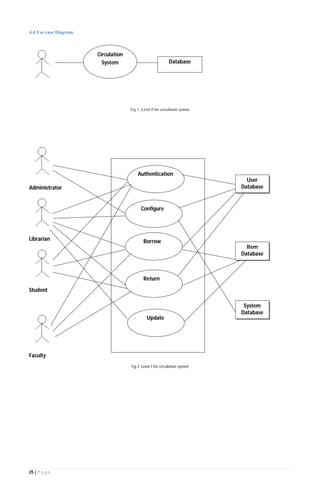
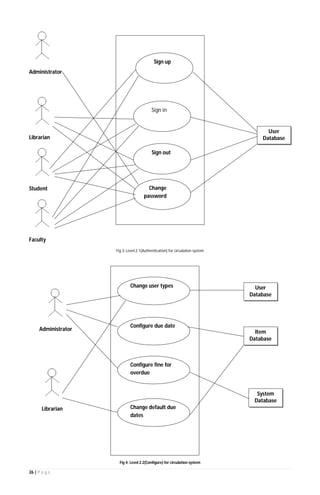
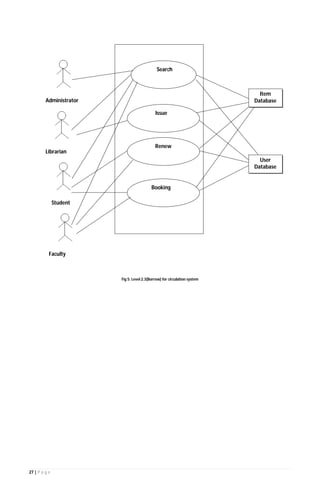
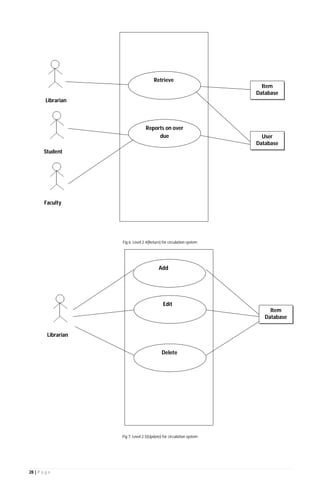
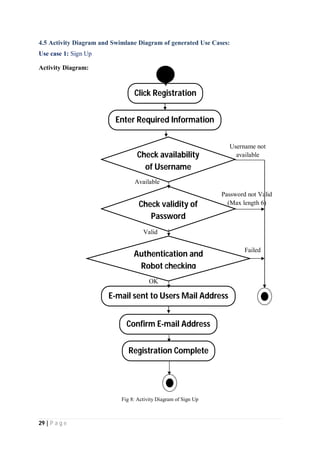
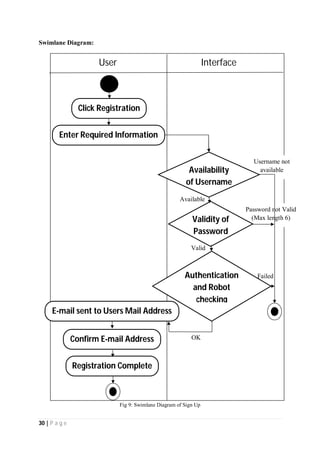
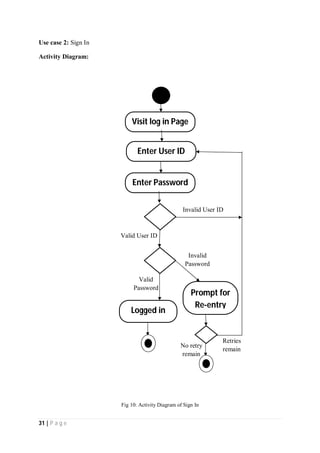
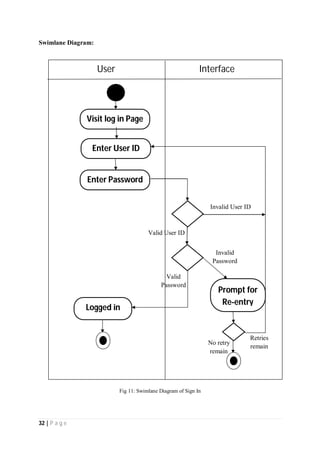
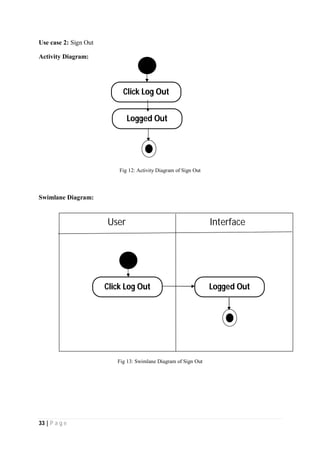
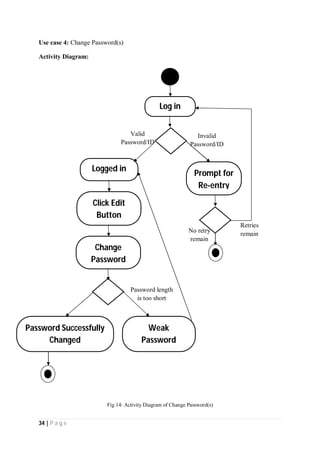
