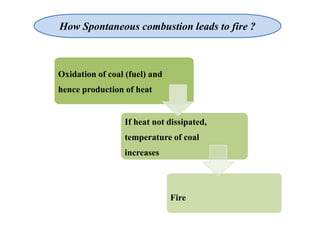
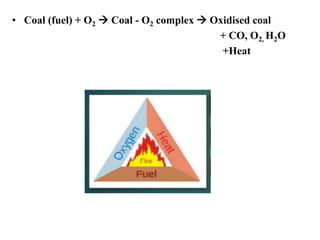
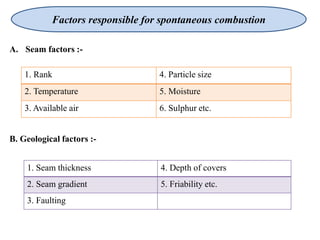
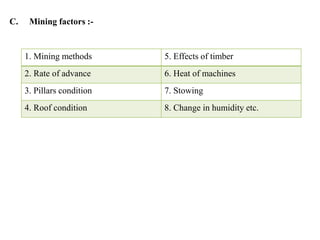
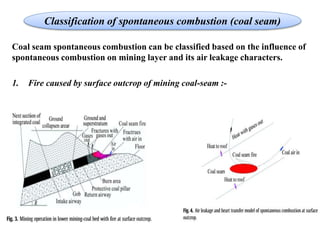
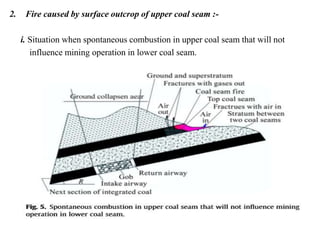
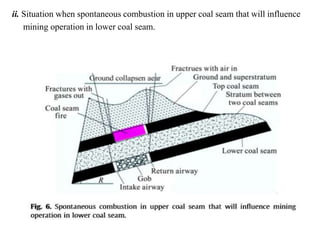
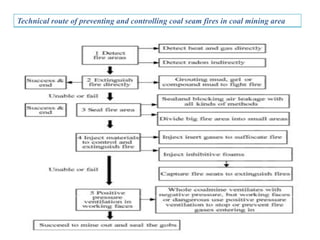
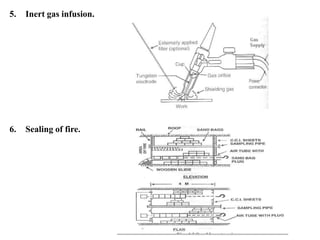
This document discusses methods for preventing and controlling spontaneous combustion of coal seams. It begins by defining spontaneous combustion as the self-heating of coal or other carbonaceous matter resulting in ignition without external heat. Factors that can lead to spontaneous combustion include the rank, temperature, and available air of the coal as well as geological and mining conditions. Early symptoms include a faint haze and odors, while later stages produce stronger odors. Detection methods include indirect monitoring of gases like radon and direct measurement of temperature and gases. Control methods include using chemical extinguishers, applying water, infusing inert materials, sealing fires, and adjusting ventilation. Advancements in technology are still needed to better apply these prevention and control techniques.