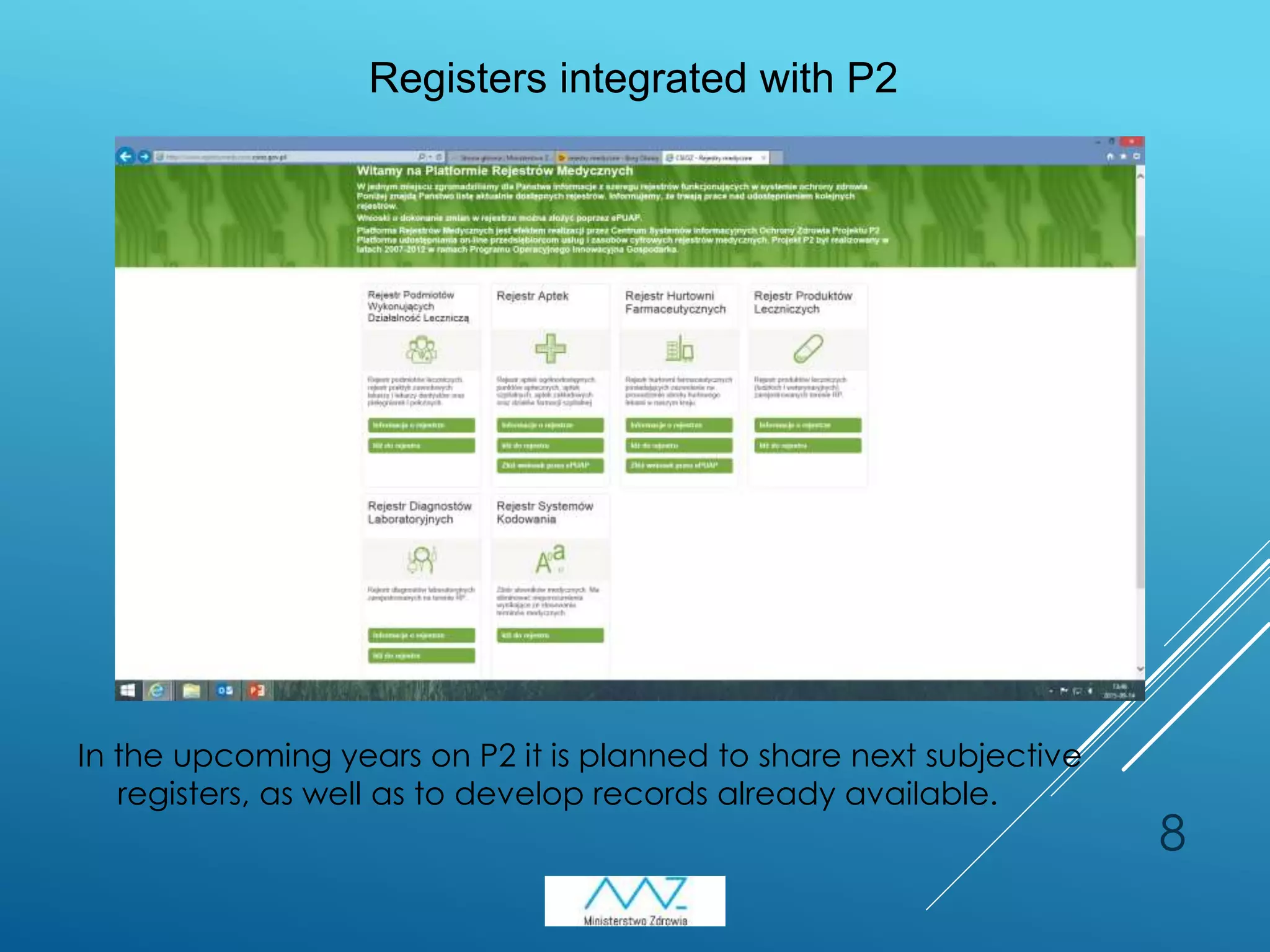
1) Poland has implemented several e-health initiatives including the Medical Information System (SIM) consisting of the P1, P2, and P4 projects. P1 enabled digital prescription filling and other functionalities. P2 allowed sharing of medical records and registers. P4 involved supplementary domain systems.
