1. Splints are used to immobilize and support injured parts of the musculoskeletal system like fractures, sprains, strains, and dislocations. They alleviate pain and allow injuries to heal properly while minimizing complications.
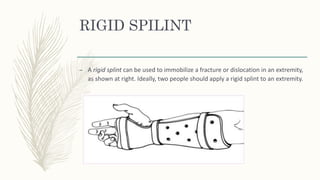
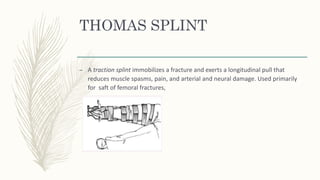
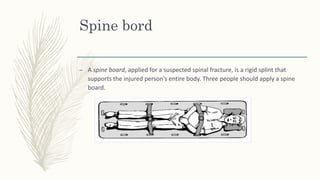
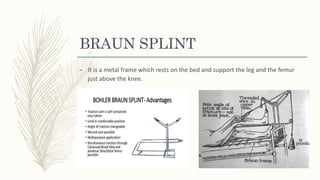
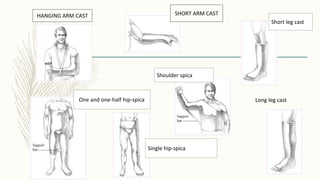
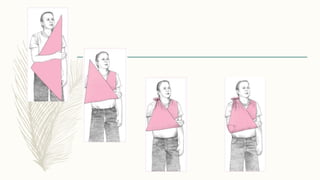
2. Different types of splints include rigid splints, cervical collars, Thomas splints, Braun splints, and spine boards. Splints come in various sizes and are applied according to the specific injury.
3. After applying a splint, the patient's vital signs, circulation, sensation, and pain levels must be monitored closely for complications.