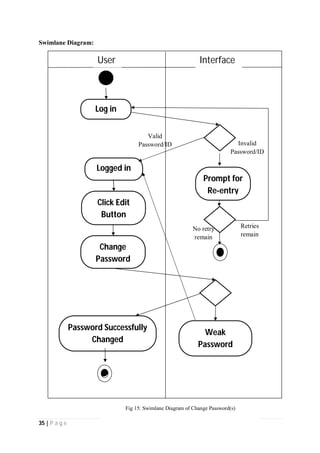
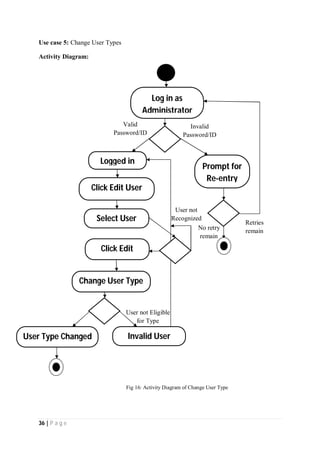
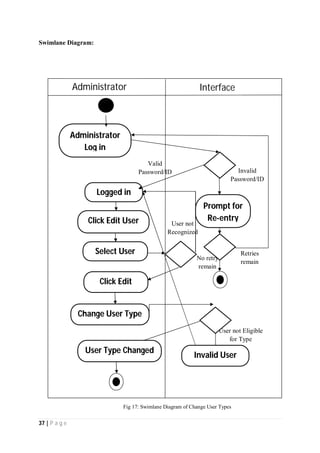
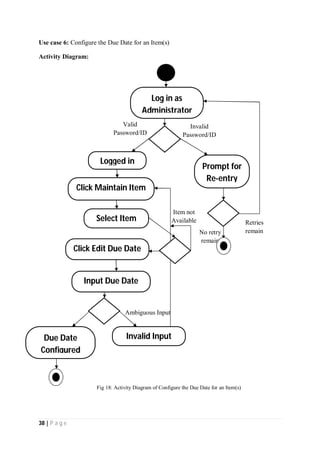
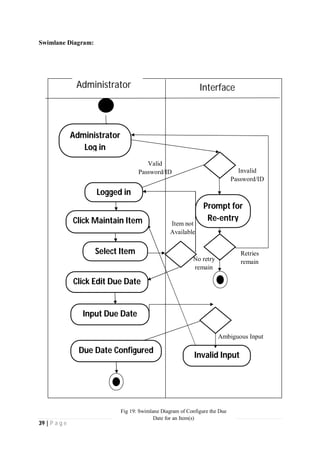
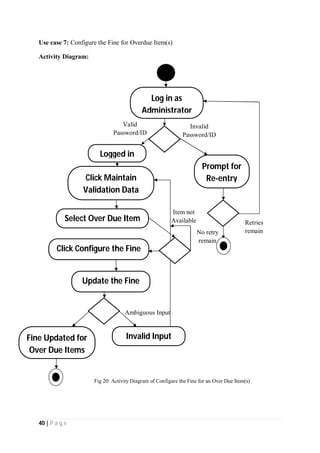
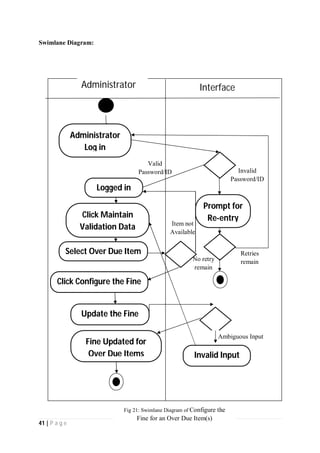
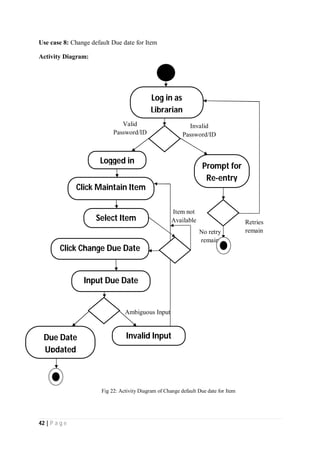
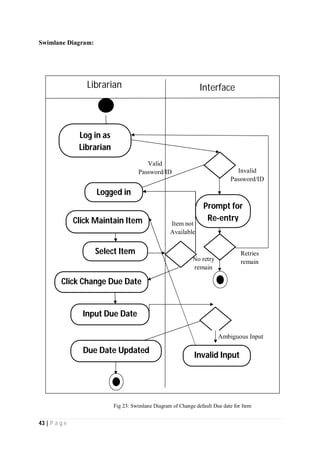
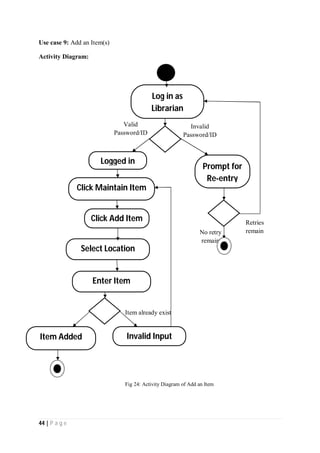
