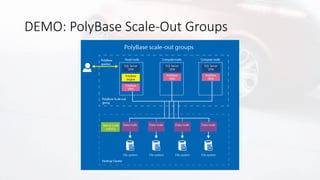
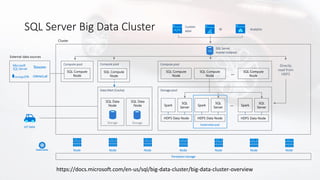
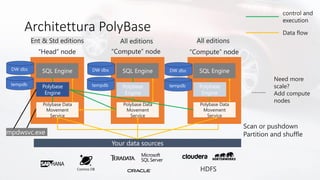
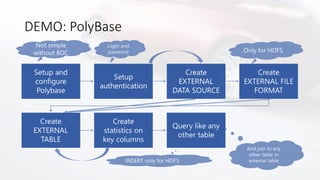
Il documento discute la virtualizzazione dei dati in SQL Server utilizzando PolyBase, evidenziando i vantaggi rispetto ai tradizionali processi ETL/ELT, come la riduzione del movimento dei dati e il miglioramento della qualità e della sicurezza. Viene anche descritto il supporto per diverse fonti di dati esterne e le funzionalità di scaling, come le viste partizionate distribuite. Inoltre, il documento menziona l'integrazione con Azure e altre soluzioni analitiche.








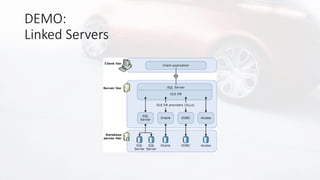



![Scale-Out con Linked Server
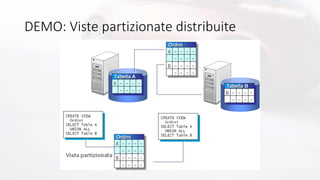
• Distributed Partioned Views
• Aka Federated Database Server in SQL Server 2000
• Partizionamento orizzontale tramite viste
• Tabelle con partizioni dati distribuite su più istanze
• Vincoli CHECK identificano la partizione
• Viste su tutti i nodi con SELECT * […] UNION ALL
• Query Processor riconosce lo scenario
• Distribuisce il carico eseguendo query remote/locali
• Predicato deve operare su colonna del vincolo CHECK
• Disponibili ancora solo con edizione Enterprise
• Funzionalità poco documentata…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlserverdatavirtualizationwithpolybase-210922145737/85/SQL-Server-Data-Virtualization-with-polybase-15-320.jpg)