2) Pilot telemedicine projects were launched in cardiology and geriatrics to provide teleconsultations, reduce wait times and unnecessary hospitalizations, and evaluate outcomes.
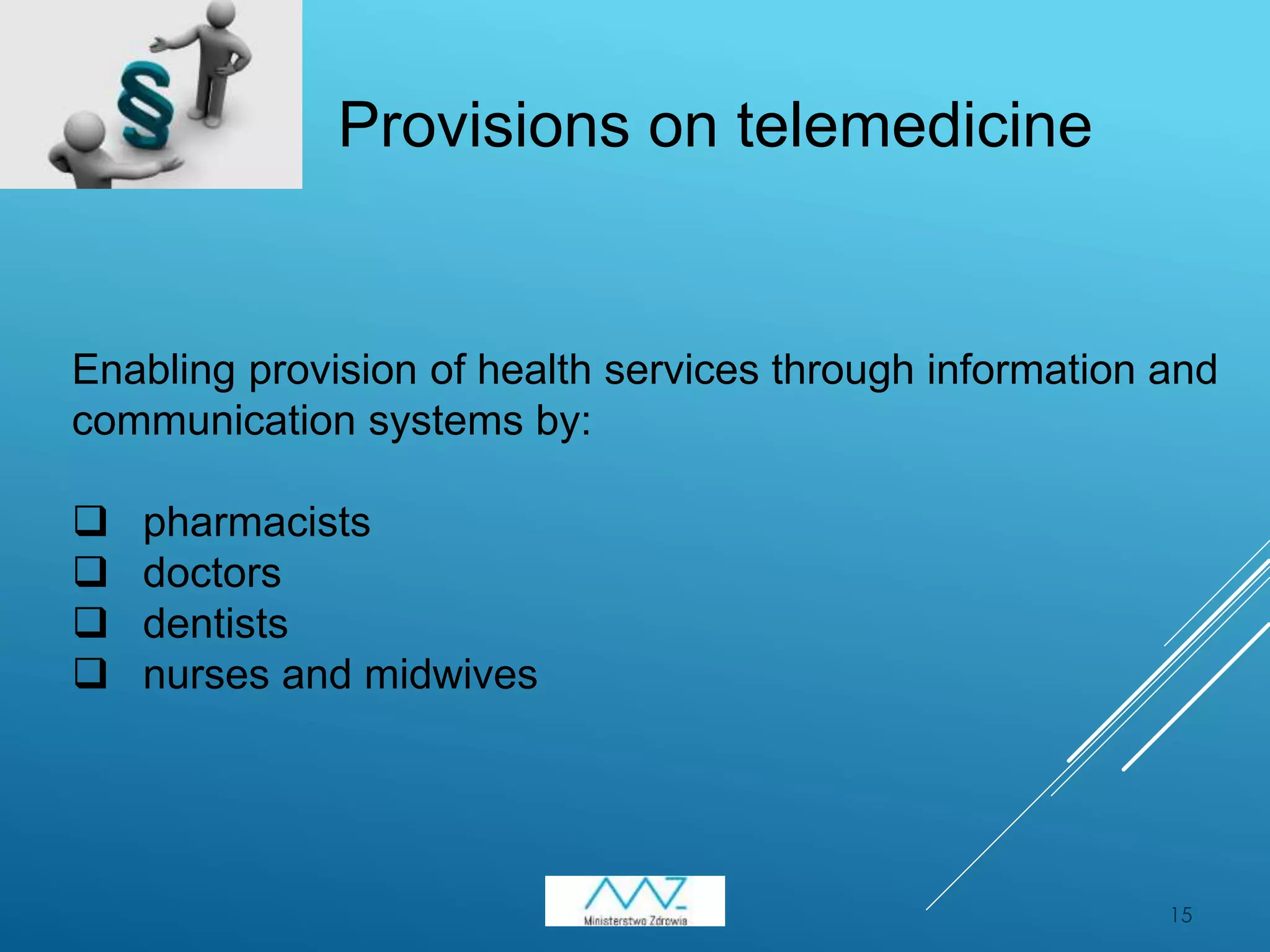
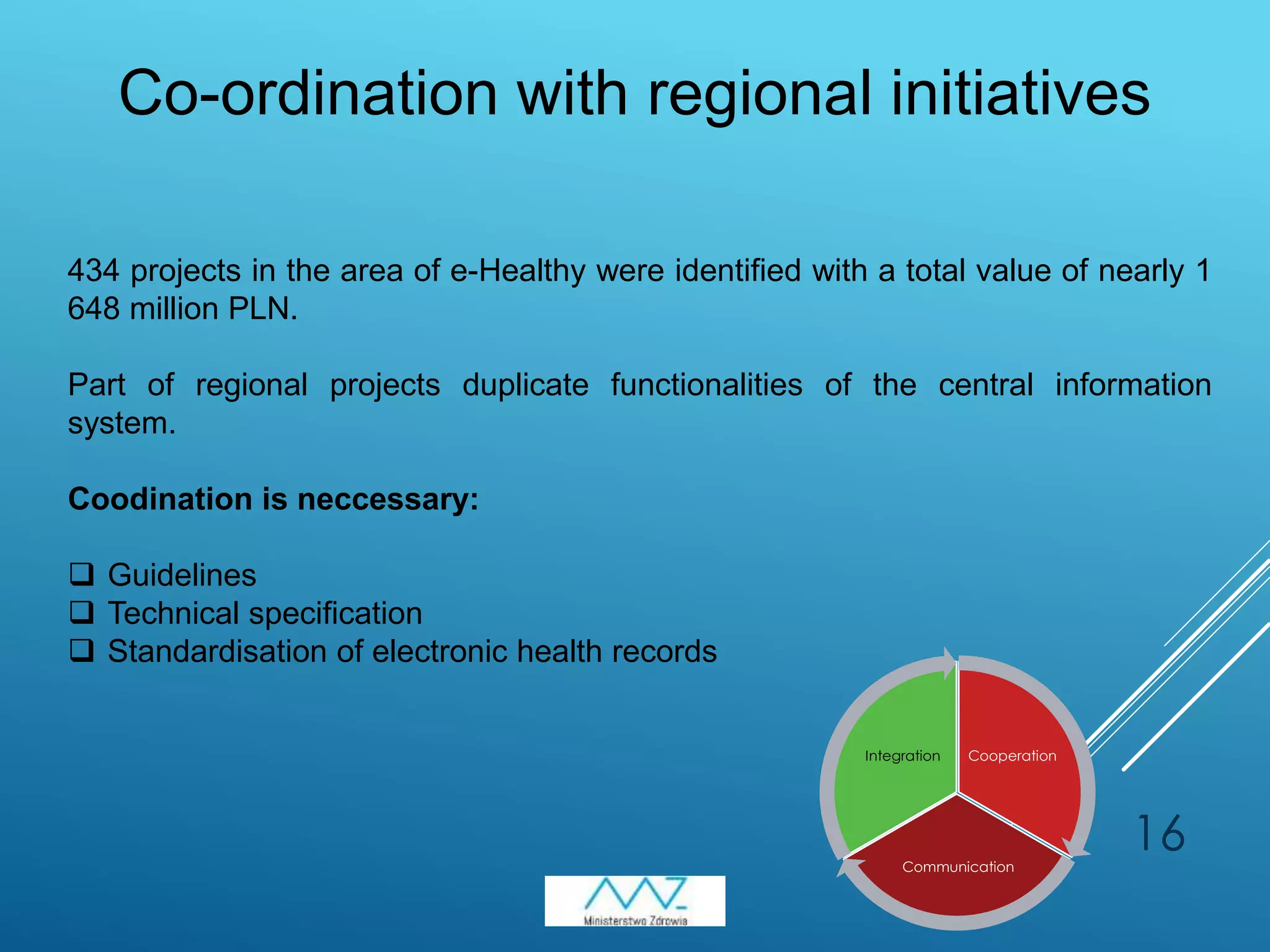
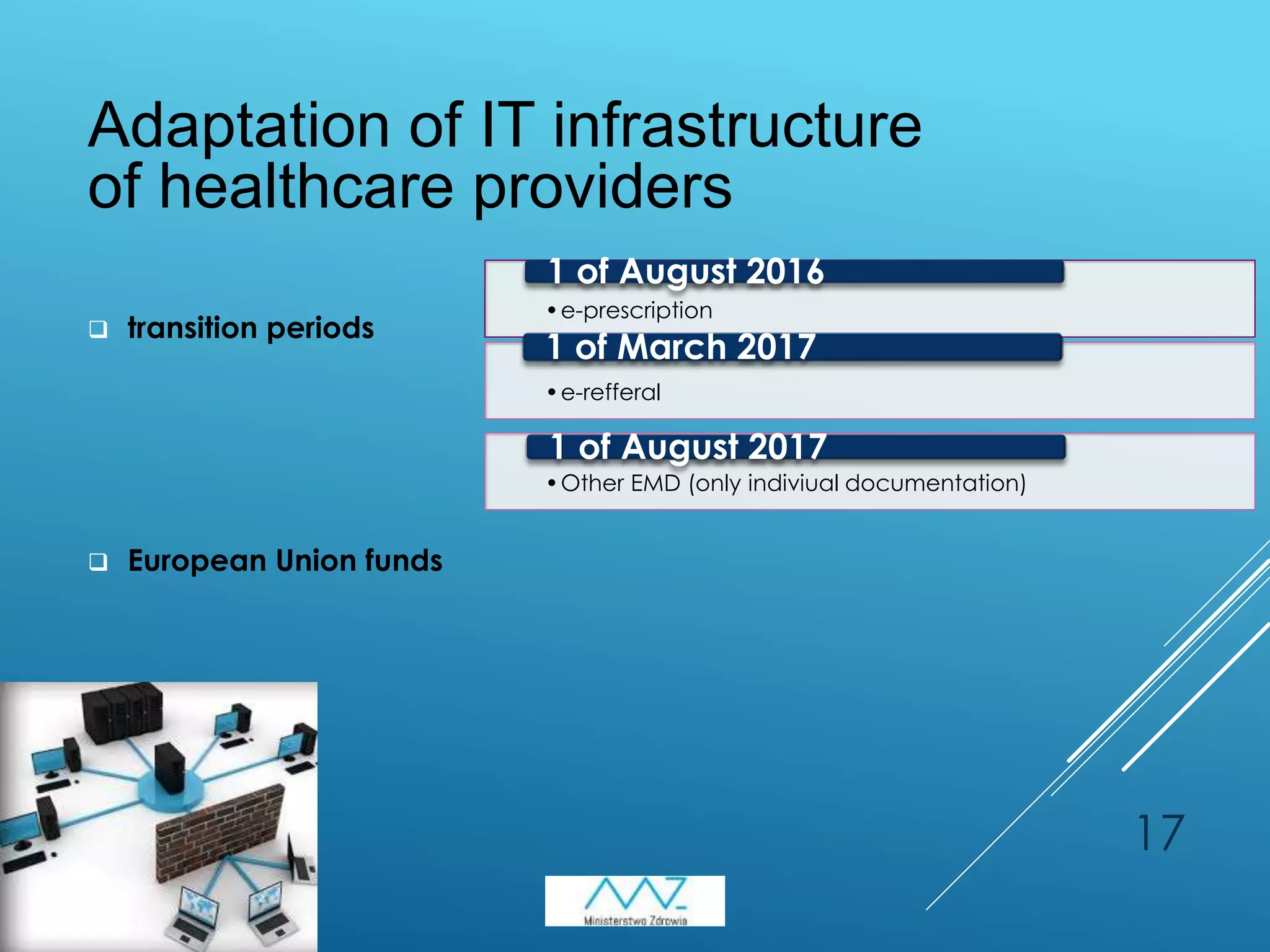
3) Upcoming amendments to the Act on the health information system will require compulsory electronic medical documentation from August 2017 and enable telemedicine services from pharmacists, doctors, and others. Coordination of regional and central e-health systems is