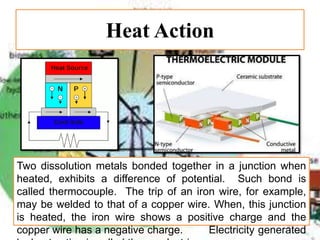
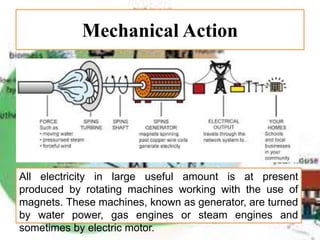
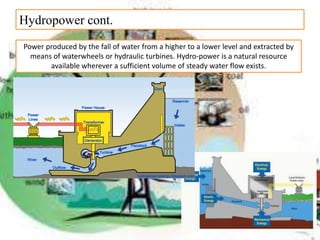
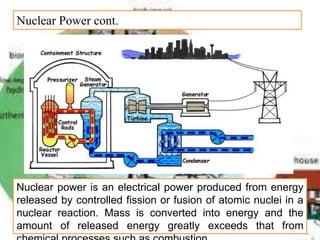
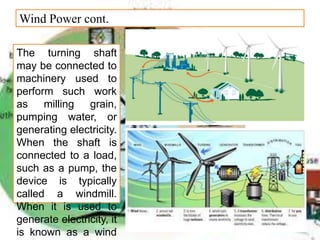
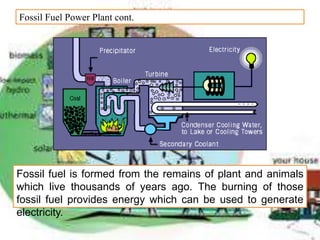
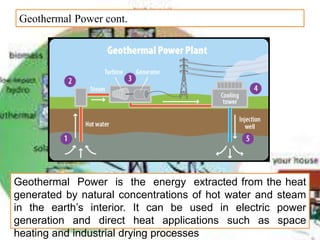
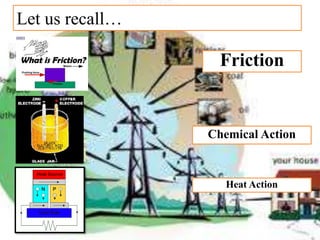
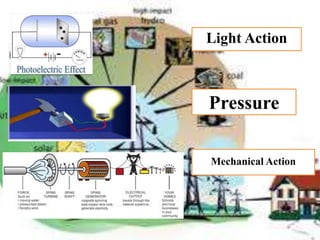
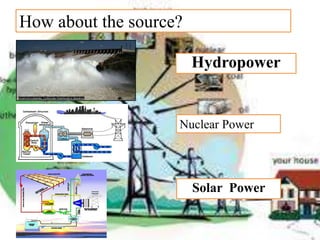
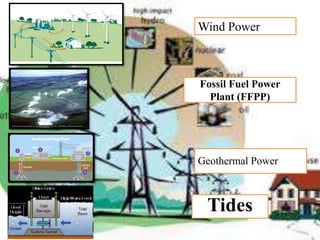
There are several different sources of electricity that are described in the document. These include static electricity generated through friction, chemical reactions in batteries, heat and light acting on materials, pressure applied to crystals, and mechanical generation using magnets and rotating machines. Some common large-scale power generation sources are also outlined, such as hydropower from flowing water, nuclear power from atomic fission, solar power from the sun's radiation, wind power from kinetic energy of wind, and fossil fuel power plants that burn fuels like coal and natural gas. Geothermal power harnesses heat from underground, while tidal power uses ocean tides to generate electricity.