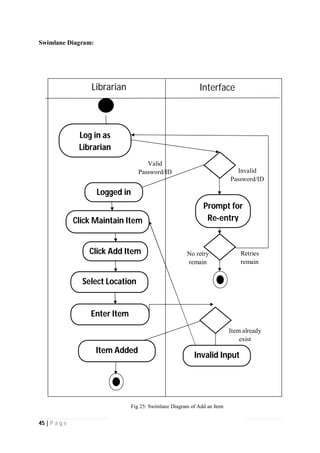
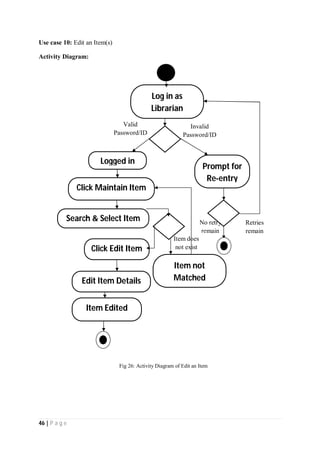
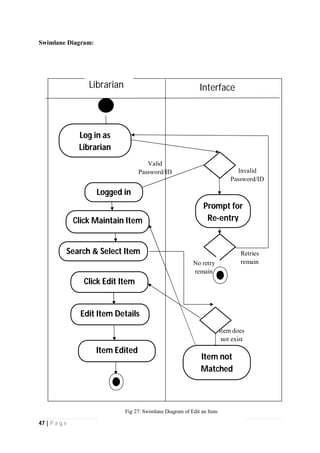
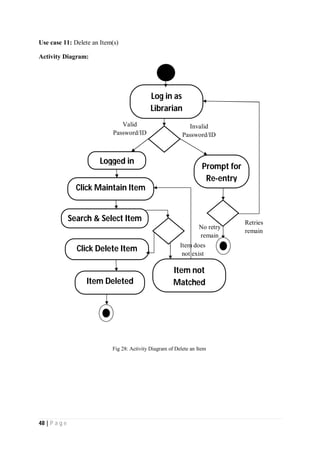
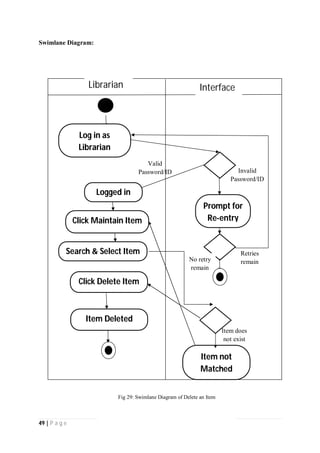
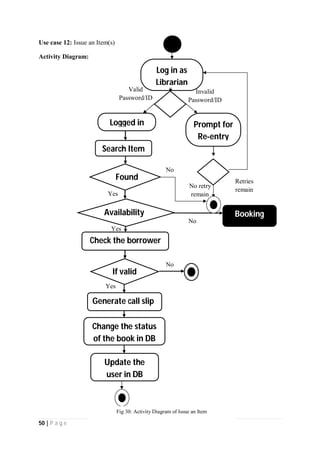
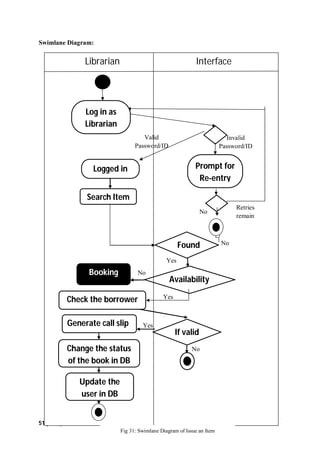
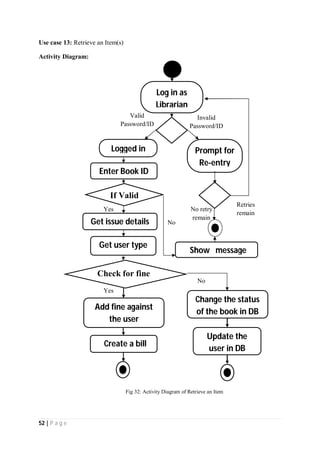
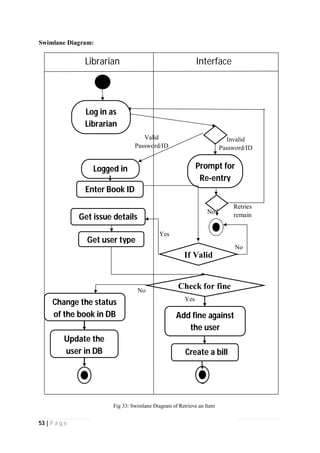
