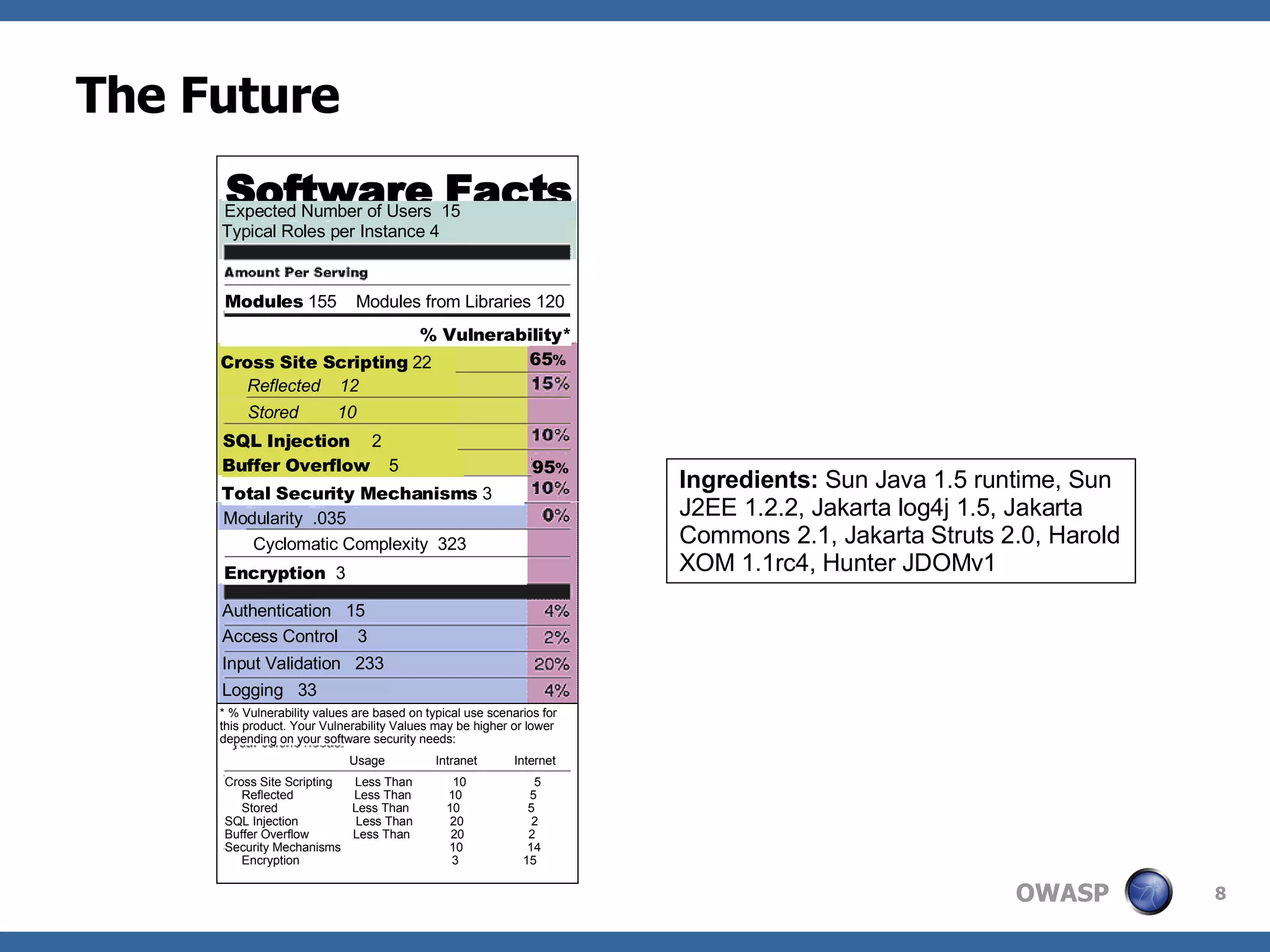
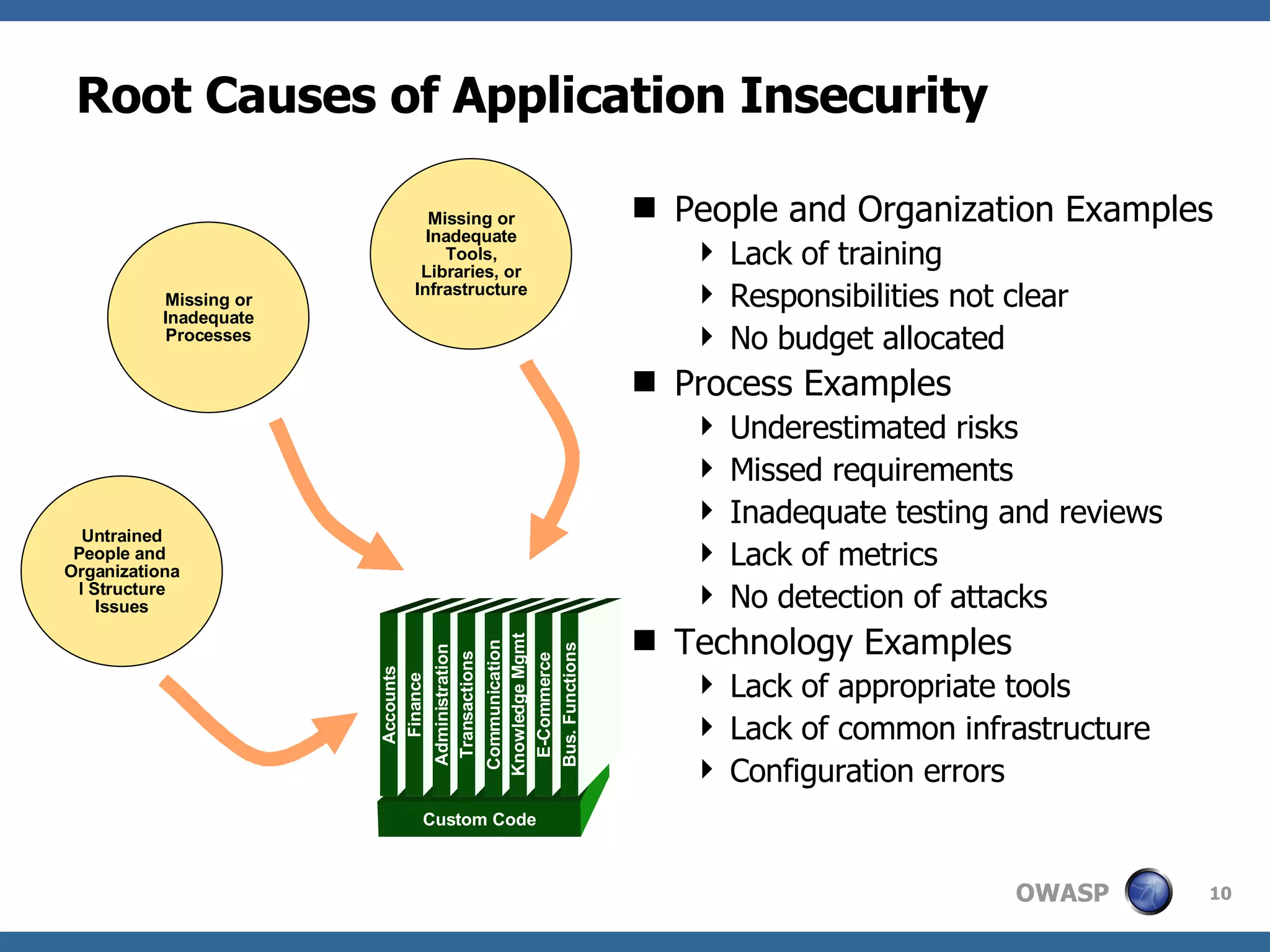
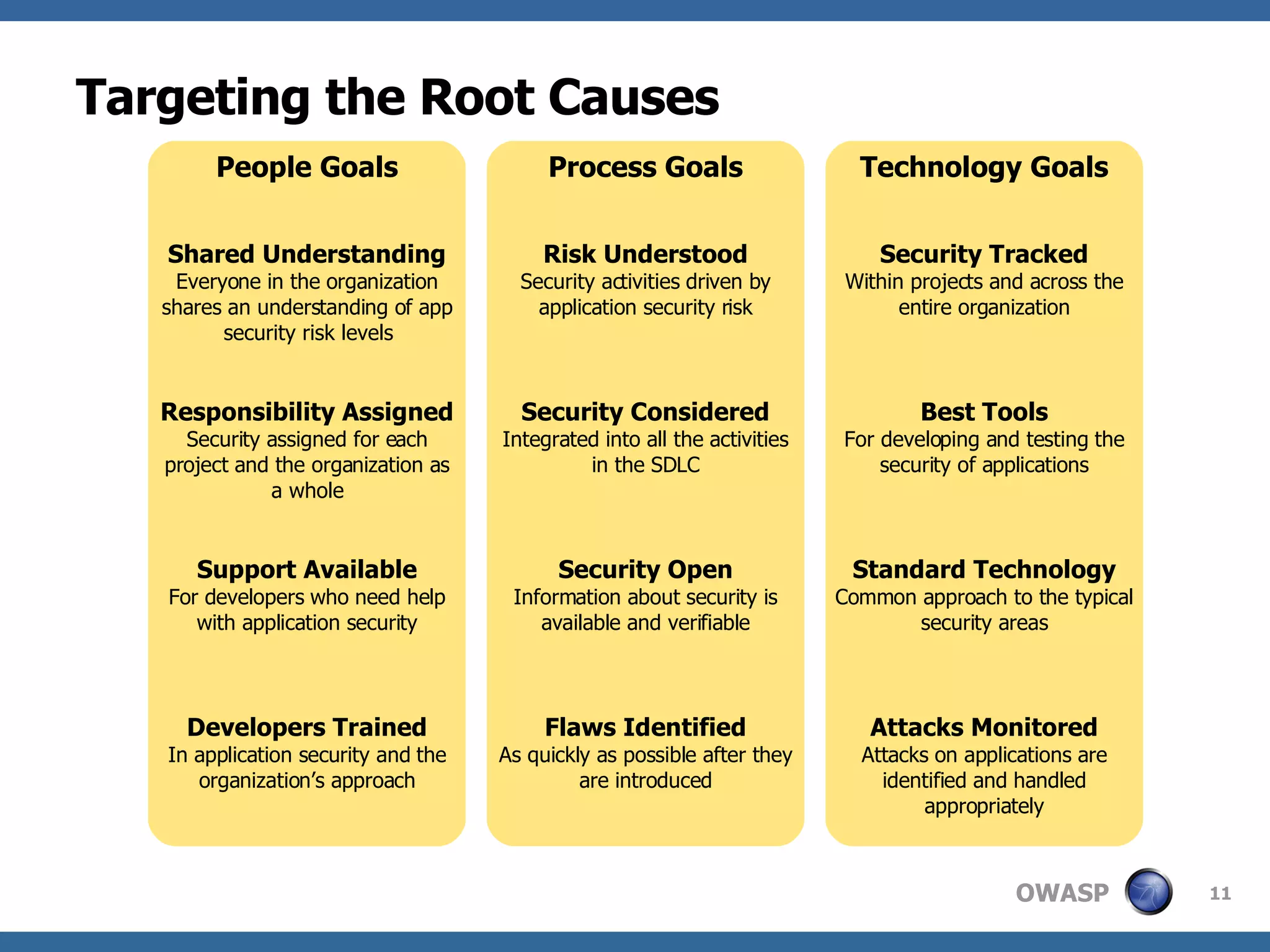
The document discusses the importance of application security, highlighting that the software market suffers from significant vulnerabilities comparable to past issues in the automobile industry. It emphasizes the need for organizations to recognize and mitigate risks associated with insecure applications and outlines methods for improving security practices, including the establishment of application security teams and training for developers. Additionally, it references the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) as a resource to aid in implementing effective security measures.
![Your Application Security Initiative – Beyond Finding Vulnerabilities Jeff Williams CEO, Aspect Security Chair, OWASP Foundation [email_address] 410-707-1487](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aspectissaapplicationsecurityinitiative-1211895153526090-9/75/slide-1-2048.jpg)