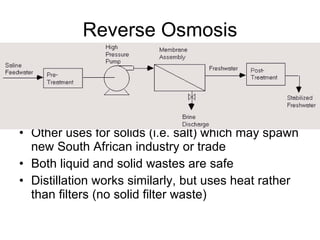
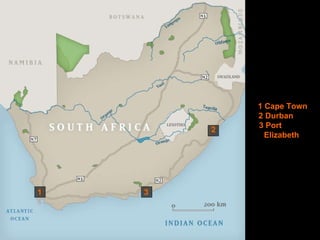
South Africa suffers from frequent droughts that negatively impact its economic development and population health. Desalination could help address South Africa's water shortages by providing a sustainable source of fresh water for drinking, industry, and agriculture. Desalination plants near Cape Town, Durban, and Port Elizabeth could produce fresh water, stimulate regional economic growth, and reduce water-borne diseases. Specialist companies could build and operate the facilities, creating local jobs and attracting foreign investment through municipal bonds.