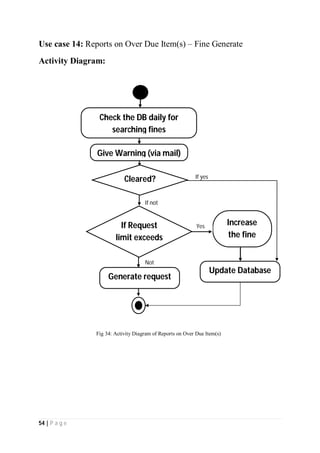
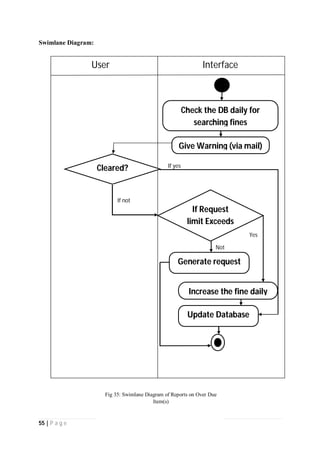
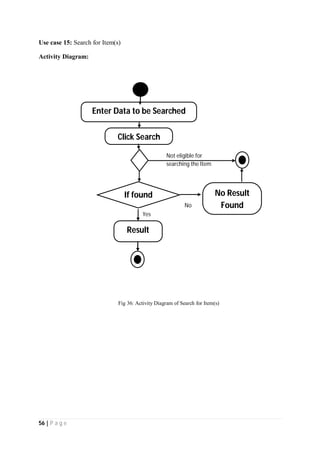
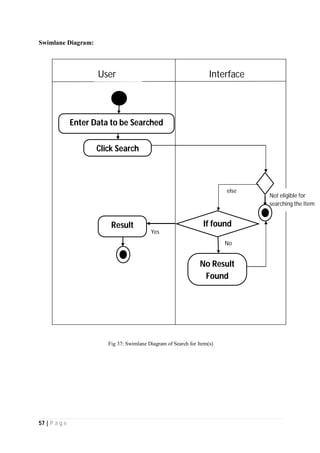
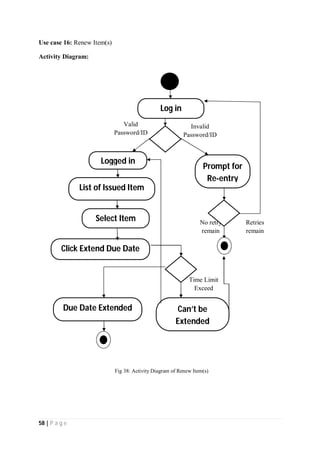
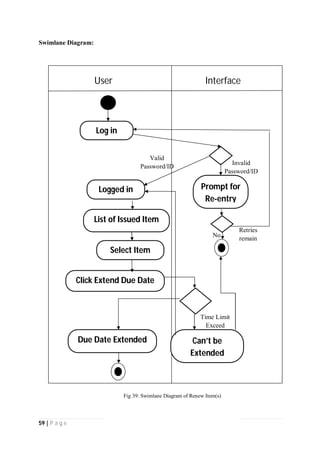
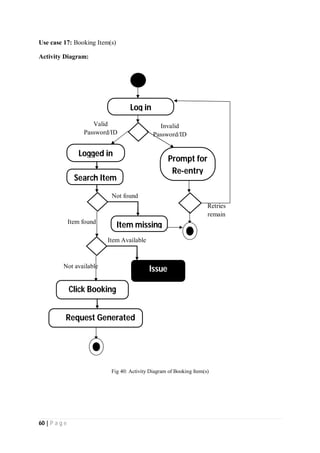
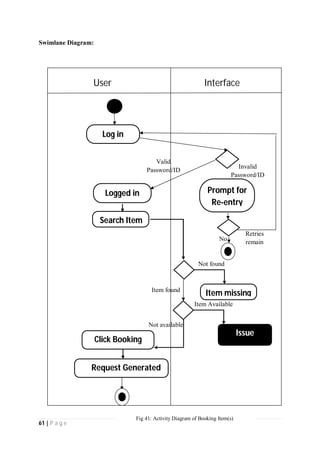
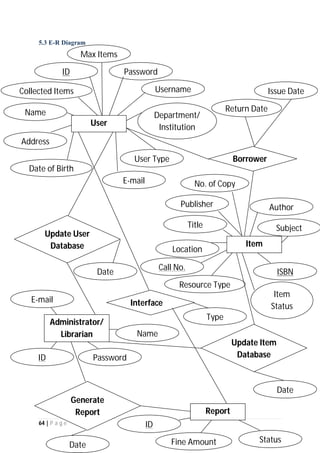
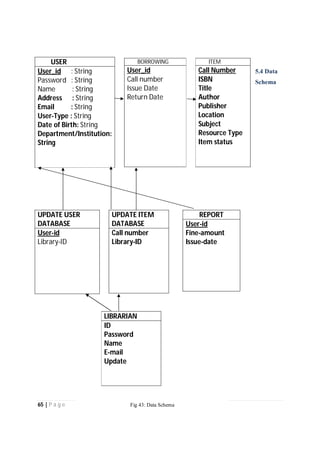
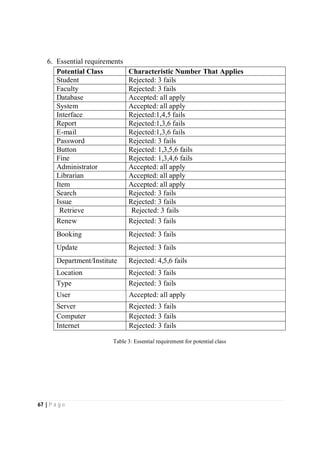
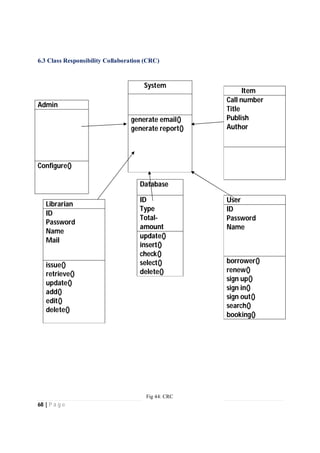
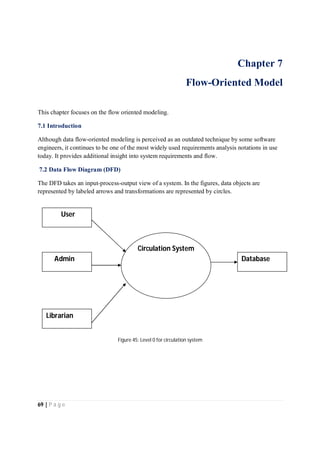
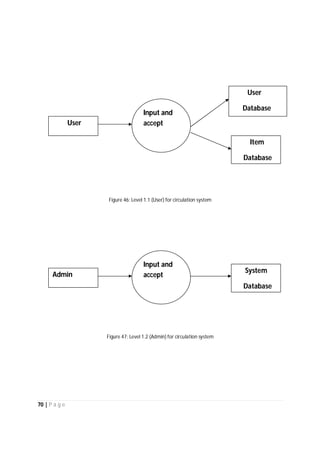
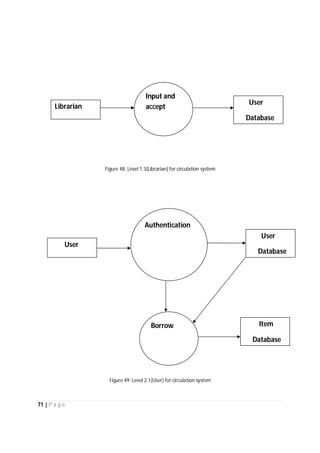
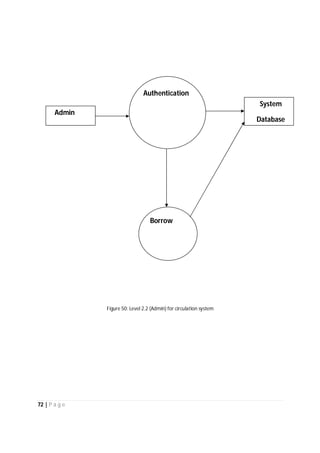
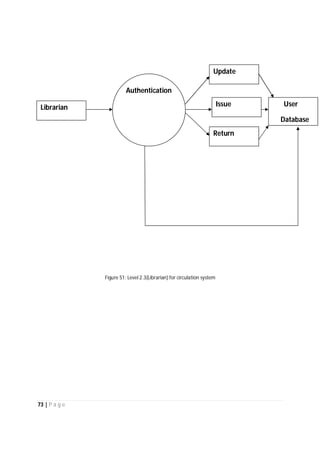
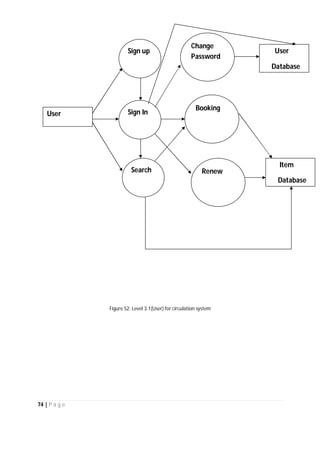
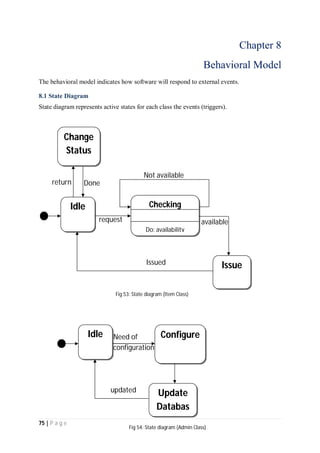
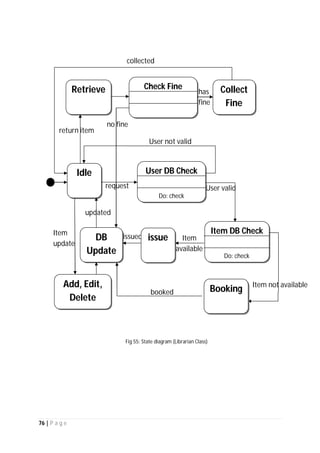
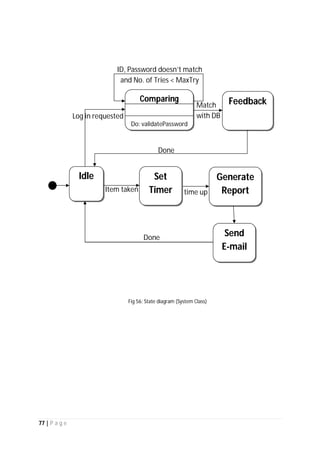
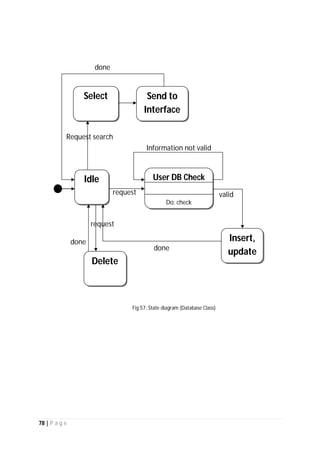
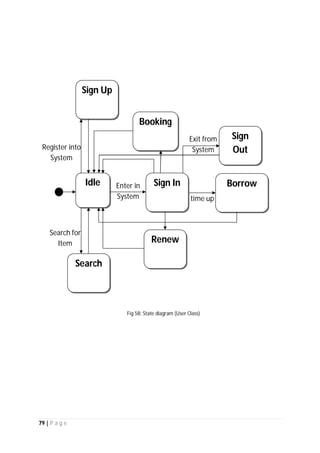
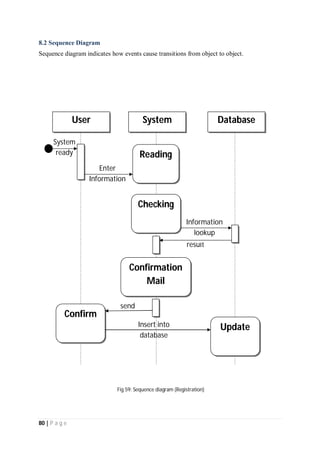
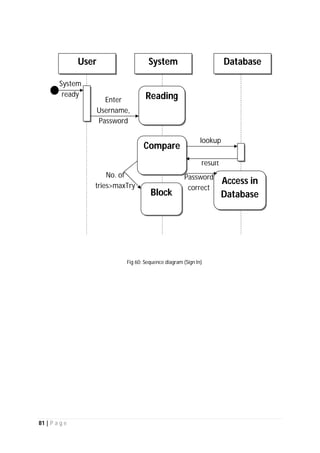
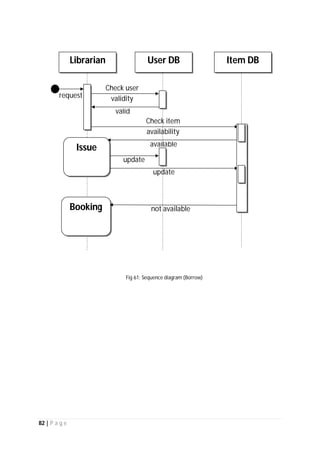
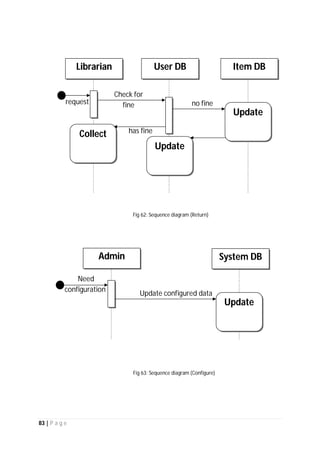
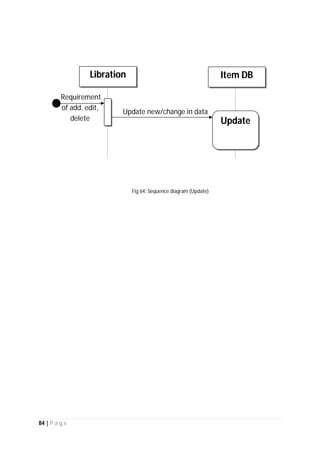
The document outlines the Software Requirements Specification (SRS) for a Library Circulation System (LCS) developed by students at the University of Dhaka. It details the system's purpose, stakeholder requirements, and the steps taken for requirements gathering, including stakeholder identification and conflict resolution. The LCS is designed to facilitate resource tracking and management for librarians, as well as allow users to search, renew, and reserve items online.